Blockchain and AI are two of the most transformative technologies of our time. Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that allows multiple parties to maintain a copy of an immutable string of records, secured by cryptography. It enhances transparency, security, and traceability in transactions. Artificial Intelligence (AI), on the other hand, refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. It involves learning from data inputs, reasoning to make decisions, and self-correction for improved accuracy over time. The integration of Blockchain and AI promises to revolutionize various sectors. Blockchain can provide a secure, transparent platform for AI to operate, while AI can offer advanced analytics and automation capabilities for blockchain systems. Together, they bring the potential for improved data security, increased efficiency, advanced decision-making, and enhanced trust and transparency. A distributed ledger in the blockchain is a database that is consensually shared and synchronized across multiple sites, institutions, or geographies. It allows transactions to have public "witnesses," thereby reducing the risk of backdoor fraud and cybercrimes. Cryptography in blockchain secures transactions and controls the creation of new units. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transactions, protecting them from being altered or tampered with. The consensus mechanism in blockchain is a fault-tolerant mechanism that is used in computer and blockchain systems to achieve the necessary agreement on a single data value or a single state of the network among distributed processes or systems. AI can increase blockchain's security by detecting anomalies and suspicious activities in the network. Machine learning algorithms can be used to monitor transactions and flag those that appear abnormal, helping to prevent potential security breaches. Blockchain's immutable nature can help increase the transparency of AI systems. By recording all data inputs, processing, and outputs on a blockchain, users can audit the decision-making process of AI, making it easier to understand and trust. Combining AI with blockchain can streamline data management processes. AI can analyze and organize vast amounts of data, while blockchain can ensure the integrity and provenance of data. This combination can lead to more efficient and reliable data management systems. The integration of blockchain and AI can significantly enhance data security. While blockchain provides a secure, tamper-proof system, AI can detect any unusual behavior or fraudulent activities, ensuring a high level of security and data privacy. With AI-powered smart contracts and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), transactional processes can be automated, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency. AI's advanced analytics combined with blockchain's secure data storage can facilitate better decision-making. The insights generated from the AI analysis of blockchain-stored data can be invaluable for businesses and institutions. Blockchain's immutable and transparent nature, coupled with AI's decision-making capability, can lead to a system that is not only efficient but also engenders trust among participants. The integration of blockchain and AI involves complex processes that require significant technical expertise. This can be a barrier to entry for many businesses and organizations. Both blockchain, especially in the mining process, and AI, in model training and execution, can consume large amounts of energy. This could have significant environmental impacts and lead to high operational costs. The integration of blockchain and AI also brings regulatory and ethical challenges. These can range from data privacy issues to accountability in decision-making processes. To fully utilize the benefits of AI, high-quality data is required. However, the standardization of data across blockchain can be a challenge, limiting the full potential of AI analysis. Banks are using blockchain and AI to streamline processes, reduce fraud, and improve customer experiences. For example, AI can be used to automate customer service, while blockchain can secure transactions and verify identities. Healthcare organizations are using blockchain to securely share patient records and AI to analyze medical data. Together, these technologies can improve patient care and reduce costs. Blockchain can provide a transparent and secure ledger for supply chain transactions, while AI can optimize logistics and inventory management. These technologies can improve the efficiency and transparency of supply chains. The energy sector is using blockchain and AI to enable peer-to-peer energy trading and optimize energy usage. This can lead to more efficient and sustainable energy systems. The integration of AI with IoT devices can lead to smarter and more autonomous systems. Blockchain can secure the data generated by these devices and provide a transparent ledger of their transactions. Organizations considering the adoption of blockchain and AI must assess the maturity of these technologies and their readiness for enterprise-level applications. The regulatory environment can significantly impact the adoption of blockchain and AI. Organizations must consider data privacy laws, financial regulations, and other regulatory factors. Ethical considerations are important in the adoption of blockchain and AI. These technologies must be used in a way that respects privacy, fairness, and other ethical principles. The acceptance of these technologies by users and the general public can significantly impact their success. User trust in the technologies and their understanding of them can influence their willingness to adopt them. The synergy of blockchain and AI heralds a transformative future in technology, fostering opportunities and innovative solutions. By leveraging blockchain's robust security and transparency alongside AI's efficiency and data analytics capabilities, we unlock vast potential across various sectors. Yet, as we tap into these benefits, it is essential to confront the accompanying challenges such as technical complexities, energy consumption, and regulatory and ethical considerations. These hurdles, however, are surmountable with continued innovation and adaptation. By effectively integrating blockchain and AI, we stand at the threshold of a future that redefines our societal and economic structures, proving once again, that the amalgamation of these technologies is far greater than the sum of their parts.What Are Blockchain and AI?
How Blockchain and AI Work
Distributed Ledger
Cryptography
Consensus Mechanism
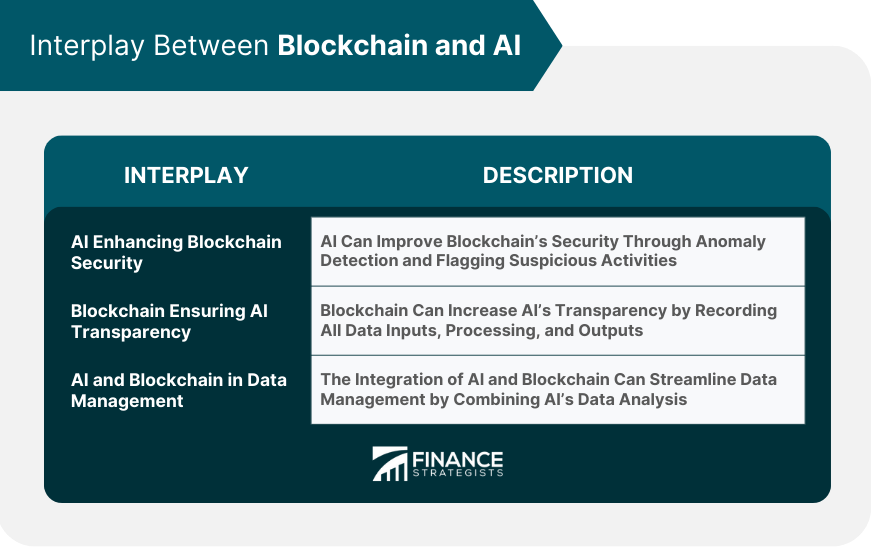
Interplay Between Blockchain and AI
AI in Enhancing Blockchain Security
Blockchain in Ensuring AI Transparency
AI and Blockchain in Data Management
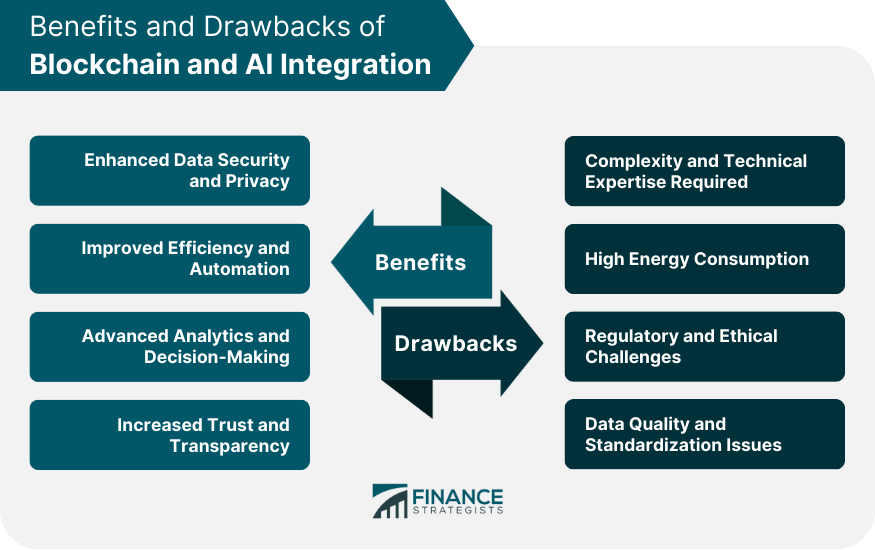
Benefits of Blockchain and AI Integration
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Improved Efficiency and Automation
Advanced Analytics and Decision-Making
Increased Trust and Transparency
Drawbacks of Blockchain and AI Integration
Complexity and Technical Expertise Required
High Energy Consumption
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
Data Quality and Standardization Issues
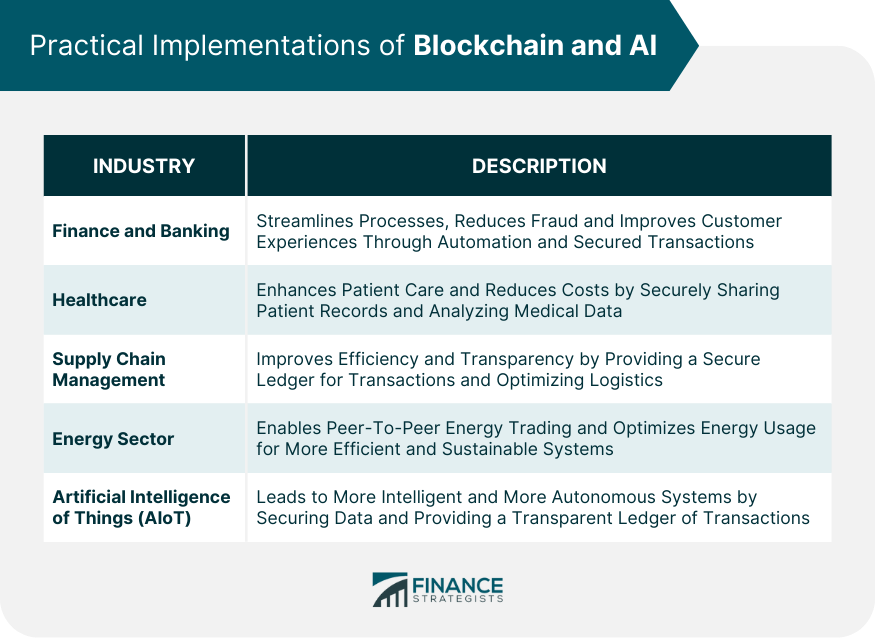
Practical Implementations of Blockchain and AI
Finance and Banking
Healthcare
Supply Chain Management
Energy Sector
Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT)
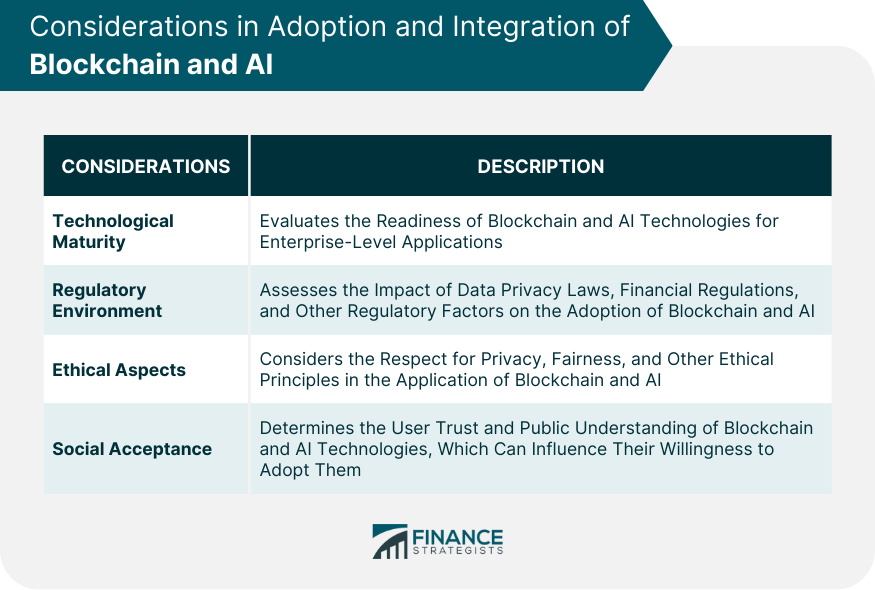
Considerations in Adoption and Integration of Blockchain and AI
Technological Maturity
Regulatory Environment
Ethical Aspects
Social Acceptance
Conclusion
Blockchain and AI FAQs
AI can significantly enhance the functionality of blockchain in several ways, including advanced data analysis, automated decision-making through smart contracts, and improved security through anomaly detection.
The integration of blockchain and AI can provide enhanced data security and privacy, improved efficiency and automation, advanced analytics and decision-making capabilities, and increased trust and transparency.
The integration of blockchain and AI poses several challenges such as technical complexity, high energy consumption, regulatory and ethical issues, and data quality and standardization problems.
The integration of blockchain and AI can have a significant impact across various sectors including finance and banking, healthcare, supply chain management, and cybersecurity.
The future of blockchain and AI integration holds promising potential with advanced data analysis, refined smart contracts, and improved security measures. However, this future is dependent on addressing the challenges related to energy consumption, technical complexity, and regulatory issues.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















