Social Security maximization refers to the process of strategically planning when and how to claim benefits to receive the highest possible payout over a person's lifetime. This includes considering factors such as retirement age, claiming strategies, and coordinating with other sources of retirement income. Maximizing Social Security benefits is essential for ensuring a comfortable and secure retirement. By optimizing the claiming strategies, retirees can significantly increase their retirement income, allowing them to maintain their desired lifestyle and meet financial obligations during retirement. Several factors can affect Social Security benefits, including the age at which benefits are claimed, lifetime earnings, marital status, and the availability of other retirement income sources. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about when and how to claim their benefits. Social Security was established in 1935 as part of the New Deal, a response to the Great Depression. The program was designed to provide financial support to retired workers, disabled individuals, and their families. Over the years, it has evolved to include additional benefits and has become a critical component of retirement planning for millions of Americans. The Primary Insurance Amount is the monthly benefit an individual is eligible to receive at their Full Retirement Age (FRA). The PIA is calculated based on the person's Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME) and a formula that takes into account the person's highest 35 years of earnings. The Average Indexed Monthly Earnings is calculated by taking an individual's highest 35 years of earnings, adjusting them for inflation, and dividing the total by the number of months in those 35 years. The AIME is a crucial factor in determining a person's PIA and, ultimately, their monthly Social Security benefit. The Full Retirement Age is the age at which an individual is eligible to receive their full Social Security benefits. The FRA varies depending on the birth year, ranging from 65 to 67 years. Individuals can also claim benefits as early as 62 or as late as 70, but doing so will impact the amount they receive. To be eligible for Social Security benefits, individuals must earn 40 credits through work. As of 2024, one credit is earned for every $1,730 in earnings, with a maximum of four credits per year. Typically, individuals need 40 credits (approximately 10 years of work) to be eligible for retirement benefits. Retirement benefits are the most common type of Social Security benefits. They are calculated based on an individual's PIA and the age at which they claim benefits. The monthly benefit can be higher or lower than the PIA, depending on whether the person claims before or after their FRA. Disability benefits are available to individuals who are unable to work due to a medical condition that is expected to last at least one year or result in death. These benefits are also based on the person's PIA and are subject to eligibility requirements, such as sufficient work credits and the severity of the disability. Survivor benefits provide financial support to the surviving spouse, dependent children, or other eligible family members of a deceased Social Security beneficiary. The amount of survivor benefits depends on the deceased worker's PIA and the age at which the survivor claims benefits. Spousal benefits are available to the spouse of a Social Security beneficiary, even if they have not earned enough credits themselves. These benefits are typically equal to 50% of the higher-earning spouse's PIA and can be claimed as early as 62, but will be reduced if claimed before the spouse's FRA. Waiting until Full Retirement Age to claim Social Security benefits ensures individuals receive their full PIA. Claiming benefits before FRA results in a permanent reduction in monthly benefits, while delaying benefits until after FRA can increase the monthly benefit amount. Delayed Retirement Credits are earned when individuals delay claiming their Social Security benefits past their FRA. For each year benefits are delayed up until age 70, the monthly benefit increases by approximately 8%. This can significantly boost retirement income for those who can afford to wait. The file and suspend strategy allowed individuals to file for Social Security benefits at FRA, then immediately suspend them to earn DRCs, while their spouse claimed spousal benefits. However, this strategy was eliminated by the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 and is no longer available for new filers. A restricted application allows individuals who have reached FRA to claim spousal benefits while allowing their own retirement benefits to continue growing with DRCs. This strategy is only available to those born before January 1, 1954, and can help maximize Social Security income for couples. Optimizing survivor and spousal benefits involve coordinating the timing of when each spouse claims their benefits. By staggering the claims and considering factors such as life expectancy, couples can maximize their combined Social Security income over their lifetimes. The Social Security earnings test applies to individuals who claim benefits before their FRA and continue to work. If they earn above a certain threshold, their benefits will be temporarily reduced. However, these reductions are not lost; they are added back to the person's benefit amount when they reach FRA. Working while receiving Social Security benefits can affect the benefit amount, particularly for those who claim benefits before their FRA. However, the additional income from work can help support a more comfortable retirement and may allow individuals to delay claiming benefits, which can result in a higher monthly benefit amount. Social Security benefits may be subject to federal income taxes, depending on the individual's total income. If the sum of the person's adjusted gross income, nontaxable interest, and half of their Social Security benefits exceeds certain thresholds, a portion of their benefits may be taxable. Income planning involves strategically managing various sources of retirement income to reduce taxable income and minimize taxes on Social Security benefits. By considering the timing and amount of income from different sources, individuals can help ensure their benefits are taxed as little as possible. Roth conversions involve transferring funds from a traditional IRA or 401(k) to a Roth IRA, which allows future withdrawals to be tax-free. By converting a portion of retirement savings to a Roth IRA, individuals can reduce their taxable income in retirement and potentially lower taxes on Social Security benefits. Tax-efficient withdrawal strategies involve strategically withdrawing funds from various retirement accounts to minimize the overall tax burden. By carefully considering which accounts to draw from and when, individuals can help reduce their taxable income and the taxes on their Social Security benefits. Evaluating retirement income needs involves estimating future expenses, considering factors such as inflation and healthcare costs. By understanding their income needs, individuals can better plan for when to claim Social Security benefits and coordinate them with other sources of retirement income. Pensions are employer-sponsored retirement plans that provide a fixed income in retirement. Coordinating pension benefits with Social Security can help individuals maximize their retirement income and ensure financial stability throughout their retirement years. Annuities are financial products that provide a guaranteed income stream in retirement. By incorporating annuities into their retirement income plan, individuals can create a more predictable income source to supplement Social Security benefits and help cover essential expenses. Personal savings and investments, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, play a crucial role in funding retirement. Coordinating withdrawals from these accounts with Social Security benefits can help individuals create a sustainable and tax-efficient retirement income plan. Medicare premiums can be influenced by an individual's income, including Social Security benefits. By understanding the impact of claiming Social Security on Medicare premiums, individuals can make informed decisions about when to claim benefits and manage their overall healthcare costs. Long-term care planning involves considering the potential need for long-term care services and evaluating ways to fund these expenses. Social Security benefits can play a role in funding long-term care, but additional sources of income or insurance may be necessary to cover the full cost. Social Security maximization involves understanding the system, strategically claiming benefits, coordinating with other sources of retirement income, and managing tax implications. Key strategies include delaying retirement, optimizing spousal and survivor benefits, and working with a financial advisor to create a personalized plan. Proactive planning is crucial for maximizing Social Security benefits and ensuring a secure retirement. By considering various factors and seeking professional guidance, individuals can make informed decisions that will have a significant impact on their financial well-being in retirement. Maximizing Social Security benefits can have a lasting effect on an individual's retirement security, providing a higher and more stable income throughout their retirement years. By implementing the strategies discussed, retirees can help ensure they have the financial resources necessary to maintain their desired lifestyle and meet their financial obligations. Financial advisors can provide valuable guidance, helping individuals develop a comprehensive retirement plan that optimizes their Social Security benefits and addresses their unique needs and circumstances.What Is Social Security Maximization?
Understanding the Social Security System
Brief History of Social Security
Calculating Social Security Benefits
Primary Insurance Amount (PIA)
Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME)
Eligibility for Social Security Benefits
Retirement Age
Credits Earned
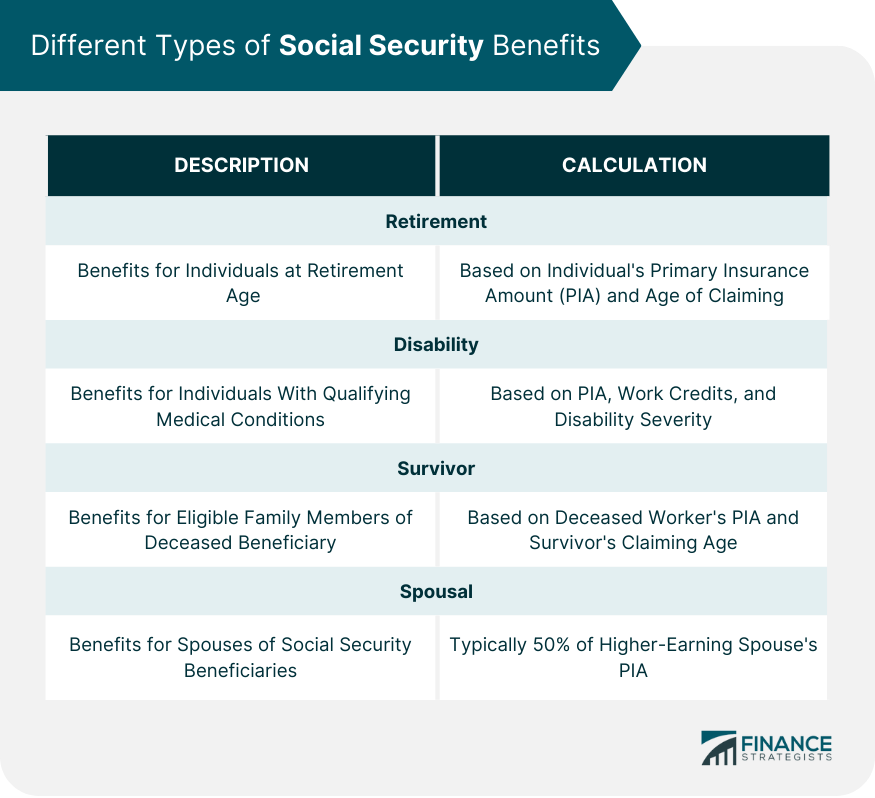
Different Types of Social Security Benefits
Retirement Benefits
Disability Benefits
Survivor Benefits
Spousal Benefits
Strategies for Social Security Benefit Maximization
Delaying Retirement for Social Security Maximization
Benefits of Waiting Until Full Retirement Age
Impact of Delayed Retirement Credits (DRCs)
Claiming Strategies for Social Security Maximization
File and Suspend
Restricted Application
Survivor and Spousal Benefits Optimization
Working While Receiving Social Security Benefits
Earnings Test
Impact on Benefits

Tax Implications and Social Security
Taxability of Social Security Benefits
Strategies to Minimize Taxes on Benefits
Income Planning
Roth Conversions
Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies
Integrating Social Security into Retirement Planning
Assessing Retirement Income Needs
Coordinating Social Security with Other Sources of Retirement Income
Pensions
Annuities
Personal Savings and Investments
Health Care Considerations and Social Security
Medicare Premiums
Long-Term Care Planning

Final Thoughts
Social Security Maximization FAQs
Social Security maximization refers to the strategic planning and decision-making process to maximize the lifetime benefits received from the Social Security program. It is crucial for retirees because it helps ensure a comfortable and financially secure retirement by optimizing the claiming strategies and coordinating benefits with other sources of retirement income.
Delaying retirement can significantly contribute to Social Security maximization, as waiting to claim benefits until Full Retirement Age (FRA) or beyond will result in higher monthly payments. Additionally, earning Delayed Retirement Credits (DRCs) can further increase benefits by approximately 8% per year until age 70, maximizing the potential retirement income.
Strategies for minimizing taxes on Social Security benefits include income planning, Roth conversions, and tax-efficient withdrawal strategies. These methods help manage taxable income, reduce taxes on benefits, and create a more tax-efficient retirement income plan, contributing to overall Social Security maximization.
Integrating other sources of retirement income, such as pensions, annuities, and personal savings, can help support Social Security maximization by creating a more diversified and stable retirement income plan. Coordinating withdrawals from these accounts with Social Security benefits can also minimize taxes and ensure financial security throughout retirement.
Seeking professional guidance is essential for Social Security maximization because each individual's situation is unique, and personalized advice can help navigate the complexities of the Social Security system. Financial advisors can provide tailored recommendations for claiming strategies, coordinate benefits with other sources of retirement income, and address specific needs and circumstances, ultimately maximizing the potential benefits.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.














