Social Security Benefits Optimization refers to the process of strategically planning and making decisions about when and how to claim Social Security benefits in order to maximize the overall lifetime value of those benefits. It involves considering various factors such as age, work history, marital status, life expectancy, and financial needs in order to make the most advantageous decisions about claiming benefits. To qualify for Social Security benefits, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements: Work Credits: Typically, a person needs 40 work credits to qualify for Social Security benefits. These credits are earned through work history and the payment of Social Security taxes. Age Requirements: The minimum age to start receiving benefits is 62, while the Full Retirement Age (FRA) varies depending on one's birth year. The Social Security benefit calculation involves three key components: 1. Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME): This figure represents an individual's highest 35 years of earnings, adjusted for inflation. 2. Primary Insurance Amount (PIA): The PIA is calculated using a three-part formula applied to the AIME. 3. Full Retirement Age (FRA): This age determines the point at which an individual can receive their full Social Security benefits, typically between 66 and 67 years old. Advantages: Access to funds earlier, helpful for those with shorter life expectancies. Disadvantages: Reduced monthly benefits, the potential for higher tax burden. Advantages: Full monthly benefits, no reduction due to early claiming. Disadvantages: Delayed access to funds, the potential for lost benefits if life expectancy is shorter. Advantages: Increased monthly benefits, potentially lower tax burden. Disadvantages: Delayed access to funds, the potential for lost benefits if life expectancy is shorter. This strategy involves filing for benefits at FRA and immediately suspending them, allowing the individual to accrue delayed retirement credits. This strategy applies to those born before January 2, 1954, allowing them to claim spousal benefits while allowing their own benefits to grow. Life expectancy Health Marital status Employment status Spouses can claim benefits based on their partner's work history, provided they are at least 62 years old and the partner has already claimed their own benefits. The maximum spousal benefit is 50% of the partner's PIA at FRA. Widows or widowers can claim survivor benefits, as long as they meet certain age and relationship requirements. Survivor benefits are calculated based on the deceased partner's PIA and the age at which the survivor claims the benefit. Social Security benefits may be subject to federal income tax, depending on one's overall income level. Timing of Withdrawals From Retirement Accounts: The timing of withdrawals from retirement accounts plays a crucial role in managing tax burdens and maximizing retirement income. Roth Conversions: Roth conversions involve transferring funds from tax-deferred accounts like traditional IRAs to Roth IRAs. While the conversion is a taxable event, future withdrawals from Roth IRAs are tax-free. Tax-Efficient Investments: Investing in tax-efficient assets can help reduce the tax burden on your investment gains, both during your working years and in retirement. Consider coordinating Social Security benefits with pension income to maximize overall retirement income. 401(k) Plans: Coordinate withdrawals from 401(k) plans with Social Security benefits to optimize tax efficiency and maintain a steady retirement income stream. Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): Strategize withdrawals from traditional and Roth IRAs to minimize taxes and ensure a stable retirement income. Annuities can provide a guaranteed income stream, and when combined with Social Security benefits, can help ensure financial stability in retirement. To optimize retirement income, prioritize tax-efficient withdrawals from various sources. This approach can help minimize the overall tax burden and make the most of your retirement savings. Balancing guaranteed and non-guaranteed income sources is crucial for maintaining financial stability throughout retirement. Guaranteed income sources, such as Social Security benefits, pensions, and annuities, provide a steady, predictable stream of income. Non-guaranteed income sources, like investments in stocks and bonds, can provide growth opportunities but come with higher risks. Adjusting withdrawal rates in response to market conditions and personal needs is key to preserving retirement savings and optimizing income throughout retirement. Social Security Benefits Optimization involves making strategic decisions about when and how to claim Social Security benefits to maximize lifetime value. Eligibility requirements for Social Security benefits include work credits and age, with the benefit calculation formula involving the AIME, PIA, and FRA. Claiming strategies include early, full retirement age, or delayed claiming, along with file and suspend and restricted application strategies. Personal factors such as life expectancy, health, marital status, and employment status should also be considered. Spousal and survivor benefits are available, and taxation of benefits can be minimized through strategies such as the timing of withdrawals, Roth conversions, and tax-efficient investments. Integrating retirement income sources such as pension plans, retirement savings accounts, and annuities can help balance guaranteed and non-guaranteed income sources and adjust withdrawal rates based on personal needs and market conditions. Finally, working with a qualified financial advisor can provide personalized guidance and expertise to navigate the complexities of Social Security benefits optimization.Definition of Social Security Benefits Optimization
Eligibility and Benefits Calculation of Social Security Benefits Optimization
Eligibility Requirements
Benefit Calculation Formula
Claiming Strategies for Social Security Benefits Optimization
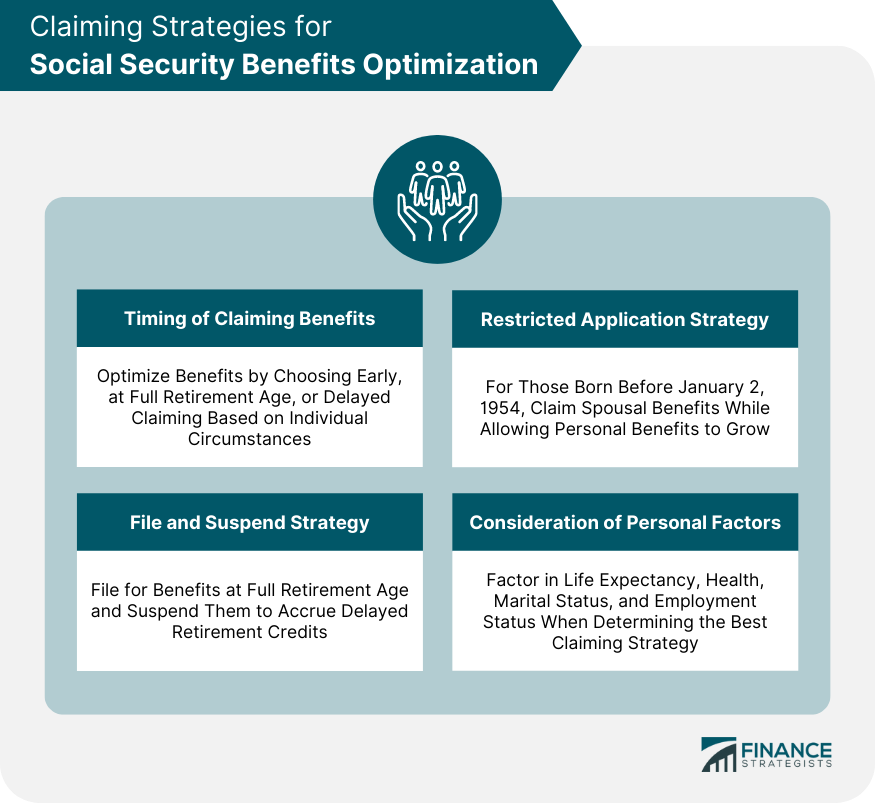
Timing of Claiming Benefits
Early claiming
Claiming at Full Retirement Age
Delayed claiming
File and Suspend Strategy
Restricted Application Strategy
Consideration of Personal Factors
Spousal and Survivor Benefits of Social Security Benefits Optimization
Spousal Benefits
Survivor Benefits
Tax Implications
Taxation of Social Security Benefits
Strategies to Minimize Tax Burden
Integrating Social Security Benefits With Other Sources of Retirement Income
Pension Plans
Retirement Savings Accounts
Annuities
Strategies for Coordinating Retirement Income Sources
Prioritize Tax-Efficient Withdrawals
Balance Guaranteed and Non-guaranteed Income Sources
Adjust Withdrawal Rates Based on Market Conditions and Personal Needs
Conclusion
Social Security Benefits Optimization FAQs
Social Security benefits optimization is the process of strategically planning when and how to claim Social Security benefits to maximize the lifetime income received. It is essential for retirees because it can significantly impact their financial security and overall quality of life during retirement years.
The timing of claiming benefits plays a critical role in Social Security benefits optimization. Early claiming (before Full Retirement Age) may result in reduced monthly benefits, while delayed claiming (after Full Retirement Age) can lead to increased monthly benefits. The optimal timing depends on personal factors such as life expectancy, health, marital status, and employment status.
Spousal and survivor benefits provide additional financial support to eligible spouses and surviving partners. Maximizing these benefits through strategic claiming can significantly enhance retirement income and contribute to overall Social Security benefits optimization.
Tax strategies that can help with Social Security benefits optimization include timing withdrawals from retirement accounts, performing Roth conversions, and investing in tax-efficient assets. These strategies can minimize the tax burden on Social Security benefits and other retirement income, allowing retirees to keep more of their hard-earned money.
A financial advisor can provide personalized guidance and expertise to navigate the complexities of Social Security benefits optimization. They can help individuals evaluate various claiming strategies, coordinate benefits with other retirement income sources, and develop a comprehensive retirement plan that considers each person's unique circumstances.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













