Periodic savings plans are financial vehicles designed to help individuals consistently save and invest money over time. Individuals can gradually build wealth and achieve their long-term financial goals by setting aside a specific amount at regular intervals. Developing a habit of regular saving is crucial for financial stability and success. Saving consistently allows individuals to accumulate funds for emergencies, retirement, or other significant life events while also taking advantage of compound interest. A structured savings plan provides a roadmap for achieving financial goals, encourages discipline in saving, and reduces the likelihood of impulsive spending. It also helps individuals monitor their progress and make necessary adjustments to stay on track with their goals. A fixed deposit is a low-risk savings option where funds are deposited at a fixed interest rate for a predetermined period. This type of savings plan is ideal for conservative investors seeking a safe and predictable return on their investment. A recurring deposit is a savings plan that allows individuals to contribute a fixed amount at regular intervals, typically monthly. This plan is suitable for those who want to save consistently over time and earn interest on their savings without worrying about market fluctuations. A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is a disciplined approach to investing in mutual funds by contributing a fixed amount at regular intervals. SIPs are ideal for long-term investors who wish to benefit from the power of compounding and minimize the impact of market volatility. 401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement savings plans that offer tax advantages and, in some cases, employer-matching contributions. These plans help employees save for retirement by automatically deducting contributions from their paychecks, making it easier to save consistently. An Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a tax-advantaged investment account designed to help individuals save for retirement. IRAs come in different types, such as traditional and Roth, each with tax benefits and eligibility requirements. Education savings plans, such as 529 plans, are tax-advantaged investment accounts designed to help families save for future education expenses. These plans offer flexibility in investment options and can be used for various education-related expenses, including tuition, fees, and room and board. When selecting a periodic savings plan, individuals should consider their specific financial goals, such as saving for retirement, funding education, or building an emergency fund. Choosing a plan aligned with one's goals ensures a more focused and effective savings strategy. Risk tolerance refers to an individual's willingness to accept investment risk in pursuit of higher returns. Understanding one's risk tolerance is essential when selecting a savings plan, as it helps determine the most suitable investment options and asset allocation. The time horizon is the length of time an individual has to save and invest before needing the funds. A longer time horizon typically allows for more aggressive investment strategies, while a shorter time horizon may require more conservative approaches to preserve capital. Tax implications play a significant role in choosing a savings plan. It is essential to understand the tax advantages and limitations of different savings options, as they can impact the overall growth and accessibility of the funds. Fees and charges associated with various savings plans can impact the overall return on investment. Individuals should carefully compare the costs of different plans and choose one that offers the best balance between fees and potential returns. Establishing achievable savings goals is critical to maintaining motivation and ensuring progress. By setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals, individuals can develop a clear plan and timeline for their savings journey. Automating savings contributions is an effective strategy to ensure consistent saving over time. By setting up automatic transfers from a checking account to a savings or investment account, individuals can save effortlessly and avoid the temptation to spend. Regularly tracking and evaluating savings progress helps individuals stay accountable and identify areas for improvement. Adjusting their savings plan as needed allows individuals to optimize their strategy to meet their financial goals more efficiently. Diversifying investments across different asset classes and sectors helps minimize risk and improve the potential for long-term returns. A well-diversified portfolio can withstand market fluctuations more effectively and provide more consistent growth. Rebalancing involves adjusting a portfolio's asset allocation to maintain the desired risk level and investment strategy. Regular rebalancing ensures the portfolio stays aligned with the individual's financial goals and risk tolerance. Delaying the start of a savings plan can have significant long-term consequences due to missed opportunities for compound interest. Overcoming procrastination and starting to save as early as possible is crucial for maximizing savings potential. Irregular or inconsistent contributions can hinder savings progress and make it difficult to achieve financial goals. Establishing and adhering to a consistent savings routine is vital for long-term success. Unplanned or impulsive spending can derail a savings plan and make it challenging to meet financial goals. Developing a budget and practicing self-discipline can help individuals resist the temptation to spend impulsively. Market fluctuations can impact investment returns and cause uncertainty for savers. Developing a long-term investment strategy and diversifying investments can help individuals navigate market volatility and stay on track with their savings plans. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, making it essential for individuals to invest in assets that can potentially outpace inflation. Incorporating investments with higher returns, such as stocks or real estate, can help protect savings from the effects of inflation. Creating an emergency fund provides a financial safety net for unexpected expenses and reduces the need to dip into long-term savings. Having a separate emergency fund helps individuals stay focused on their financial goals and maintain their savings momentum. Cutting unnecessary expenses and finding ways to increase income can help individuals save more and reach their financial goals faster. By closely monitoring spending habits and seeking additional income opportunities, individuals can accelerate their savings progress. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance and personalized recommendations for optimizing a savings plan. Professional advice can help individuals make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of personal finance. Periodic reviews and adjustments of a savings plan ensure that it remains relevant and effective. By reassessing financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment performance, individuals can make necessary changes to stay on track with their savings objectives. Recognizing and celebrating savings milestones can boost motivation and reinforce the importance of diligent saving. Acknowledging progress and rewarding oneself for achieving goals can help maintain enthusiasm and commitment to the savings plan. Periodic savings plans are crucial for financial stability and success. It is important to consider factors such as financial goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, tax implications, and fees when choosing a plan. Strategies such as setting realistic savings goals, automating contributions, monitoring progress, diversifying investments, and rebalancing the portfolio can help individuals achieve their objectives. However, procrastination, inconsistency in contributions, impulsive spending, market fluctuations, and inflation are common challenges that must be overcome. Establishing an emergency fund, reducing expenses, seeking professional advice, regularly reviewing and adjusting the plan, and celebrating milestones are some tips for staying on track with a periodic savings plan. With discipline and commitment, individuals can gradually build wealth and achieve their long-term financial goals.What Are Periodic Savings Plans?
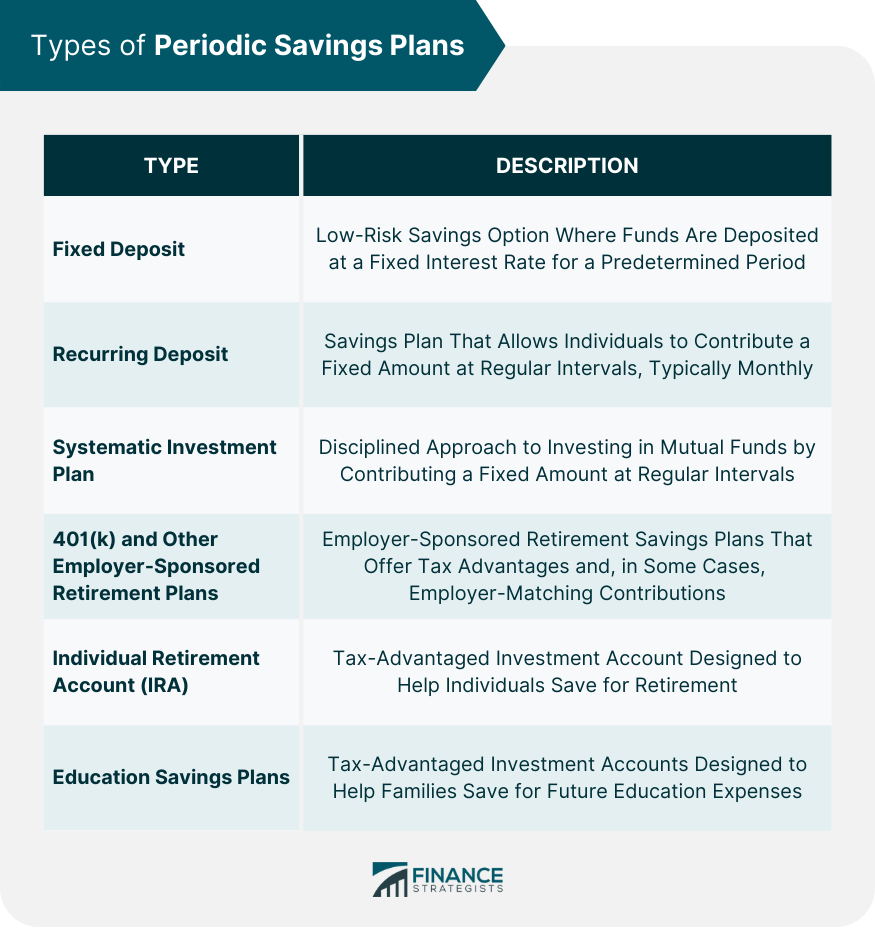
Types of Periodic Savings Plans
Fixed Deposit
Recurring Deposit
Systematic Investment Plan (SIP)
401(k) and Other Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans
Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
Education Savings Plans
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Periodic Savings Plan
Financial Goals
Risk Tolerance
Time Horizon
Tax Considerations
Fees and Charges

Strategies for Effective Periodic Savings Plans
Setting Realistic Savings Goals
Automating Savings Contributions
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting as Needed
Diversifying Investments
Rebalancing Portfolio

Common Challenges and Pitfalls in Periodic Savings Plans
Procrastination
Inconsistency in Contributions
Impulsive Spending
Market Fluctuations
Inflation
Tips for Staying on Track With a Periodic Savings Plan

Establishing an Emergency Fund
Reducing Expenses and Increasing Income
Seeking Professional Financial Advice
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting the Plan
Celebrating Milestones and Achievements
Final Thoughts
Periodic Savings Plans FAQs
Periodic savings plans provide a roadmap for achieving financial goals, encourage disciplined saving, reduce impulsive spending, and help individuals monitor their progress and make necessary adjustments to stay on track with their objectives.
Popular periodic savings plans for long-term financial goals include fixed deposits, recurring deposits, Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs), 401(k) and other employer-sponsored retirement plans, Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), and education savings plans (e.g., 529 plans).
To optimize periodic savings plans, individuals should set realistic savings goals, automate their savings contributions, monitor their progress and adjust as needed, diversify their investments, and periodically rebalance their portfolios.
Some common challenges and pitfalls in periodic savings plans include procrastination, inconsistency in contributions, impulsive spending, market fluctuations, and inflation. Developing strategies to overcome these challenges and stay on track with the savings plan is essential.
Tips for staying on track with periodic savings plans include establishing an emergency fund, reducing expenses and increasing income, seeking professional financial advice, regularly reviewing and adjusting the plan, and celebrating milestones and achievements.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.














