Blockchain Authentication is a secure verification process in the blockchain network that enhances transaction security and transparency. It utilizes cryptographic keys and digital signatures to authenticate users, devices, or systems, preventing identity theft and fraud. This authentication is crucial in sectors like finance, healthcare, and supply chain, offering robust defense against data breaches and ensuring trust. Despite challenges such as technological complexity and regulatory uncertainties, blockchain authentication plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of data, preventing unauthorized access, and revolutionizing various industries through secure transactions. The blockchain structure is decentralized, meaning that it operates on a network of computers, with each having access to the entire blockchain. It uses encryption to ensure that transactions are secure, with each block containing a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. The process of authentication in blockchain involves the verification of transactions. Each transaction is signed using a private key, and then it is broadcasted to the network. The network nodes validate the transaction using the corresponding public key. The process of hashing ensures that the data hasn't been tampered with, thereby verifying the authenticity of the transaction. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They play a pivotal role in blockchain authentication as they enforce and automate the execution of a contract once predefined conditions are met. This feature further adds to the security, efficiency, and trustworthiness of the authentication process. Understanding the technology behind blockchain is crucial for the successful implementation of blockchain authentication. Blockchain is complex, and to work with it effectively, a certain level of technological proficiency is necessary. Additionally, issues related to blockchain scalability, or the ability of a blockchain to handle an increasing amount of transactions, can influence the effectiveness of blockchain authentication. Blockchain authentication operates in a rapidly evolving regulatory environment. Global regulations concerning blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies vary widely, which can pose challenges for its adoption. Furthermore, compliance with data protection and privacy laws can influence how blockchain authentication is implemented and used. Blockchain's cryptographic measures ensure enhanced security. Each transaction is linked to the preceding one via cryptographic hashes, making it nearly impossible to alter data. This secure design significantly reduces the risk of fraud. Blockchain operates on a public ledger, which is accessible and auditable by all parties in the network. This openness fosters transparency and enhances trust in transactions. Blockchain authentication leverages automation to streamline verification processes. This automation eliminates the need for intermediaries, thereby reducing administrative costs and improving transaction speed. Despite its benefits, blockchain authentication presents technological challenges. The complexity of blockchain technology can be daunting, and a lack of understanding can hinder its adoption. In addition, scalability issues, or the ability of a blockchain network to manage increasing volumes of transactions, can impact the efficacy of blockchain authentication. Uncertainty around global regulation is another significant drawback. The rapidly evolving legal landscape and the absence of universal standards can pose difficulties. Moreover, compliance with data protection and privacy laws can be challenging, particularly given the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain. Finally, despite its potential, there can be a reluctance to embrace blockchain authentication. Skepticism about the security of the technology, alongside the potential for misuse or manipulation, can hamper its acceptance. These trust issues are significant obstacles to overcome for blockchain authentication to reach its full potential. Blockchain authentication is a new and innovative way to verify identity that is more secure and efficient than traditional methods. This makes it ideal for a variety of applications, including: Financial Services: Blockchain authentication can be used to verify the identity of customers and employees in the financial services industry. This can help to prevent fraud and money laundering. Government: Blockchain authentication can be used to verify the identity of citizens and government officials. This can help to improve the efficiency of government services and reduce the risk of identity theft. Healthcare: Blockchain authentication can be used to verify the identity of patients and healthcare providers. This can help to improve the security of patient data and reduce the risk of medical errors. Logistics: Blockchain authentication can be used to verify the identity of shippers, carriers, and consignees. This can help to improve the security of the supply chain and prevent counterfeiting. Blockchain authentication stands as a potent solution to address the escalating need for secure, transparent, and efficient transactions in today's digitally driven world. It leverages cryptographic keys and digital signatures for validating identities, reducing the risk of fraud, and fostering trust, especially within financial systems. While it brings immense benefits, such as enhanced security, improved transparency, and increased efficiency, it also presents considerable challenges. These include technological complexity, the fast-paced regulatory environment, and issues related to adoption and trust. Understanding these complexities is essential for businesses and individuals navigating this new terrain. Despite the obstacles, as technological understanding improves and legal landscapes continue to evolve, the transformative potential of blockchain authentication in various sectors becomes increasingly clear. Ultimately, this innovative technology holds significant promise for the future of secure and trustworthy digital transactions.Blockchain Authentification Overview
How Blockchain Authentication Works
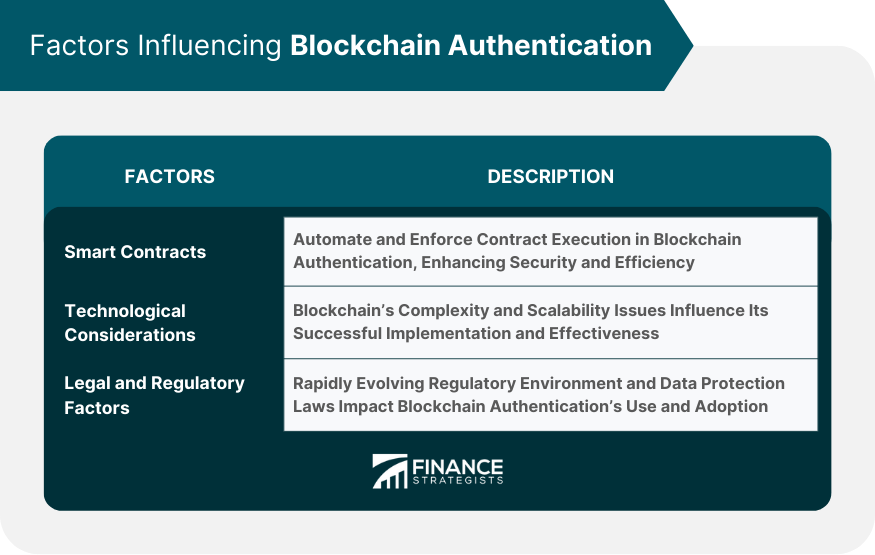
Factors Influencing Blockchain Authentication
Smart Contracts
Technological Considerations
Legal and Regulatory Factors
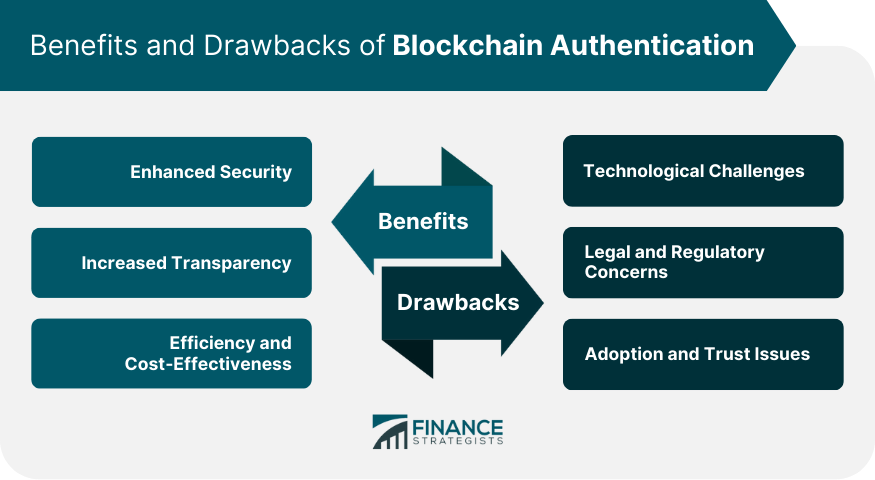
Benefits of Blockchain Authentication
Enhanced Security
Increased Transparency
Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness
Drawbacks of Blockchain Authentication
Technological Challenges
Legal and Regulatory Concerns
Adoption and Trust Issues
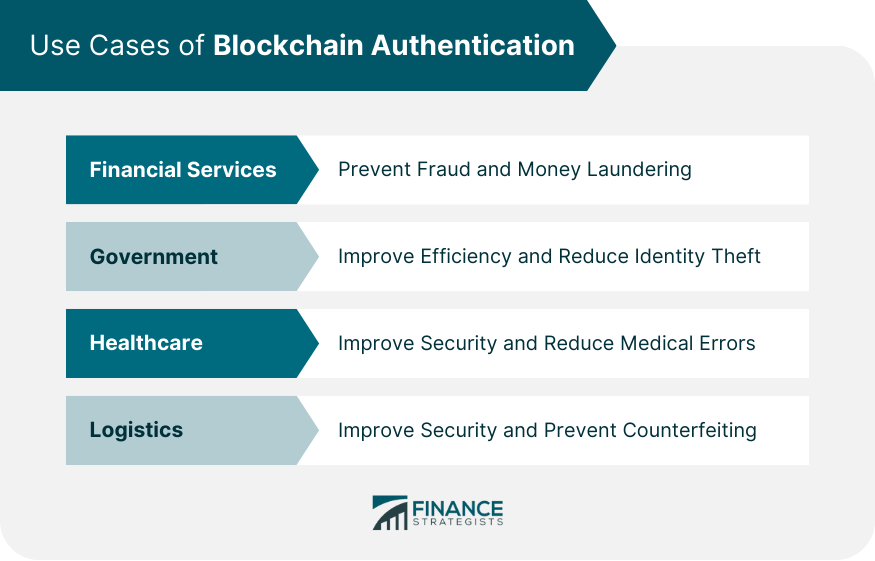
Use Cases of Blockchain Authentication
Conclusion
Blockchain Authentication FAQs
Blockchain authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user, device, or system within the blockchain network. It uses cryptographic keys and digital signatures to ensure the authenticity of data or transactions.
Blockchain authentication works by verifying transactions within the network. A transaction is signed using a private key and broadcasted to the network. The nodes validate the transaction using the corresponding public key, and a process called hashing ensures the data hasn't been tampered with.
Blockchain authentication is important in financial systems as it enhances the security and transparency of transactions. It can prevent fraudulent transactions and reduce the risk of data breaches, which is critical in industries where trust and security are paramount.
The benefits of blockchain authentication include enhanced security through cryptographic measures, increased transparency due to the public ledger system, and improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness through the automation of verification processes.
The drawbacks of blockchain authentication include technological challenges due to its complexity, uncertainty around global regulations, and trust issues stemming from a reluctance to embrace this new technology and the potential for misuse.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















