Passive portfolio management is an investment strategy that aims to achieve long-term growth while minimizing costs and risks by investing in a diversified portfolio of assets and tracking the performance of a particular market index or asset class. This type of portfolio management involves a more hands-off approach to investing. Passive portfolio managers typically rely on pre-defined rules and algorithms to construct and manage portfolios, which reduces the need for human intervention and decision-making. Passive portfolio management is particularly appealing to investors who prioritize low costs and long-term growth over short-term gains. It is also a popular investment strategy for novice investors who lack the knowledge or resources to actively manage their portfolios. By investing in a passive portfolio, investors can gain exposure to a wide range of assets, diversify their portfolios, and achieve market returns without incurring high fees and expenses. There are several passive portfolio management strategies that investors can choose from, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks. Here are three popular strategies: Index investing involves constructing a portfolio that mirrors the performance of a particular market index, such as the S&P 500. Index investors aim to achieve returns that match the overall market, rather than trying to outperform it. By investing in an index fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF), investors can gain exposure to a broad range of assets while minimizing costs and risks. Diversifying a portfolio across various asset classes such as bonds, stocks, and cash is known as asset allocation. This technique helps investors to mitigate risk and attain a more stable return on investment by avoiding overexposure to any single asset class. Asset allocation strategies can be tailored to an investor's risk tolerance and investment goals, and can be adjusted over time to reflect changing market conditions. Buy-and-hold investing involves purchasing stocks or other assets and holding onto them for an extended period, rather than trading them frequently. Buy-and-hold investors aim to achieve long-term growth by investing in high-quality assets and allowing them to appreciate over time. This approach minimizes transaction costs and taxes, and allows investors to take advantage of compounding returns. Passive portfolio management has several benefits for investors, including: Passive portfolio management strategies typically involve lower fees and expenses compared to active portfolio management since there is less work required in managing the portfolio. This can result in a higher net return for investors. These strategies tend to have lower portfolio turnover compared to active management strategies. This means that investors do not need to make as many trades, which can help to reduce transaction costs and minimize taxes. This approach is designed to track the performance of a specific market index or asset class, which reduces the risk of underperforming the market. This is especially beneficial for novice investors who may not have the knowledge or resources to actively manage their portfolios. Passive portfolio management is not without its drawbacks, including: Passive portfolio management strategies typically follow pre-defined rules, such as tracking a particular index or asset class. This lack of flexibility can be a disadvantage if the market conditions change or if the investor's goals or risk tolerance change. These strategies are designed to track market indices or asset classes, which means that they are exposed to the same risks as the broader market. In the event of a market downturn, passive portfolios can experience significant losses, and investors may have to wait for a recovery to regain their losses. Passive portfolio managers may not be able to perfectly track the index or asset class they are trying to replicate, resulting in a tracking error. This error can result in underperformance or overperformance of the portfolio relative to the benchmark. While the tracking error is usually small, it can accumulate over time and impact long-term returns. Passive portfolios can be constructed using several different methodologies. Here are three popular types of passive portfolios: Market-cap weighted portfolios allocate more weight to companies with larger market capitalizations. This approach is based on the assumption that larger companies tend to be more stable and less risky than smaller ones. However, this approach can also lead to an over-concentration in a few large-cap stocks, which could increase risk. Equal-weighted portfolios allocate the same weight to all stocks in the portfolio, regardless of their market capitalization. This approach can help to diversify the portfolio and reduce the risk of over-concentration in a few large-cap stocks. It may also result in a higher allocation to smaller, riskier companies. Factor-based portfolios aim to capture specific investment factors, such as value, momentum, or quality, by investing in stocks that exhibit those characteristics. These portfolios are constructed using rules-based strategies and are designed to outperform the market over the long term. Passive portfolio management requires careful consideration of several key factors, including: Choosing the right assets to include in a passive portfolio is critical to achieving long-term growth. Investors should consider the characteristics of the asset, such as its historical performance, volatility, and correlation with other assets in the portfolio. Asset allocation is the process of determining the optimal mix of assets for a portfolio based on an investor's goals and risk tolerance. Asset allocation should be tailored to the individual investor and adjusted over time as market conditions and investment goals change. Rebalancing involves adjusting the portfolio's asset allocation periodically to ensure that it remains aligned with the investor's goals and risk tolerance. Rebalancing can help to reduce risk and maximize returns over the long term. Investors should regularly monitor the performance of their passive portfolios to ensure that they are meeting their investment goals. This may involve reviewing performance metrics, such as returns and volatility, and making adjustments to the portfolio as needed. Passive portfolio management is an investment strategy that aims to achieve long-term growth while minimizing costs and risks by tracking the performance of a particular market index or asset class. This type of portfolio management employs strategies that include index investing, asset allocation, and buy-and-hold Investing. The benefits of passive portfolio management include lower fees, reduced portfolio turnover, and reduced risk of underperforming the market. However, drawbacks such as limited flexibility, exposure to market downturns, and tracking error should also be taken into consideration. Passive portfolios can be constructed using several different methodologies such as market-cap weighted portfolios, equal-weighted portfolios, and factor-based portfolios. Investors should also consider key factors such as asset selection, asset allocation, rebalancing, and monitoring performance to ensure optimal portfolio management. For those who lack the time or expertise to manage their own portfolio, a professional wealth management service may be a valuable resource to help tailor and manage a passive portfolio.What is Passive Portfolio Management?
Passive Portfolio Management Strategies
Index Investing
Asset Allocation
Buy-And-Hold Investing

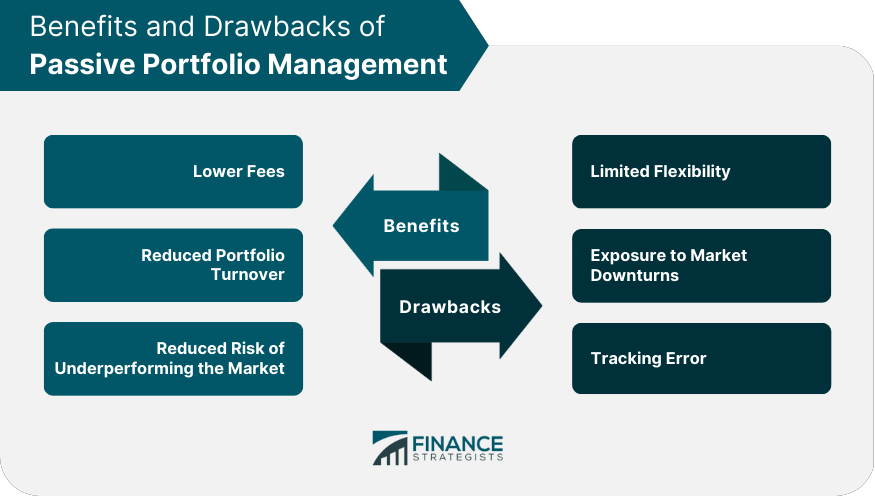
Benefits of Passive Portfolio Management
Lower Fees
Reduced Portfolio Turnover
Reduced Risk of Underperforming the Market
Drawbacks of Passive Portfolio Management
Limited Flexibility
Exposure to Market Downturns
Tracking Error
Types of Passive Portfolios
Market-Cap Weighted Portfolios
Equal-Weighted Portfolios
Factor-Based Portfolios
Key Factors to Consider for Passive Portfolio Management
Asset Selection
Asset Allocation
Rebalancing
Monitoring Performance
Bottom Line
Passive Portfolio Management FAQs
Passive portfolio management is an investment strategy that aims to achieve long-term growth while minimizing costs and risks by investing in a diversified portfolio of assets and tracking the performance of a particular market index or asset class.
The benefits of passive portfolio management include lower fees, reduced portfolio turnover, and reduced risk of underperforming the market.
Common passive portfolio management strategies include index investing, asset allocation, and buy-and-hold investing.
Drawbacks of passive portfolio management include limited flexibility, exposure to market downturns, and tracking error.
Investors should consider factors such as asset selection, asset allocation, rebalancing, and monitoring performance when implementing a passive portfolio management strategy.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















