Microfinance investments refer to investments made in institutions that provide financial services to individuals or small businesses that are often excluded from traditional banking services. These institutions, known as microfinance institutions (MFIs), provide microloans, microinsurance, and other financial products to individuals or businesses who lack access to formal banking services due to factors such as poverty, lack of collateral, or lack of credit history. Microfinance investments play a crucial role in promoting global development by channeling funds to Microfinance Institutions (MFIs), which in turn provide financial services to marginalized communities. By facilitating access to finance, microfinance investments contribute to poverty alleviation, financial inclusion, and socioeconomic development. MFIs are the primary intermediaries that provide financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses. These institutions include banks and credit unions, cooperatives, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). MFIs play a vital role in ensuring the effective allocation of microfinance investments to reach the intended beneficiaries. Microloans are small, short-term loans extended to low-income borrowers. These loans are the most common form of microfinance investment and are primarily used for working capital, business expansion, or consumption purposes. Some MFIs issue bonds or notes to raise capital from investors. These debt securities pay periodic interest to investors and return the principal upon maturity. Investors can acquire ownership stakes in MFIs through direct equity investments. This form of investment allows investors to share in the profits and growth of the MFI, while also having a say in its governance. Private equity funds pool capital from multiple investors to invest in a portfolio of MFIs or other microfinance-related businesses. These funds offer investors diversification and professional management of their investments. Convertible loans are debt instruments that can be converted into equity at a later date. This feature provides investors with the potential for capital gains if the MFI performs well, while still offering periodic interest payments. Mezzanine financing is a hybrid of debt and equity financing, typically involving a combination of loans and warrants or options to purchase equity. This type of financing offers investors the potential for higher returns while preserving some downside protection. As mentioned earlier, MFIs are the primary intermediaries that provide financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses. They are the main recipients of microfinance investments and are responsible for allocating the funds to the intended beneficiaries. DFIs are government-backed institutions that provide financial support for private sector development in emerging markets. They play a significant role in microfinance investments by offering funding, guarantees, and technical assistance to MFIs. Some commercial banks invest in microfinance, either by lending to MFIs, purchasing their debt securities, or making direct equity investments. These banks are attracted to the potential financial returns and social impact of microfinance investments. NGOs are often involved in microfinance investments as providers of grants, loans, or equity capital to MFIs. They also play a critical role in promoting best practices, capacity building, and social performance management in the microfinance sector. Impact investors and social investment funds are investment vehicles that focus on generating both financial returns and positive social or environmental impacts. These investors are increasingly interested in microfinance investments, as they align with their goals of promoting financial inclusion and poverty reduction. Crowdfunding platforms enable individual and institutional investors to pool their resources and invest in microfinance projects or MFIs directly. These platforms provide a more accessible and democratic way for investors to participate in microfinance investments. Microfinance investments contribute to poverty alleviation by providing financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses, enabling them to grow their incomes, create jobs, and improve their living standards. By extending financial services to underserved populations, microfinance investments help bridge the gap between the formal financial sector and marginalized communities, fostering financial inclusion and socioeconomic development. Microfinance investments often target women borrowers, who typically face greater barriers to accessing finance. By providing women with the resources to start and grow businesses, microfinance investments contribute to gender equality and women's empowerment. Microfinance investments are generally uncorrelated with traditional financial markets, offering investors an opportunity to diversify their portfolios and reduce overall risk. Investing in microfinance allows investors to gain exposure to different regions and sectors, further enhancing portfolio diversification. Microfinance investments typically exhibit high repayment rates, as low-income borrowers often prioritize repaying their loans to maintain access to future credit. As the microfinance sector continues to grow and innovate, there are increasing opportunities for investors to achieve financial returns while contributing to social impact. Investors in microfinance face credit risk, as borrowers may default on their loans due to various factors, such as economic shocks or business failures. Investments in microfinance are subject to market risk, including changes in interest rates, economic conditions, and currency fluctuations, which can affect the value of the investments. Investors must consider the operational and governance risk associated with the MFIs they invest in, as poor management, weak internal controls, or fraud can lead to losses. Microfinance investments may be exposed to regulatory and political risks, as changes in laws, regulations, or political stability can impact the operations and performance of MFIs. The fluctuation of interest rates can affect the profitability of microfinance investments, as it influences the cost of borrowing and the returns on savings products. Over-indebtedness of borrowers and inadequate client protection practices can pose risks to the reputation and long-term sustainability of microfinance investments. ROA measures the profitability of an MFI relative to its total assets, indicating how efficiently the MFI is using its assets to generate profits. ROE measures the profitability of an MFI relative to its equity, reflecting the return on investment for equity holders. PAR is the percentage of an MFI's loan portfolio at risk of default, which serves as an indicator of the overall credit quality and potential credit losses. The number of active borrowers is an indicator of the MFI's outreach and scale, reflecting its ability to reach and serve low-income individuals and small businesses. The percentage of women borrowers measures the MFI's commitment to promoting gender equality and women's empowerment. The average loan size provides insight into the target market of the MFI, with smaller loans typically indicating a focus on low-income borrowers. Investors should assess the MFI's management team and governance structure, ensuring that they have the necessary skills, experience, and integrity to operate the institution effectively. A thorough analysis of the MFI's financial performance, including profitability, growth, efficiency, and credit quality, is essential to understand the potential risks and returns of the investment. Investors should evaluate the MFI's social performance, considering its outreach, target market, and commitment to client protection and responsible lending practices. The adoption of mobile banking and payment platforms is expected to increase the efficiency and reach of microfinance services, offering new opportunities for investors. Peer-to-peer lending platforms are reshaping the microfinance landscape, enabling investors to directly fund borrowers and bypass traditional intermediaries. The development of microinsurance products, such as health, life, and crop insurance, offers new opportunities for microfinance investments to support the resilience of low-income individuals and communities. The expansion of microsavings products can help foster financial inclusion and asset-building, providing new avenues for microfinance investments. Microleasing enables low-income individuals and small businesses to access productive assets, such as equipment and machinery, presenting new investment opportunities in the microfinance sector. Aligning microfinance investments with the SDGs can help investors contribute to global development priorities while pursuing financial returns. Microfinance investments can play a crucial role in promoting climate change resilience and green financing, by supporting low-carbon technologies, sustainable agriculture, and other environmentally-friendly practices. Microfinance investments offer a unique opportunity for investors to generate financial returns while contributing to social impact, poverty alleviation, and financial inclusion. By understanding the various types of microfinance investments, the key players involved, and the potential risks and rewards, investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and values. As the microfinance sector continues to evolve and innovate, it holds immense promise for fostering sustainable development and inclusive growth. By channeling capital to underserved populations and supporting their economic empowerment, microfinance investments can play a crucial role in shaping a more equitable and resilient global economy. To maximize the benefits of microfinance investments and navigate the complexities of the sector, we encourage investors to engage the services of a reputable wealth management firm. By partnering with experienced professionals, investors can access tailored investment strategies, comprehensive due diligence, and ongoing support to ensure their microfinance investments align with their financial objectives and create lasting social impact.What Are Microfinance Investments?
Microfinance investments can take many forms, including equity investments, debt investments, or a combination of both. Investors who are interested in supporting microfinance typically seek out opportunities to invest in MFIs or in funds that specialize in microfinance investments.
These investments are often considered socially responsible investments, as they provide financial support to individuals and businesses who are often overlooked by traditional financial institutions.The Importance of Microfinance Investments in Global Development
The Role of Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
Types of Microfinance Investments
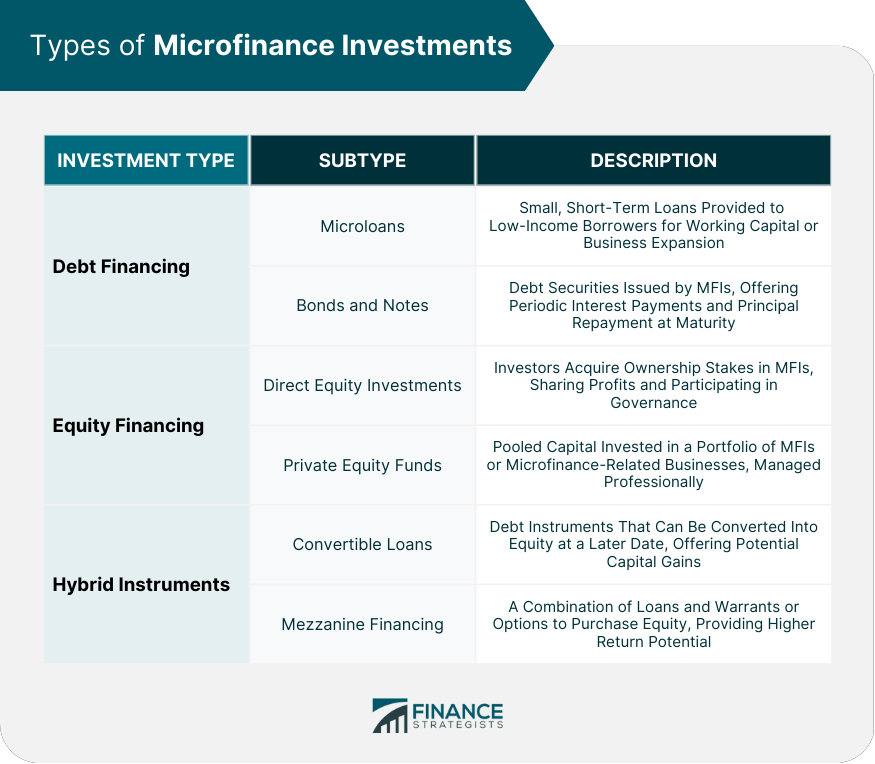
Debt Financing
Microloans
Bonds and Notes
Equity Financing
Direct Equity Investments
Private Equity Funds
Hybrid Instruments
Convertible Loans
Mezzanine Financing
Key Players in Microfinance Investments
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
Development Finance Institutions (DFIs)
Commercial Banks
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
Impact Investors and Social Investment Funds
Crowdfunding Platforms
Benefits of Microfinance Investments
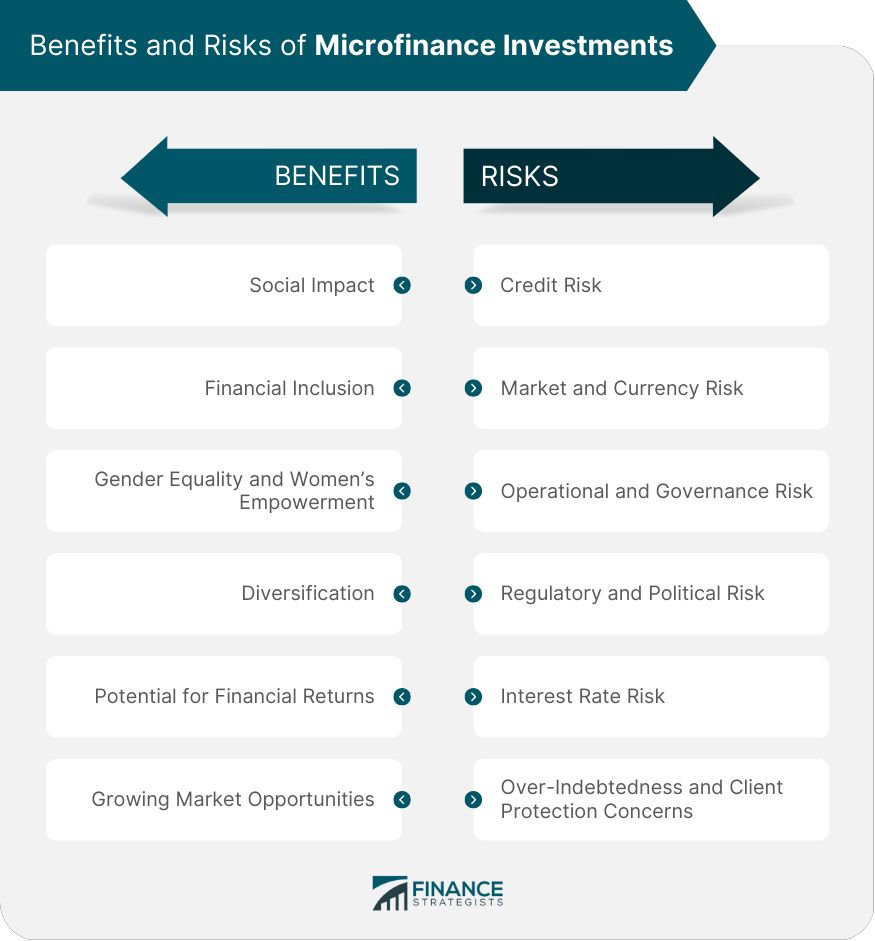
Social Impact
Poverty Alleviation
Financial Inclusion
Gender Equality and Women Empowerment
Diversification
Unrelated to Traditional Financial Markets
Exposure to Different Regions and Sectors
Potential for Financial Returns
High Repayment Rates
Growing Market Opportunities
Risks of Microfinance Investments
Credit Risk
Market and Currency Risk
Operational and Governance Risk
Regulatory and Political Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Over-Indebtedness and Client Protection Concerns
Assessing Microfinance Investments
Financial Performance Metrics
Return on Assets (ROA)
Return on Equity (ROE)
Portfolio at Risk (PAR)
Social Performance Metrics
Number of Active Borrowers
Percentage of Women Borrowers
Average Loan Size
Due Diligence Process
Assessment of MFI Management and Governance
Evaluation of Financial Performance
Analysis of Social Impact
Future Trends and Opportunities in Microfinance Investments
Technology and Digital Innovations
Mobile Banking and Payment Platforms
Peer-To-Peer Lending Platforms
Expansion to New Sectors and Services
Microinsurance
Microsavings
Microleasing
Collaboration With Other Development Initiatives
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Climate Change Resilience and Green Financing
Conclusion
Microfinance Investments FAQs
Microfinance investments primarily include debt financing (such as microloans and bonds), equity financing (like direct equity investments and private equity funds), and hybrid instruments (including convertible loans and mezzanine financing). These investments enable investors to support the growth of microfinance institutions and contribute to financial inclusion.
Microfinance investments drive social impact by channeling funds to microfinance institutions that provide financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses. These investments contribute to poverty alleviation, financial inclusion, gender equality, and women's empowerment by enabling access to much-needed financial resources and opportunities.
The key risks and challenges in microfinance investments include credit risk, market and currency risk, operational and governance risk, regulatory and political risk, interest rate risk, and over-indebtedness and client protection concerns. Investors should carefully assess these risks before making investment decisions in the microfinance sector.
Investors can evaluate microfinance investments using financial performance metrics (such as return on assets, return on equity, and portfolio at risk) and social performance metrics (including the number of active borrowers, percentage of women borrowers, and average loan size). Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence on the management, financial performance, and social impact of microfinance institutions is essential for informed decision-making.
Future trends and opportunities in microfinance investments include technology and digital innovations (such as mobile banking and peer-to-peer lending platforms), expansion to new sectors and services (like microinsurance, microsavings, and microleasing), and collaboration with other development initiatives (such as Sustainable Development Goals and climate change resilience). These trends offer potential for investors to achieve financial returns while contributing to social and environmental goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















