Gold and precious metals investing is a strategy that involves buying and holding assets such as gold, silver, platinum, and palladium to achieve various financial objectives. Investors are drawn to these tangible assets for their unique properties, such as rarity, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Historically, precious metals have served as a store of value and a hedge against inflation, currency fluctuations, and economic uncertainty. Today, there are numerous investment vehicles available for those interested in gaining exposure to precious metals, ranging from physical bullion to exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mining stocks. Gold has played a crucial role in human civilization for thousands of years. The metal's unique properties, such as its rarity, durability, and resistance to corrosion, have made it a symbol of wealth, power, and beauty. Gold has been used as currency, as a means of exchange, and as a store of value throughout history. It has also been a critical component of various religious and cultural practices. As civilizations advanced and financial systems became more complex, the importance of precious metals as investment assets grew. Gold and other precious metals began to be traded on commodity exchanges, and their prices became subject to market forces. Over time, various investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, were developed to offer investors exposure to the performance of precious metals without the need to own and store the physical assets. In the modern financial world, gold and other precious metals continue to serve as valuable investment assets. These metals are often considered a safe haven during times of economic and political uncertainty, as they tend to hold their value when other investments lose ground. Additionally, investing in precious metals can help to diversify an investment portfolio, potentially reducing overall risk. Gold is the most well-known and widely traded precious metal. Its history as a store of value and a symbol of wealth make it a popular choice for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and protect against economic downturns. Silver is another popular precious metal for investment purposes. While it has similar properties to gold, silver is more abundant and has a wider range of industrial applications. This makes silver prices more volatile than gold prices, but it also provides the potential for higher returns. Platinum is a rare precious metal with a wide range of industrial uses, particularly in the automotive industry. Due to its rarity and unique properties, platinum is often considered more valuable than gold. However, its price can be more volatile than gold and silver, as it is heavily influenced by industrial demand. Palladium is another rare precious metal with significant industrial applications, particularly in the electronics and automotive sectors. Like platinum, its price is heavily influenced by industrial demand and can be quite volatile. In addition to the more widely recognized precious metals, investors may also consider metals such as rhodium, iridium, and osmium. These metals are much rarer than gold and silver, and their prices can be highly volatile. However, they may offer unique investment opportunities for those seeking exposure to niche markets. One of the most traditional ways to invest in precious metals is by purchasing physical bullion bars. These bars are typically made of gold, silver, platinum, or palladium and are available in various weights and purities. Coins Coins are another popular form of physical bullion. Many countries mint their own gold, silver, platinum, and palladium coins, which can be purchased by investors. Coins often carry a premium over the spot price of the metal due to their collectible value and limited production. Rounds Rounds are similar to coins but are not issued by a government and do not have a face value. They are generally made of gold, silver, platinum, or palladium and can be purchased in various weights and purities. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer investors a convenient way to gain exposure to precious metals without the need to own and store the physical assets. Precious metal ETFs typically track the performance of a specific metal or a basket of metals, allowing investors to buy and sell shares on an exchange just like a stock. Investing in mining stocks and mutual funds provides exposure to precious metals indirectly through the performance of companies engaged in the exploration, production, and processing of these metals. This approach offers the potential for higher returns, as mining stocks can outperform the underlying metals, but it also comes with additional risks related to the performance of individual companies and the mining industry as a whole. Futures and options contracts are financial instruments that allow investors to speculate on the future price movements of precious metals. These contracts can be used for both hedging and speculative purposes and are typically traded on organized exchanges. Certificates and pooled accounts represent ownership of a specific amount of precious metal held by a financial institution or other third party. These investment vehicles offer the benefits of owning physical metals without the need to store and insure the assets. However, they also come with counterparty risks, as the investor's ownership is dependent on the trustworthiness of the issuing institution. Digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies and tokens, can be backed by precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, and palladium. These assets can be bought, sold, and traded on various digital asset exchanges, offering investors a modern and potentially more accessible way to invest in precious metals. The fundamental driver of precious metal prices is the balance between supply and demand. Factors that can impact supply include mining production, recycling, and changes in central bank reserves. Demand for precious metals can be influenced by jewelry and industrial uses, as well as investment demand. Economic conditions, such as inflation, interest rates, and overall economic growth, can have a significant impact on precious metal prices. In general, precious metals tend to perform well during periods of economic uncertainty or when inflation is high. Geopolitical events, such as wars, political unrest, and changes in government policies, can create uncertainty in financial markets and increase demand for safe-haven assets like gold and other precious metals. As precious metals are often priced in U.S. dollars, changes in the value of the dollar can have a direct impact on metal prices. A weaker dollar can make precious metals more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially increasing demand and driving prices higher. Central banks around the world hold significant amounts of gold as part of their reserves. Changes in central bank policies, such as buying or selling gold, can influence the supply and demand dynamics in the market and affect gold prices. Technological advancements can impact the demand for certain precious metals, particularly those with significant industrial uses. For example, innovations in the automotive and electronics industries can influence the demand for platinum and palladium. Precious metal prices can be subject to significant short-term fluctuations due to factors such as economic data releases, geopolitical events, and changes in investor sentiment. This volatility can create opportunities for short-term traders, but it can also pose risks for long-term investors. Investors who choose to own physical precious metals must consider the costs and risks associated with storage and security. Storing metals at home can expose them to theft, while storing them in a professional vault or depository can incur additional fees. Additionally, transporting and insuring physical metals can be both costly and logistically challenging. Investing in precious metal certificates, pooled accounts, or digital assets backed by precious metals involves relying on third parties to fulfill their obligations. If the issuing institution or custodian fails to honor their commitments, investors may lose some or all of their investment. While some precious metal investments, such as ETFs and mining stocks, are highly liquid and can be easily bought and sold on exchanges, others may be more difficult to sell. Physical metals, in particular, may require additional time and effort to find a buyer, especially in less-common forms or less-liquid markets. Changes in government regulations, such as taxes, import/export restrictions, or reporting requirements, can impact the attractiveness of precious metal investments. Investors should stay informed about potential regulatory changes and consider how they may affect their investment strategy. Investors who believe in the long-term value of precious metals may choose to buy and hold physical bullion, ETFs, or mining stocks as a long-term investment. This approach can help to protect against inflation and provide portfolio diversification, but it may also require patience and a tolerance for market volatility. Short-term traders may look to capitalize on price fluctuations in precious metals by using instruments such as futures, options, or leveraged ETFs. This approach can offer the potential for higher returns but also carries increased risks and requires a thorough understanding of market dynamics and trading strategies. Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount in precious metals at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This strategy can help to reduce the impact of market volatility and average out the cost basis of the investment over time. Incorporating precious metals into a diversified investment portfolio can help to reduce overall risk by providing a hedge against economic uncertainty and currency fluctuations. Investors should consider their individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon when determining the appropriate allocation to precious metals. Working with a financial advisor or investment professional can help investors develop a customized precious metals investment strategy that aligns with their unique financial goals and risk tolerance. Profits realized from the sale of precious metals are subject to capital gains taxes. The tax rate and holding period requirements can vary depending on the type of investment and the investor's country of residence. In some jurisdictions, precious metals such as gold and silver coins may be considered collectibles and subject to higher tax rates than other types of investments. Certain investment vehicles, such as ETFs or individual retirement accounts (IRAs), may offer tax advantages for investors looking to gain exposure to precious metals. Investors should consult a tax professional to understand the specific tax implications of their chosen investment strategy. Investing in gold and other precious metals can provide valuable diversification benefits and serve as a hedge against economic uncertainty, currency fluctuations, and inflation. It is essential for investors to understand the various investment vehicles available, such as physical bullion, ETFs, mining stocks, and digital assets backed by precious metals. Incorporating precious metals into a diversified investment portfolio can help reduce overall risk and improve long-term returns. Navigating the world of precious metals investing can be complex, and the right strategy can make a significant difference in achieving your financial goals. By engaging with professional wealth management services, you can gain access to expert advice, customized investment strategies, and a comprehensive understanding of the risks and rewards associated with gold and precious metals investing. Overview of Gold and Precious Metals Investing
History of Gold and Precious Metals Investing
Gold's Significance Throughout History
Evolution of Precious Metal Investments
Role of Precious Metals in Modern Finance
Types of Precious Metals for Investment
Gold
Silver
Platinum
Palladium
Lesser-Known Precious Metals
Investment Vehicles for Precious Metals
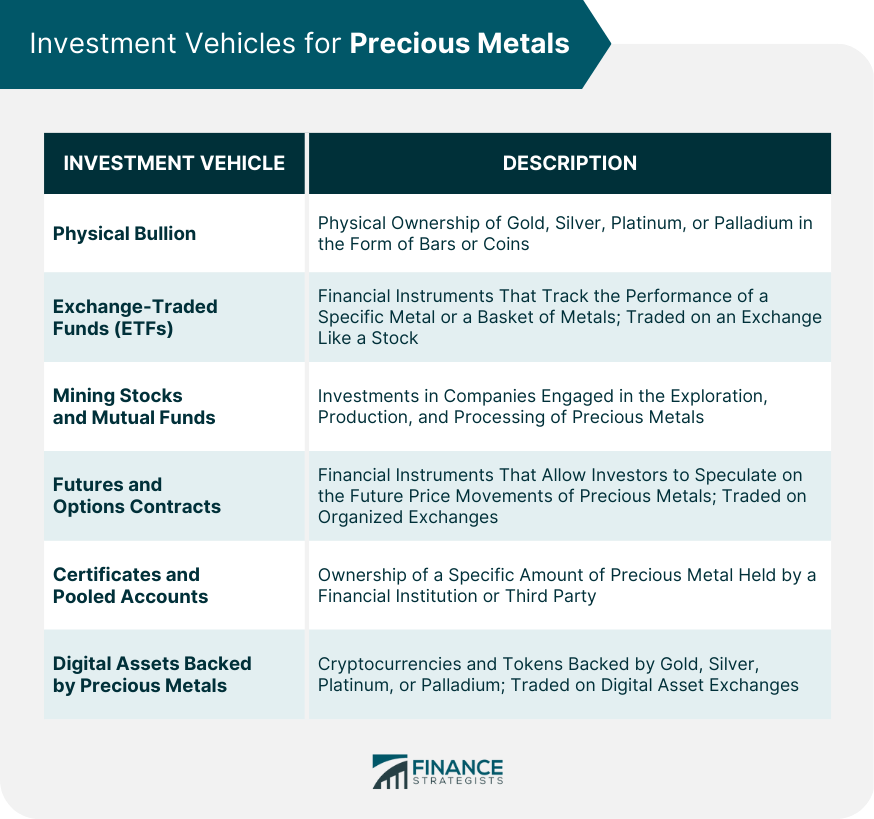
Physical Bullion
Bars
Exchange-Traded Funds
Mining Stocks and Mutual Funds
Futures and Options Contracts
Certificates and Pooled Accounts
Digital Assets Backed by Precious Metals
Factors Affecting Precious Metal Prices
Supply and Demand
Economic Conditions
Geopolitical Events
Currency Fluctuations
Central Bank Policies
Technological Advancements
Risks Associated With Investing in Precious Metals

Market Volatility
Storage and Security Concerns
Counterparty Risks
Liquidity Issues
Regulatory Changes
Strategies for Investing in Precious Metals

Long-Term Investment
Short-Term Trading
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Diversification
Leveraging Professional Advice
Tax Implications of Precious Metals Investing
Capital Gains Taxes
Collectible Tax Rates
Tax-Efficient Investment Vehicles
Final Thoughts
Gold and Precious Metals Investing FAQs
Gold and precious metals investing offers several advantages, including portfolio diversification, protection against inflation, and a hedge against currency fluctuations and economic uncertainty. These tangible assets have a history of maintaining their value over time, making them an attractive addition to a well-balanced investment portfolio.
There are various investment vehicles available for gold and precious metals investing, such as physical bullion (bars and coins), exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mining stocks, futures and options contracts, certificates and pooled accounts, and digital assets backed by precious metals. Each option has its unique characteristics, benefits, and risks, so it's essential to research and choose the one that best aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Numerous factors can affect the prices of gold and precious metals, including supply and demand dynamics, economic conditions (e.g., inflation, interest rates, and overall economic growth), geopolitical events, currency fluctuations, central bank policies, and technological advancements. These factors can cause short-term price fluctuations and influence long-term trends in precious metals investing.
Some risks associated with gold and precious metals investing include market volatility, storage and security concerns, counterparty risks, liquidity issues, regulatory changes, and tax implications. It's crucial for investors to understand and carefully consider these risks when developing their precious metals investment strategy.
Professional wealth management services can provide expert advice, customized investment strategies, and a comprehensive understanding of the risks and rewards associated with gold and precious metals investing. By working with a trusted wealth management advisor, you can build a more resilient and diversified investment portfolio that aligns with your financial goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











