Financial plan assumptions are the key variables, estimates, and predictions used to develop a company's financial projections and strategy. They serve as the foundation for forecasting revenues, costs, investments, and taxes, among other elements. Assumptions are critical in financial planning because they help businesses set realistic goals, allocate resources efficiently, and identify potential risks and opportunities. They also enable management to make informed decisions based on the best available data and industry insights. Financial plan assumptions aim to create a comprehensive picture of a company's future financial performance by incorporating a range of factors. These assumptions are designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing for adjustments as new information becomes available or market conditions change. The sales growth rate is a crucial revenue assumption that estimates the percentage increase in a company's sales over a specific period. This rate takes into account factors such as historical sales data, market trends, and promotional efforts. Pricing strategies help determine the prices of a company's products or services. Assumptions related to pricing may include competitor pricing, price elasticity of demand, and the company's overall pricing objectives. Market share assumptions predict a company's percentage of total sales within a specific market. Estimations consider factors such as target customer segments, marketing strategies, and product or service differentiation. Customer acquisition and retention assumptions estimate the number of new customers acquired and existing customers retained. These assumptions depend on factors such as marketing efforts, customer service quality, and competitive positioning. Fixed and variable costs are essential components of a company's financial plan. Fixed costs include expenses that remain constant, regardless of production levels or sales, such as rent and salaries. Variable costs vary with production or sales, including raw materials and shipping costs. COGS is the total cost of producing goods or services sold by a company. Key assumptions for COGS may include production costs, labor costs, and manufacturing overheads. Operating expenses are the costs associated with running a business, excluding COGS. Assumptions for operating expenses may include marketing costs, administrative expenses, and research and development expenditures. The inflation rate assumption estimates the increase in the general price level over time. This assumption affects various cost projections, such as wages, raw materials, and utilities. Capital expenditures represent the funds a company invests in long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment. Assumptions for capital expenditures may include the anticipated level of investment, the useful life of assets, and depreciation methods. Working capital assumptions estimate the funds needed to cover short-term operating expenses and maintain sufficient liquidity. These assumptions may include projections for inventory levels, accounts receivable, and accounts payable. Financing assumptions help determine how a company will fund its operations and investments. These assumptions include the mix of debt and equity financing, interest rates, and repayment terms. Corporate tax rate assumptions estimate the percentage of a company's profits subject to taxation. These assumptions take into account federal, state, and local tax rates, as well as any changes to tax laws. Tax credits and incentives are reductions in tax liability offered by governments to encourage specific business activities. Assumptions related to tax credits may include eligibility criteria, application deadlines, and the expected amount of tax savings. Tax planning strategies are methods used by companies to minimize their tax liabilities. Assumptions related to tax planning may include the use of tax-efficient structures, deductions, and loss carryforwards. Gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate assumptions estimate the overall economic growth of a country or region. These assumptions impact a company's revenue projections, as they help gauge the general health of the economy and consumer spending. Interest rate assumptions estimate the cost of borrowing or lending money. These rates affect a company's financing costs, investment decisions, and overall financial performance. Unemployment rate assumptions predict the percentage of the labor force without jobs. High unemployment rates can impact consumer spending and may indicate a sluggish economy, affecting a company's sales projections. Market size and growth assumptions help estimate the overall potential of an industry and the opportunities it presents for a company. Factors considered may include historical data, demographic trends, and technological advancements. Technological advancements can disrupt industries and create new markets. Assumptions related to technology may include the adoption of new technologies, the impact of innovations on the market, and the potential for competitive advantage. Regulatory changes can significantly impact a company's operations and financial performance. Assumptions related to regulation may include potential changes in laws, compliance requirements, and the effects on the industry landscape. Competitive landscape assumptions evaluate a company's position within its industry and the level of competition it faces. These assumptions may consider factors such as market share, competitor strategies, and barriers to entry. Sensitivity analysis and scenario planning involve identifying key variables and uncertainties in a company's financial plan. These variables may include economic factors, industry trends, or company-specific factors. Scenario planning involves creating alternative future scenarios based on varying assumptions. Companies develop multiple scenarios to explore the potential impact of different events, trends, and risks on their financial performance. Companies analyze the impact of different scenarios on their financial performance to identify potential risks and opportunities. This analysis helps management make informed decisions and adapt their strategies as needed. Based on the results of sensitivity analysis and scenario planning, companies develop risk mitigation and contingency plans. These plans help companies prepare for potential challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Regularly reviewing and updating financial plan assumptions is essential to ensure their continued relevance and accuracy. Ongoing monitoring helps companies stay informed of market changes and adapt their strategies accordingly. The frequency of assumption updates depends on the nature of the company and its industry. Companies operating in rapidly changing environments may need to update their assumptions more frequently than those in more stable industries. As new information and data become available, companies should incorporate them into their financial plan assumptions. This ensures that the assumptions remain relevant and provide an accurate basis for decision-making. Based on updated assumptions, companies may need to adjust their financial plans to reflect changes in market conditions, industry trends, or company-specific factors. Regular adjustments help maintain the accuracy and relevance of financial projections. Financial plan assumptions play a crucial role in the development of a company's financial strategy and projections. By incorporating a wide range of factors and estimates, assumptions help create a comprehensive picture of a company's future financial performance. Regularly reviewing and updating financial plan assumptions is essential for ensuring their continued relevance and accuracy. As new information becomes available or market conditions change, companies must adapt their assumptions and adjust their financial plans accordingly. Sensitivity analysis and scenario planning are valuable tools for managing risks and identifying potential opportunities. By analyzing the impact of different scenarios on a company's financial performance, management can make informed decisions and develop risk mitigation and contingency plans. In conclusion, financial plan assumptions are critical components of a company's financial planning process. By incorporating a wide range of factors and regularly reviewing and updating these assumptions, companies can create accurate financial projections, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make informed decisions that drive their long-term success.What Are Financial Plan Assumptions?
Key Financial Plan Assumptions
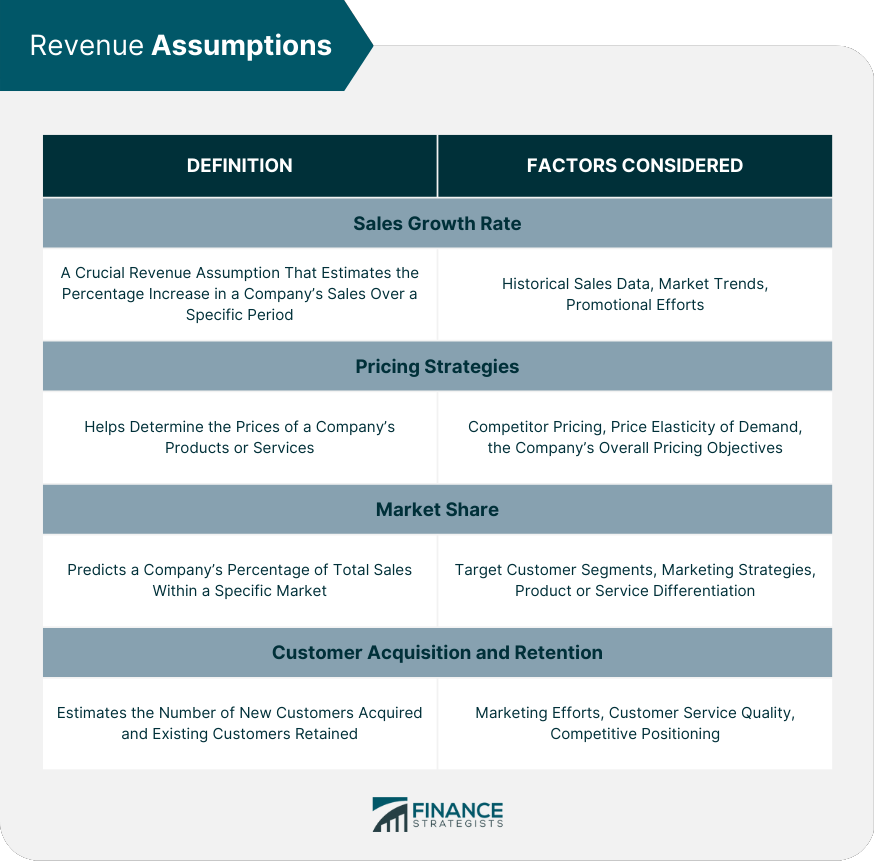
Revenue Assumptions
Sales Growth Rate
Pricing Strategies
Market Share
Customer Acquisition and Retention
Cost Assumptions
Fixed and Variable Costs
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Operating Expenses
Inflation Rate
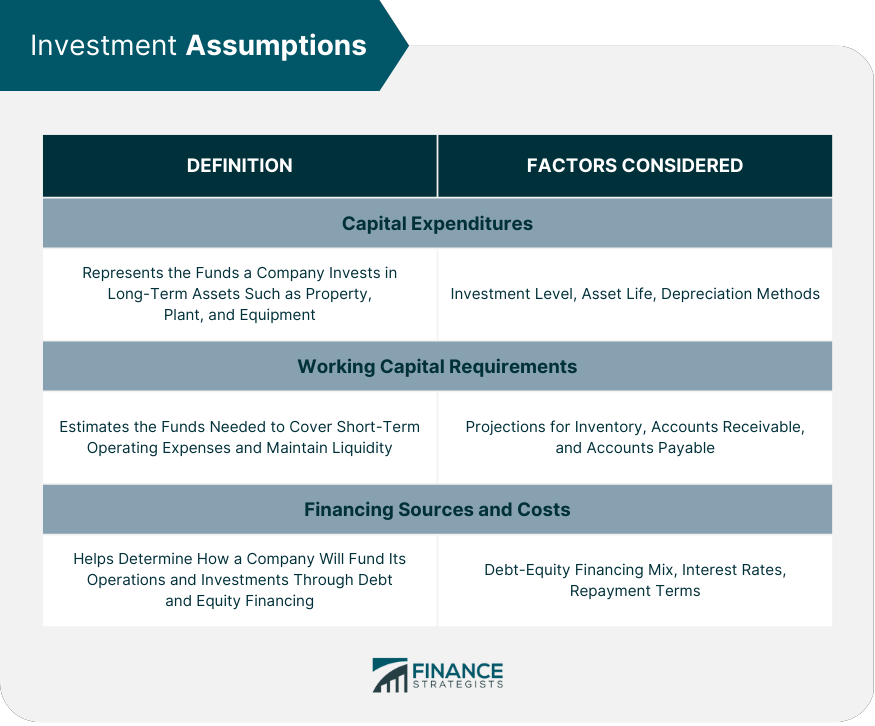
Investment Assumptions
Capital Expenditures
Working Capital Requirements
Financing Sources and Costs
Tax Assumptions
Corporate Tax Rates
Tax Credits and Incentives
Tax Planning Strategies
Economic and Industry Assumptions
Macroeconomic Factors
GDP Growth
Interest Rates
Unemployment Rates

Industry Trends and Competition
Market Size and Growth
Technological Advancements
Regulatory Changes
Competitive Landscape
Sensitivity Analysis and Scenario Planning
Identifying Key Variables and Uncertainties
Developing Scenarios and Assumptions
Analyzing the Impact on Financial Performance
Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Regular Review and Update of Assumptions
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring
Frequency of Assumption Updates
Incorporating New Information and Data
Adjusting Financial Plans as Needed
Conclusion
Financial Plan Assumptions FAQs
Financial plan assumptions are the underlying estimates and predictions that a financial plan is based upon. They are essential because they provide the framework for determining how much money you need to save, how much you can expect to earn on your investments, and how long your money will last in retirement.
The right financial plan assumptions will depend on your personal circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. You should consider your current income, expenses, debts, and assets when selecting your assumptions. Additionally, you should consider factors such as inflation, investment returns, and life expectancy.
Common financial plan assumptions used by financial planners include assumptions about inflation rates, investment returns, life expectancy, and tax rates. Other assumptions may include future expenses such as college tuition or medical costs, changes in income or employment, and changes in interest rates.
You should review and update your financial plan assumptions regularly, at least annually, and whenever there are significant changes in your life circumstances, such as a new job, a significant change in income or expenses, or a change in your investment portfolio.
Relying on incorrect financial plan assumptions can lead to a variety of risks, including not saving enough for retirement, running out of money in retirement, or being unable to meet other financial goals. Additionally, incorrect assumptions can lead to poor investment decisions, resulting in lower investment returns and higher taxes. It is essential to ensure that your financial plan assumptions are as accurate as possible to help you achieve your financial goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















