The Securities Act of 1933, often referred to as the '33 Act, is a landmark piece of legislation that marked the beginning of federal securities regulation in the United States. The primary purpose of the Act is to protect investors by requiring companies that issue securities to provide accurate and transparent information about their financial condition and business operations. The Securities Act of 1933 was enacted in response to the stock market crash of 1929, which led to the Great Depression. The crash exposed significant weaknesses in the US financial system, including widespread fraud, market manipulation, and a lack of transparency in the securities markets. The Great Depression that followed the stock market crash highlighted the need for increased regulation and oversight in the financial sector. Investors lost confidence in the markets, and the government recognized the necessity of restoring trust and stability to the financial system. In response to these challenges, Congress passed the Securities Act of 1933 to establish a regulatory framework for the issuance and trading of securities. The Act aimed to protect investors by requiring companies to disclose accurate and complete information about their financial health and business operations. The '33 Act requires companies that issue securities to register them with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Registration involves providing detailed financial information about the issuer, as well as a description of the securities being offered. The SEC reviews these filings and may require additional disclosures or amendments before granting approval. A key component of the Securities Act of 1933 is the requirement for companies to provide a prospectus to potential investors. This document contains essential information about the company's financial condition, management, and business operations, as well as a description of the securities being offered. In addition to the prospectus, the '33 Act requires companies to submit annual and quarterly financial reports to the SEC. These filings ensure that investors have ongoing access to accurate and up-to-date information about the company's financial health. The Securities Act of 1933 provides several exemptions from registration, including: Securities offered to a limited number of sophisticated investors, known as accredited investors, may be exempt from registration under certain conditions. Securities offered exclusively within one state may be exempt from federal registration if they meet specific criteria. Securities issued by the US government, state governments, or municipal entities are generally exempt from registration under the '33 Act. The '33 Act contains anti-fraud provisions that prohibit the use of false or misleading information in connection with the issuance or trading of securities. Violations of these provisions can result in civil and criminal penalties. The SEC is the primary regulatory body responsible for enforcing the provisions of the Securities Act of 1933. The agency has the authority to investigate potential violations, bring enforcement actions against wrongdoers, and impose civil and criminal penalties for violations. The SEC conducts investigations into potential violations of the '33 Act and can bring enforcement actions against individuals or companies found to have violated the law. These actions may result in penalties such as fines, disgorgement of ill-gotten gains, or even criminal charges in severe cases. The primary impact of the Securities Act of 1933 is the increased protection it provides to investors. By requiring companies to disclose accurate and complete information about their financial health and business operations, the '33 Act helps investors make informed decisions about their investments. The '33 Act has also contributed to greater transparency and efficiency in the securities markets. The registration and disclosure requirements help to ensure that accurate and relevant information is available to all market participants, promoting more informed decision-making and reducing information asymmetry. By imposing strict disclosure requirements and anti-fraud provisions, the Securities Act of 1933 has also promoted better corporate governance and accountability. Companies are required to maintain accurate financial records, and executives are held responsible for the accuracy of their company's disclosures. The Securities Act Amendments of 1996 introduced several changes to the '33 Act, including the creation of a safe harbor for forward-looking statements made by companies. These changes aimed to encourage companies to provide more information to investors without fear of liability for unforeseen future events. The Jumpstart Our Business Startups (JOBS) Act of 2012 made further changes to the '33 Act, including easing some registration and disclosure requirements for small and emerging companies. The JOBS Act also expanded the exemptions available for private offerings, making it easier for companies to raise capital without going through the full registration process. One of the main criticisms of the Securities Act of 1933 is the regulatory burden it imposes on small businesses. Some argue that the registration and disclosure requirements are overly burdensome for smaller companies, which may lack the resources to comply fully. Another ongoing debate surrounding the '33 Act concerns the balance between investor protection and capital formation. While the Act's disclosure requirements provide valuable information to investors, they can also impose significant costs on companies, potentially hindering their ability to raise capital and grow. The Securities Act of 1933 stands as a landmark piece of legislation that has had a profound and lasting impact on the US securities markets. By establishing a robust framework for the registration and disclosure of securities offered to the public, the Act sought to address the information asymmetry that had contributed to the speculative excesses of the 1920s and the subsequent market crash. The Act's core provisions, which mandate the registration of securities offerings and require issuers to provide detailed and accurate information to investors, have been instrumental in fostering transparency, accountability, and investor confidence. While the Securities Act has not been without its critics and has been the subject of debates over its scope, effectiveness, and regulatory burden, it has undeniably played a central role in shaping the modern securities landscape. As the foundation of the federal securities regulatory regime, the Securities Act of 1933 continues to serve as a bulwark against fraud and misrepresentation, helping to ensure the integrity of the capital markets and protect the interests of investors. Its legacy is a testament to the importance of sound regulation in promoting financial stability and economic prosperity.What Is the Securities Act of 1933?
Historical Context of the Securities Act of 1933
Stock Market Crash of 1929
The Great Depression
The Need for Regulation in the Securities Market
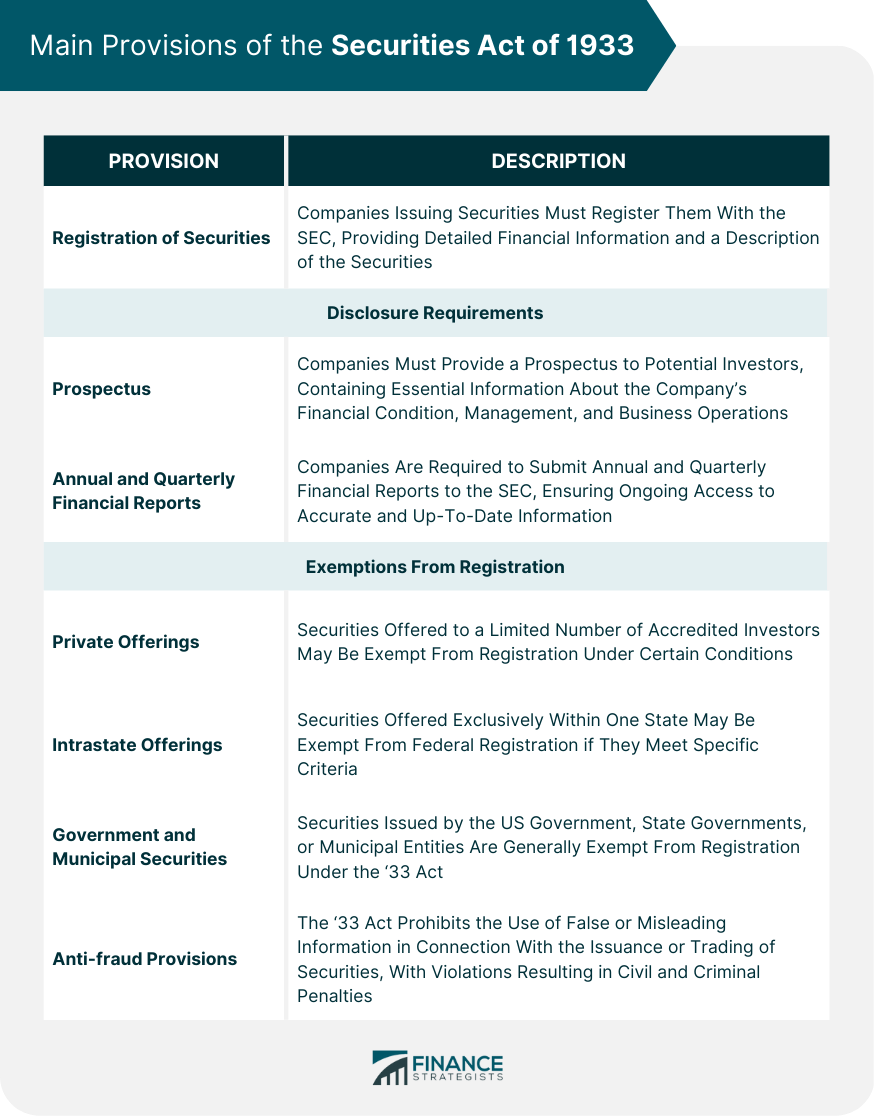
Main Provisions of the Securities Act of 1933
Registration of Securities
Disclosure Requirements
Prospectus
Annual and Quarterly Financial Reports
Exemptions From Registration
Private Offerings
Intrastate Offerings
Government and Municipal Securities
Anti-fraud Provisions
Enforcement and Compliance of the Securities Act of 1933
Role of the Securities and Exchange Commission
Investigations and Enforcement Actions
Impact of the Securities Act of 1933
Investor Protection
Market Transparency and Efficiency
Corporate Governance and Accountability
Modern Developments and Amendments to the Securities Act of 1933
Securities Act Amendments of 1996
The JOBS Act of 2012
Criticisms and Debates Surrounding the Securities Act of 1933
Regulatory Burden on Small Businesses
Balancing Investor Protection and Capital Formation
Conclusion
Securities Act of 1933 FAQs
The Securities Act of 1933 is a federal law that regulates the offer and sale of securities to protect investors from fraud and misrepresentation.
The Securities Act of 1933 covers a wide range of securities, including stocks, bonds, and other investment instruments offered to the public.
The Securities Act of 1933 aims to protect investors by ensuring that they receive accurate and complete information about securities offerings and preventing fraudulent practices in the securities industry.
Under the Securities Act of 1933, securities issuers must register their offerings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and provide detailed information about the securities being offered, the issuer, and the risks associated with the investment.
The Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 work together to regulate the securities industry. The Securities Act of 1933 focuses on the initial offering of securities, while the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 regulates the ongoing trading of securities in the secondary market.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















