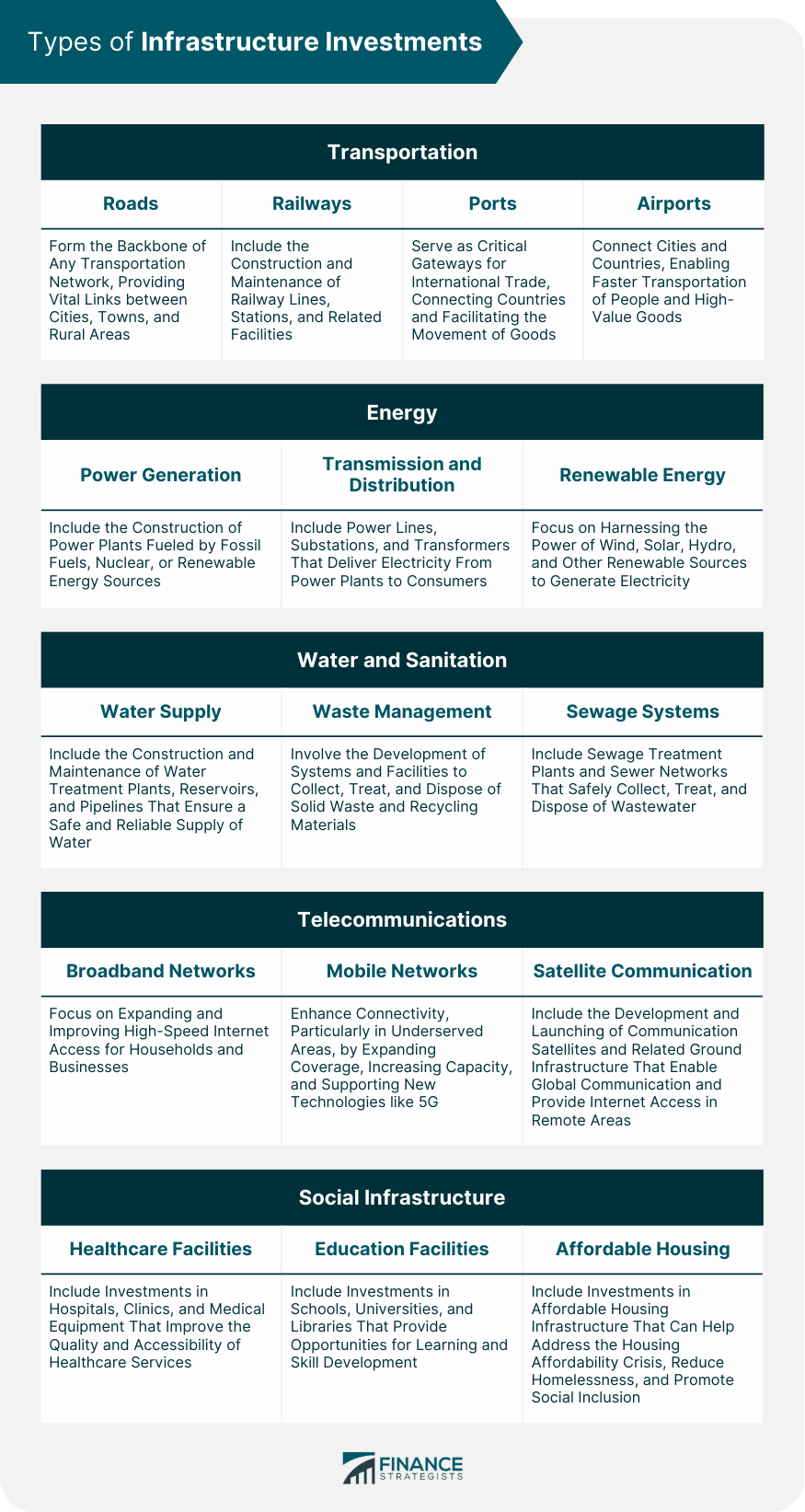
Infrastructure investment refers to the allocation of funds towards the development, improvement, and maintenance of essential physical structures and systems that support economic activities. These include transportation networks, energy facilities, water and sewage systems, communication networks, and public amenities like schools and hospitals. Infrastructure investments play a crucial role in driving economic development and growth by providing essential services that facilitate the movement of people, goods, and information. Governments, private companies, and institutional investors typically engage in infrastructure projects, either directly or through public-private partnerships. Such investments often require substantial capital and long-term commitments due to the large-scale nature of infrastructure projects. They are viewed as attractive assets offering stable cash flows and potential for steady returns over extended periods. Roads form the backbone of any transportation network, providing vital links between cities, towns, and rural areas. Investment in road infrastructure ensures efficient movement of people and goods, reduces travel time, and improves overall accessibility. Railway infrastructure investments include the construction and maintenance of railway lines, stations, and related facilities. Rail transport offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to road transport and can efficiently carry large volumes of cargo and passengers over long distances. Ports serve as critical gateways for international trade, connecting countries and facilitating the movement of goods. Investing in port infrastructure, such as container terminals, bulk cargo facilities, and modern equipment, can enhance a country's trade capacity and competitiveness. Airports connect cities and countries, enabling faster transportation of people and high-value goods. Investment in airport infrastructure ensures efficient operations, passenger safety, and the ability to accommodate growing air traffic demands. Power generation infrastructure investments include the construction of power plants, whether they are fueled by fossil fuels, nuclear, or renewable energy sources. These investments are crucial for meeting the growing energy needs of a country and ensuring a stable power supply. Transmission and distribution infrastructure includes power lines, substations, and transformers that deliver electricity from power plants to consumers. Investing in these facilities helps to ensure reliable and efficient power supply across the country. Renewable energy investments focus on harnessing the power of wind, solar, hydro, and other renewable sources to generate electricity. These investments are essential for promoting a sustainable energy mix and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Investments in water supply infrastructure include the construction and maintenance of water treatment plants, reservoirs, and pipelines that ensure a safe and reliable supply of water for households, businesses, and agriculture. Waste management infrastructure investments involve the development of systems and facilities to collect, treat, and dispose of solid waste and recycling materials. These investments help to reduce pollution and promote a cleaner environment. Investing in sewage infrastructure, such as sewage treatment plants and sewer networks, is essential for protecting public health and the environment by safely collecting, treating, and disposing of wastewater. Broadband infrastructure investments focus on expanding and improving high-speed internet access for households and businesses. This facilitates communication, access to information, and the growth of the digital economy. Investments in mobile network infrastructure help to enhance connectivity, particularly in underserved areas, by expanding coverage, increasing capacity, and supporting new technologies like 5G. Satellite communication infrastructure investments include the development and launching of communication satellites and related ground infrastructure. These investments enable global communication and provide internet access in remote areas. Investing in healthcare infrastructure, such as hospitals, clinics, and medical equipment, helps to improve the quality and accessibility of healthcare services, leading to better health outcomes and increased well-being for citizens. Investments in education infrastructure, such as schools, universities, and libraries, provide opportunities for learning and skill development, leading to a more educated and productive workforce and contributing to long-term economic growth. Investments in affordable housing infrastructure can help address the housing affordability crisis, reduce homelessness, and promote social inclusion. Infrastructure investments require significant financial resources, and financing can come from various sources. These include: Governments can fund infrastructure investments through budget allocations, which can come from various sources, such as taxes, fees, and royalties. Governments can also borrow money to finance infrastructure projects. Governments can issue bonds to raise funds for infrastructure investments. Bonds are debt securities that investors purchase, with the promise of repayment plus interest over a set period. Governments can also secure loans from financial institutions or multilateral development banks. PPPs involve a partnership between the public and private sectors to finance, build, and operate infrastructure projects. In a PPP, the private sector partner can provide financing, technical expertise, and management skills, while the government provides regulatory oversight and public interest protection. Equity investments involve the purchase of shares in infrastructure projects, providing investors with a stake in the project's ownership and potential profits. Debt financing involves providing loans to infrastructure projects, with the expectation of repayment with interest over a set period. MDBs are financial institutions that provide loans and grants to support infrastructure investments in developing countries. The World Bank and regional development banks, such as the Asian Development Bank and the African Development Bank, are examples of MDBs. Infrastructure financing faces various challenges, such as the high cost of capital, the complexity of project financing, and the difficulty of accurately assessing and managing risks. However, opportunities exist to increase investment in infrastructure by leveraging innovative financing mechanisms, such as green bonds and crowdfunding, and exploring new sources of funding, such as institutional investors and sovereign wealth funds. Infrastructure investments can have significant economic impacts, including: Infrastructure investments create jobs in construction, engineering, and other related fields. Moreover, infrastructure development can attract businesses and industries, leading to additional job creation. Infrastructure investments can increase productivity by reducing transportation and communication costs, improving supply chain efficiency, and providing better access to markets and resources. Investments in social infrastructure, such as healthcare and education facilities, can improve the quality of life of citizens by providing access to essential services and promoting well-being. Infrastructure investments can attract foreign direct investment by creating a favorable investment climate and supporting economic growth. Infrastructure investments can promote regional development and integration by improving connectivity between countries and facilitating cross-border trade and investment. Infrastructure investments can have significant environmental and social impacts, and these should be carefully considered and managed. Key considerations include: Infrastructure investments should be sustainable and resilient, taking into account the potential impacts of climate change and other environmental factors. Infrastructure investments can help mitigate climate change by promoting the use of renewable energy sources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Infrastructure projects should also consider the potential impacts of climate change and incorporate adaptation measures. Infrastructure investments should promote inclusive development, ensuring that all citizens have access to essential services and opportunities for economic and social advancement. Infrastructure investments should involve public engagement and transparency to ensure that projects are developed in consultation with affected communities and that the benefits and impacts of infrastructure investments are widely understood. Infrastructure investments are expected to evolve in response to changing economic, social, and environmental conditions. Key trends and innovations include: Smart infrastructure investments involve the integration of technology, such as sensors and data analytics, into infrastructure projects, enabling real-time monitoring and decision-making to optimize operations and enhance user experience. Green infrastructure investments focus on the development of environmentally sustainable infrastructure projects, such as renewable energy and green buildings, and the promotion of circular economy principles. The integration of technology in infrastructure projects is expected to continue to advance, with the use of artificial intelligence, automation, and robotics to enhance efficiency and productivity. Infrastructure investment in developing countries is expected to increase, with the focus on closing infrastructure gaps, promoting regional integration, and addressing environmental and social challenges. Infrastructure investments play a vital role in driving economic development and growth, improving the quality of life of citizens, and promoting sustainable and resilient societies. Financing infrastructure investments can be challenging, but opportunities exist to leverage innovative financing mechanisms and explore new sources of funding. The economic impacts of infrastructure investments can be significant, and careful consideration of environmental and social considerations is critical to ensure sustainable and inclusive development. The future of infrastructure investments is expected to evolve, with the integration of technology and the promotion of sustainable and resilient infrastructure. Increased investment in infrastructure, particularly in developing countries, is essential to promote economic growth and address environmental and social challenges. Wealth management can provide opportunities for investors to participate in infrastructure investments, creating potential benefits for both the investors and the communities in which the infrastructure is developed.What Are Infrastructure Investments?
Types of Infrastructure Investments
Transportation
Roads
Railways
Ports
Airports
Energy
Power Generation
Transmission and Distribution
Renewable Energy
Water and Sanitation
Water Supply
Waste Management
Sewage Systems
Telecommunications
Broadband Networks
Mobile Networks
Satellite Communication
Social Infrastructure
Healthcare Facilities
Education Facilities
Affordable Housing
Financing Infrastructure Investments
Public Funding
Government Budget Allocations
Bonds and Loans
Private Funding
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Equity Investments
Debt Financing
Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs)
Challenges and Opportunities in Infrastructure Financing
Economic Impacts of Infrastructure Investments
Job Creation
Increased Productivity
Improved Quality of Life
Attraction of Foreign Investment
Regional Development and Integration
Environmental and Social Considerations
Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Inclusive Development
Public Engagement and Transparency
Future Trends and Innovations
Smart Infrastructure
Green Infrastructure
Integration of Technology in Infrastructure Projects
Infrastructure Investment in Developing Countries
Conclusion
Infrastructure Investments FAQs
Infrastructure investments refer to investments made in the development and maintenance of essential systems, facilities, and structures that support economic and social activities. These include transportation, energy, water and sanitation, telecommunications, and social infrastructure.
Infrastructure investments are crucial for promoting economic development and growth, improving the quality of life of citizens, and addressing social and environmental challenges. They can create jobs, increase productivity, attract foreign investment, and promote regional integration.
Infrastructure investments can be financed through public funding, private funding, multilateral development banks, and innovative financing mechanisms. Public funding includes government budget allocations and bonds and loans, while private funding includes public-private partnerships, equity investments, and debt financing.
Infrastructure investments can have significant economic impacts, including job creation, increased productivity, improved quality of life, attraction of foreign investment, and regional development and integration.
Wealth management firms can support infrastructure investments by providing financing, expertise, and innovative solutions. They can also offer opportunities for investors to participate in infrastructure investments, providing potential benefits for both the investors and the communities in which the infrastructure is developed.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















