Fee benchmarking is a systematic process of comparing the fees and service offerings of companies or providers within a specific industry or market. This practice helps organizations understand their position in the market and make informed decisions on pricing and service offerings. Fee benchmarking is essential across industries as it helps companies remain competitive, identify cost-saving opportunities, and ensure transparency. This practice is widely used in financial services, healthcare, technology, and professional services. The primary objectives of fee benchmarking include assessing market competitiveness, identifying areas for improvement, and enhancing service offerings. It also serves to improve negotiation power and promote transparency within the industry. The first step in fee benchmarking is to identify the scope of services being compared. This ensures that organizations compare like-for-like offerings and obtain meaningful insights from the process. Choosing the right set of comparable companies or providers is crucial for accurate fee benchmarking. The selected companies should have similar service offerings, operate in the same industry, and cater to a comparable client base. Collecting data on fees and service offerings is the next step in the fee benchmarking process. This data can be sourced from public records, industry surveys, or through direct outreach to comparable companies. Asset Management: Fee benchmarking in asset management allows firms to compare management fees, performance fees, and other charges to ensure they remain competitive and deliver value to clients. Banking: In the banking industry, fee benchmarking is used to assess fees for various products and services, such as loans, credit cards, and account maintenance, helping banks stay competitive and attract customers. Insurance: Insurance companies use fee benchmarking to compare premium rates, commissions, and administrative fees, enabling them to identify areas for improvement and ensure their offerings are competitively priced. Hospitals: Hospitals use fee benchmarking to compare prices for various medical procedures and services. This practice helps hospitals identify cost-saving opportunities and ensure they provide quality care at competitive prices. Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceutical companies utilize fee benchmarking to compare the prices of drugs and treatments. This enables them to make informed decisions about pricing strategies and maintain a competitive edge in the market. Medical Devices: Medical device manufacturers use fee benchmarking to assess the prices of their products against competitors. This information helps them develop pricing strategies that align with market trends and deliver value to customers. • Software Development: Software development companies use fee benchmarking to compare pricing models and service offerings, ensuring they stay competitive and deliver value to their clients. This practice helps them develop pricing strategies that align with market trends and deliver value to customers. Legal: Law firms use fee benchmarking to compare hourly rates, retainers, and alternative fee arrangements, ensuring they remain competitive and offer value to clients. Accounting: Accounting firms utilize fee benchmarking to assess fees for various services, such as audits, tax preparation, and consulting. This helps them remain competitive and offer cost-effective solutions to their clients. Consulting: Consulting firms employ fee benchmarking to compare their fees with those of competitors, ensuring they stay competitive and deliver value to their clients. Fee benchmarking helps organizations maintain their competitiveness in the market by comparing their fees and service offerings with those of their competitors, enabling them to make informed decisions about pricing strategies. By analyzing and comparing fees across the industry, companies can identify areas for cost savings and implement strategies to reduce expenses and improve profitability. Fee benchmarking equips organizations with valuable insights about market rates, empowering them to negotiate better deals with suppliers or vendors and obtain cost-effective solutions. By understanding how their fees and services compare with competitors, companies can enhance their service offerings to deliver better value to clients, ultimately fostering customer loyalty and long-term business success. Fee benchmarking promotes transparency within the industry by shedding light on pricing structures and service offerings. This, in turn, encourages companies to adopt best practices and maintain a competitive edge. One main challenge of fee benchmarking is obtaining accurate and reliable data on fees and service offerings, as this information is often proprietary and confidential. Fee benchmarking can lead to inaccurate comparisons if companies fail to account for differences in service offerings, quality, and value provided by the compared organizations. Companies conducting fee benchmarking may inadvertently introduce biases in data selection, leading to skewed results and misleading conclusions. Misinterpreting fee benchmarking results can lead to erroneous decisions and unintended consequences. Companies must exercise caution in interpreting and acting upon the insights obtained from fee benchmarking. To ensure accurate and up-to-date insights, organizations should regularly update their fee benchmarks, incorporating new data and market trends. Organizations can enhance the reliability of fee benchmarking by leveraging external data sources, such as industry surveys, research reports, and public records. In addition to quantitative data, companies should consider qualitative factors, such as service quality, customer satisfaction, and reputation, to comprehensively understand their market position. Companies can benefit from collaborating with industry peers and sharing insights, best practices, and lessons learned from their fee benchmarking experiences. Organizations can streamline the fee benchmarking process and improve accuracy by using specialized tools and software designed to gather, analyze, and visualize data. Fee benchmarking is a systematic process of comparing fees and service offerings of companies or providers within a specific industry or market to help businesses stay competitive, identify cost-saving opportunities, and ensure transparency. The fee benchmarking process involves identifying the scope of services, selecting comparable companies, and gathering data on fees and service offerings. Fee benchmarking is essential in different industries, including financial services, healthcare, technology, and professional services. The benefits of fee benchmarking include ensuring competitiveness in the market, identifying areas for cost savings, improving negotiation power with suppliers or vendors, enhancing service offerings, and encouraging transparency and best practices. However, fee benchmarking also poses challenges and pitfalls, such as data availability and reliability, inaccurate comparisons, potential biases in data selection, and misinterpretation of results. Best practices for effective fee benchmarking include regularly updating benchmarks, leveraging external data sources, incorporating qualitative factors, collaborating with industry peers, and utilizing fee benchmarking tools and software. Organizations looking to optimize their fee structures and enhance their service offerings should consider seeking the guidance of a financial advisor.What Is Fee Benchmarking?
Fee Benchmarking Process

Identifying the Scope of Services
Selecting Comparable Companies or Providers
Gathering Data on Fees and Service Offerings
Fee Benchmarking in Different Industries
Financial Services
Healthcare
Technology
• IT Services: Fee benchmarking in IT services helps companies compare rates for various services, such as consulting, support, and maintenance. This enables them to identify areas for improvement and ensure their services are competitively priced.
• Hardware Manufacturing: Hardware manufacturers employ fee benchmarking to compare the prices of their products with those of their competitors.Professional Services
Benefits of Fee Benchmarking
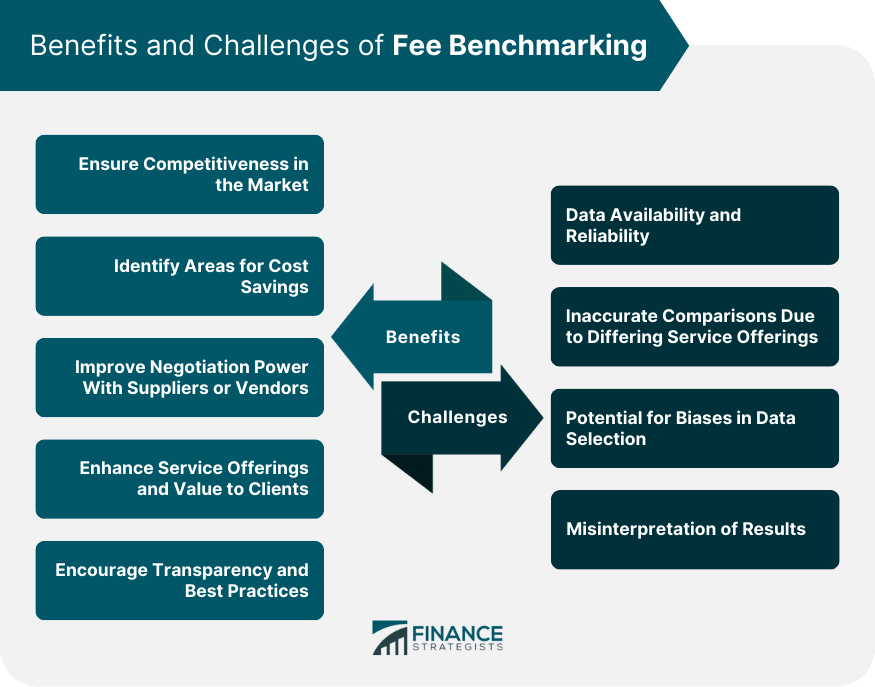
Ensuring Competitiveness in the Market
Identifying Areas for Cost Savings
Improving Negotiation Power with Suppliers or Vendors
Enhancing Service Offerings and Value to Clients
Encouraging Transparency and Best Practices
Challenges and Pitfalls of Fee Benchmarking
Data Availability and Reliability
Inaccurate Comparisons Due to Differing Service Offerings
Potential for Biases in Data Selection
Misinterpretation of Results
Best Practices for Effective Fee Benchmarking

Regularly Updating Benchmarks
Leveraging External Data Sources
Incorporating Qualitative Factors
Collaborating With Industry Peers for Shared Learning
Utilizing Fee Benchmarking Tools and Software
Final Thoughts
Fee Benchmarking FAQs
Fee benchmarking is a process of comparing fees and service offerings of companies within a specific industry or market to improve pricing and service strategies.
Fee benchmarking is widely used in financial services, healthcare, technology, and professional services to assess market competitiveness, identify cost-saving opportunities, and ensure transparency.
Fee benchmarking helps companies maintain competitiveness in the market, identify areas for cost savings, improve negotiation power, enhance service offerings, and encourage transparency and best practices.
The challenges of fee benchmarking include obtaining accurate and reliable data, accounting for differences in service offerings, avoiding biases in data selection, and avoiding misinterpretation of results.
The best practices for effective fee benchmarking include regularly updating benchmarks, leveraging external data sources, incorporating qualitative factors, collaborating with industry peers, and utilizing specialized tools and software.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











