A market sector is a term used in economics and finance to refer to a specific segment of the economy. It is typically a broader term than an industry, which refers to a group of companies that sell similar goods and services and compete directly with each other. Market sectors are important because they help investors and analysts understand how various companies are performing in relation to others within the same space. Analysts typically divide the stock market into different sectors to organize companies into comparable groups. One of the most common ways of classifying market sectors is through the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS). This system breaks down the market into 11 sectors: communication services, consumer discretionary, consumer staples, energy, financials, healthcare, industrials, information technology, materials, real estate, and utilities. Each sector has its own set of industries, which are further broken down into individual companies. Investors need to understand market sectors because companies within the same sector tend to be affected by similar economic conditions. For example, all companies within the energy sector will be impacted by oil price fluctuations. In contrast, those in the healthcare sector will be influenced by factors such as government regulations and patent laws. By understanding these trends and factors, investors can make informed decisions about where to invest their money. The Global Industry Classification Standard is a system developed by Standard & Poor's (S&P) and Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) to classify publicly traded companies into different market sectors based on their primary business activities. The GICS was introduced in 1999 and is now widely used by investors, analysts, and financial institutions worldwide. The GICS consists of 11 market sectors, which are further divided into 158 sub-industries. Each company is assigned a GICS code based on its primary business activity, which helps investors easily identify and compare companies within the same sector or sub-industry. This system provides a common language for investors and analysts to communicate about different sectors and sub-sectors of the economy. The GICS is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the global economy and emerging industry trends. For example, in 2016, real estate was added as a separate sector to the GICS, reflecting the growing importance of the real estate industry as an asset class. Previously, real estate companies were classified under the financial sector. The GICS has several benefits for investors and financial institutions. It provides a standardized system for classifying companies that are widely recognized and used. This makes it easier for investors to compare companies within the same sector or sub-industry and to identify investment opportunities. It helps investors to diversify their portfolios by investing in different sectors and sub-industries. This can help to reduce risk and improve returns over time. The GICS provides a framework for analyzing and understanding different sectors and industries, which can be helpful for making informed investment decisions. Market sectors play a crucial role in finance and investments. Understanding market sectors is important for investors to make informed decisions and build a diversified portfolio. Here are some benefits and importance of market sectors in finance: Organizing Stocks. Market sectors provide a structure to categorize stocks and companies that operate in similar industries. This helps investors to organize their investments and make informed decisions. Identifying Economic Trends. Market sectors provide an overview of the performance of different industries and their contribution to the overall economy. This allows investors to identify economic trends and take advantage of investment opportunities. Diversification. Investing in multiple market sectors helps to diversify investments and reduce the overall risk of the portfolio. Diversification helps to balance the portfolio and minimize losses in one market sector by spreading investments across multiple sectors. Risk Management: By understanding market sectors, investors can assess the risk of investing in different sectors and adjust their portfolios accordingly. This helps to manage risks and ensure a more stable investment portfolio. Comparison of Performance. By comparing the performance of different market sectors, investors can identify and invest in sectors that outperform the market. This helps to maximize returns and achieve investment goals. Decision-Making. Market sectors help investors to make informed investment decisions by providing a structure to evaluate companies based on their performance within their respective sectors. Market sector and market segment are two distinct terms used in business, marketing, and finance. Understanding the differences between the market sector and market segment can help businesses identify and target their customers more effectively, allocate resources more efficiently, and make informed investment decisions. Here are some of the key differences between the market sector and the market segment: The market sector refers to a segment of the economy that is generally larger than the industry. It is a grouping of companies that operate in the same space and are affected by similar economic conditions. The Global Industry Classification Standard is the most common way of classifying market sectors. On the other hand, a market segment refers to a group of customers who share similar needs, preferences, or characteristics. Market segmentation is a marketing strategy that divides a broad target market into smaller subgroups with distinct needs and characteristics. Companies can use market segmentation to develop and market products and services that meet the specific needs of each segment. Market sector classification aims to provide investors with a framework for understanding the performance and outlook of different parts of the economy. By grouping companies according to their industry or sector, investors can compare the performance of different companies in the same sector, identify trends and patterns, and make informed investment decisions. Market segmentation, on the other hand, is a marketing strategy that helps businesses identify and target specific groups of customers who are most likely to buy their products or services. By understanding the unique needs and characteristics of each market segment, companies can tailor their marketing messages and offerings to meet the specific needs of each group. Market sector classification is based on the type of industry or sector in which a company operates. Companies are grouped according to the nature of their business activities and their products or services. For example, a company involved in producing and distributing energy would be classified under the energy sector. Market segmentation, on the other hand, is based on customer characteristics, such as demographics, psychographics, behavior, or geographic location. Companies use market research and data analysis to identify common characteristics among customers and group them into segments. For example, a company that sells sports equipment might segment its market by age, income, and gender and develop marketing strategies that target each segment differently. Understanding the differences between the market sector and market segment is important for businesses for several reasons. For example, companies that operate in a specific market sector need to understand the economic conditions and trends that affect that sector. By staying informed about the performance and outlook of the sector, companies can make informed decisions about investing, expanding, or divesting their businesses. Companies that use market segmentation can benefit from a more targeted approach to marketing and customer acquisition. By identifying the unique needs and characteristics of each market segment, companies can develop products and services that meet the specific needs of each group and tailor their marketing messages and offerings accordingly. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and profitability. Investing in market sectors can be a smart way to diversify your portfolio and take advantage of different economic conditions or industry trends. Some important considerations should be noted when one would like to invest in market sectors. When investing in market sectors, keep in mind the following: Before investing in any market sector, it is important to clearly understand your investment goals and risk tolerance. Your investment goals should dictate how much you are willing to invest and how long you plan to stay invested. Risk tolerance refers to your willingness to accept volatility and uncertainty in the markets. Understanding your risk tolerance can help you make informed decisions about which market sectors to invest in and how much to invest. Diversification is the practice of spreading your investments across different sectors and asset classes to reduce risk. By investing in multiple sectors, you can reduce the impact of any one sector's performance on your overall portfolio. It is important to note that diversification does not guarantee a profit or protect against loss, but it can help reduce overall risk. When investing in market sectors, it is important to be aware of the fees associated with different investment options, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, and individual stocks. Each investment option comes with its own set of fees, including management fees, transaction fees, and expense ratios. These fees can eat into your returns over time, so selecting investment options with low fees is important whenever possible. Finally, when investing in market sectors, selecting investments that align with your investment strategy is important. For example, if you are a long-term investor with a low-risk tolerance, you may want to focus on investing in sectors that have a history of stable growth, such as consumer staples or utilities. On the other hand, if you are a more aggressive investor with a high-risk tolerance, you may want to focus on investing in sectors that have a higher potential for growth, such as technology or healthcare. By selecting investments that align with your investment strategy, you can help maximize your returns and minimize your risk. Here are some investment options to consider: ETFs are a type of investment fund that trades like a stock on an exchange. They are similar to mutual funds in that they hold a basket of securities but differ in how they are bought and sold. ETFs are traded throughout the day on stock exchanges, whereas mutual funds are bought and sold at the end of the trading day at the net asset value (NAV) price. ETFs offer several advantages for investors looking to invest in market sectors. They provide exposure to a specific market sector or industry without requiring investors to buy individual stocks. This makes diversifying across multiple companies within a sector easier, which can help reduce risk. Additionally, ETFs typically have lower fees than mutual funds, making them a cost-effective option for investors. Mutual funds are another type of investment fund that holds a basket of securities. Unlike ETFs, mutual funds are bought and sold at the end of the trading day at the NAV price. They are managed by professional portfolio managers who invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities, depending on the fund's investment objective. Mutual funds offer several advantages for investors looking to invest in market sectors. They provide exposure to a specific market sector or industry without requiring investors to buy individual stocks. They also offer diversification across multiple companies within a sector, which can help reduce risk. However, mutual funds typically have higher fees than ETFs, making them a less cost-effective option for investors. Investors can also invest in individual stocks within a specific market sector. This approach requires investors to research and analyze individual companies within a sector and select stocks that align with their investment strategy. While investing in individual stocks can provide the potential for higher returns, it also comes with higher risk, as the performance of a single company can have a significant impact on the value of an investor's portfolio. Investing in individual stocks requires significant research and analysis to make informed investment decisions. It also requires investors to actively manage their portfolios, which can be time-consuming and require high expertise. Market sectors are specific segments of the economy that help investors and analysts understand how companies are performing in relation to others within the same space. The Global Industry Classification Standard is the most common way of classifying market sectors and provides a standardized system for classifying companies. Understanding market sectors is important for investors to make informed decisions and build a diversified portfolio, as companies within the same sector tend to be affected by similar economic conditions. It also helps investors to identify economic trends, diversify their portfolios, manage risks, and compare the performance of different market sectors. When investing in market sectors, investors should consider their investment goals and risk tolerance, diversify their portfolios, be aware of the fees associated with different investment options, and select investments that align with their investment strategy. Investors may consider investment options such as exchange-traded funds, mutual funds, and individual stocks. It is highly recommended to consult wealth management services for guidance on investing in market sectors.What Is Market Sector?
Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS) for Market Sectors
Benefits and Importance of Market Sectors in Finance

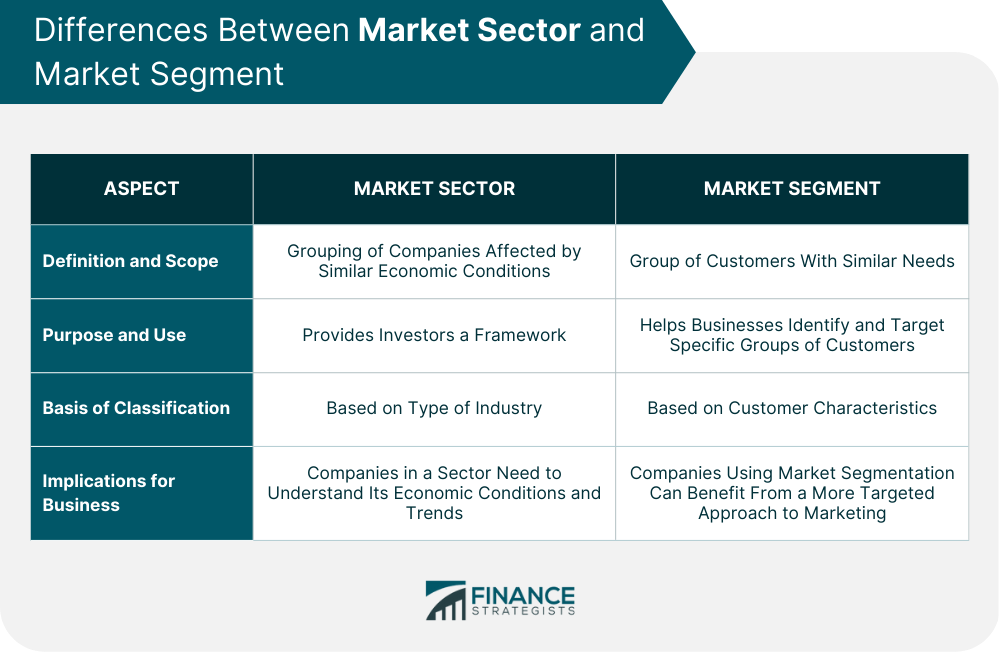
Differences Between Market Sector and Market Segment
Definition and Scope
Purpose and Use
Basis of Classification
Implications for Business
How to Invest in Market Sectors
Key Considerations When Investing in Market Sectors
Your Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
Diversification of Your Portfolio Across Multiple Sectors and Asset Classes to Reduce Risk
Fees Associated With Different Investment Options
Investments That Align With Your Investment Strategy
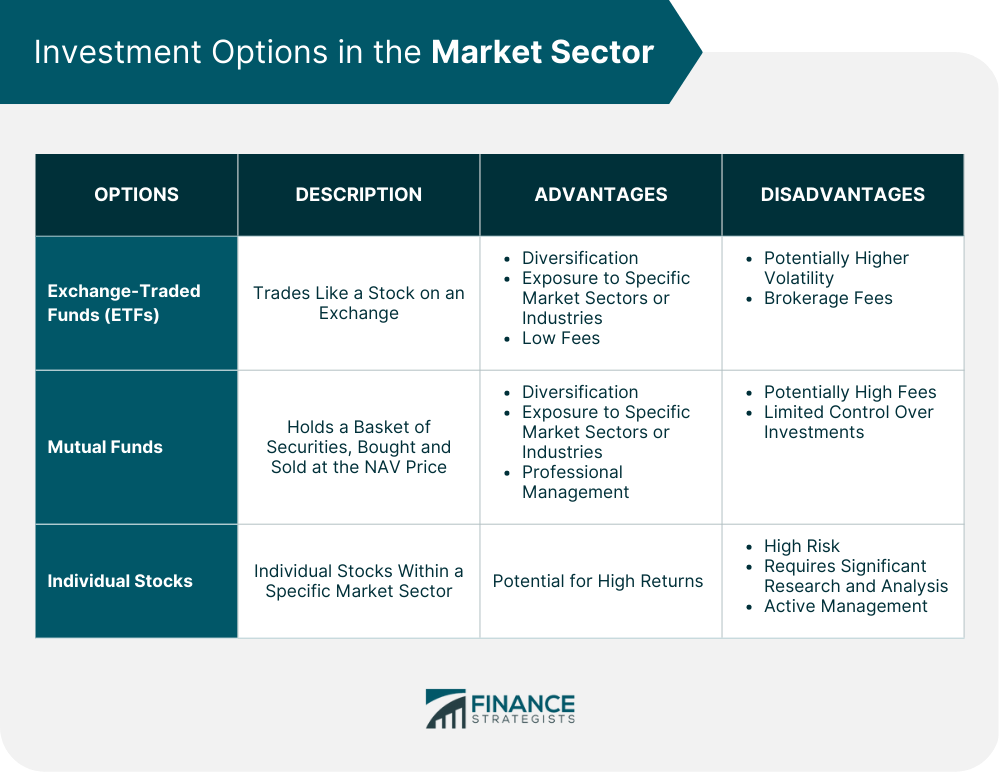
Investment Options
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Mutual Funds
Individual Stocks
Final Thoughts
Market Sector FAQs
A market sector is a specific segment of the economy that groups together companies that operate in the same space and are affected by similar economic conditions.
The GICS is a system Standard & Poor's (S&P) and Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI) developed to classify publicly traded companies into different market sectors based on their primary business activities.
Understanding market sectors is important for investors to make informed decisions and build a diversified portfolio. Companies within the same market sector tend to be affected by similar economic conditions, so understanding these trends and factors can help investors identify investment opportunities and manage risks.
Investors can invest in market sectors through options such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, and individual stocks within a specific market sector. It's important to consider investment goals, risk tolerance, and the fees associated with different investment options when choosing how to invest in market sectors.
A market sector refers to a segment of the economy that is generally larger than an industry and groups together companies that operate in the same space. On the other hand, a market segment refers to a group of customers who share similar needs, preferences, or characteristics. Understanding the differences between market sectors and market segments can help businesses target their customers more effectively and make informed investment decisions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















