Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the process of systematically analyzing and forecasting an organization's current and future human resource needs, and developing strategies to meet those needs. This involves identifying the right number of employees with the appropriate skills, knowledge, and experience to effectively accomplish the organization's goals and objectives. HRP is a crucial component of business planning and finance, as it ensures that an organization's workforce is aligned with its strategic direction and can adapt to changes in the business environment. HRP directly impacts an organization's ability to achieve its goals and objectives by ensuring that the workforce is well-prepared, skilled, and motivated. HRP also contributes to the financial health of a company by optimizing workforce productivity, minimizing costs associated with hiring and training, and reducing employee turnover. Additionally, effective HRP enables businesses to respond more quickly and efficiently to changes in the external environment, such as technological advancements, economic fluctuations, and shifting market demands. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage and achieving long-term success. The HRP process begins with environmental scanning, which involves collecting and analyzing information about the internal and external factors that may impact an organization's workforce. This can include examining economic trends, technological advancements, demographic changes, industry competition, and government regulations, as well as assessing the company's internal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). By conducting a thorough environmental scan, organizations can gain valuable insights into the factors that may affect their workforce and identify potential opportunities and challenges that need to be addressed through HRP. Forecasting is a critical step in the HRP process, as it involves estimating the future demand for and supply of human resources within the organization. This includes predicting the number of employees needed, the types of skills and competencies required, and the availability of internal and external talent to meet these needs. Forecasting can be accomplished through various methods, such as trend analysis, regression analysis, or expert judgment. Accurate forecasting is essential for developing effective HRP strategies and ensuring that the organization has the right people in the right roles at the right time. Job analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and documenting information about the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of each job within an organization. This information is used to create detailed job descriptions and specifications, which are essential for HRP as they provide a clear understanding of the skills, knowledge, and abilities required for each role. A thorough job analysis helps organizations identify the competencies needed to perform each job effectively and serves as a foundation for workforce planning, recruitment, training, performance management, and career development initiatives. Supply analysis involves assessing the current workforce's skills, knowledge, and abilities to determine whether the organization has the necessary human resources to meet its strategic objectives. This includes evaluating the number of employees, their skills and competencies, and their potential for growth and development. By conducting a supply analysis, organizations can identify existing talent gaps and develop targeted strategies to address them, such as training and development programs, succession planning, or external recruitment. Demand analysis focuses on estimating the organization's future human resource requirements based on its strategic goals and objectives. This involves projecting the number of employees needed, the skills and competencies required, and the anticipated changes in workforce composition due to factors such as turnover, retirements, and promotions. A comprehensive demand analysis enables organizations to develop targeted HRP strategies that align their workforce with their strategic direction and ensure they have the right people in place to achieve their goals. Gap analysis is the process of comparing the organization's current human resource supply with its future demand to identify any discrepancies. This includes evaluating the differences in the number of employees, skills, and competencies required to meet the organization's strategic objectives. By conducting a gap analysis, organizations can determine whether they have a surplus or shortage of human resources and develop appropriate strategies to address these gaps. This can include recruitment and hiring initiatives, training and development programs, or workforce restructuring efforts. Action planning is the final step in the HRP process, which involves developing and implementing strategies to address the identified gaps between the current workforce supply and future demand. This can include initiatives such as recruiting new employees, providing training and development opportunities for existing staff, implementing succession planning, or adjusting organizational structures to better align with strategic objectives. Effective action planning requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation to ensure that the HRP strategies are achieving the desired results and that the organization remains well-prepared to respond to changes in its internal and external environment. By ensuring that the organization has the right number of employees with the appropriate skills and competencies, HRP helps to optimize the use of human resources and enables employees to work more efficiently and effectively. This increased productivity can lead to higher levels of employee engagement, job satisfaction, and overall organizational performance, ultimately contributing to the company's bottom line. HRP can result in significant cost savings for organizations by helping to minimize expenses associated with hiring, training, and retaining employees. Through effective workforce planning, companies can reduce the costs of recruiting and onboarding new staff, as well as the expenses associated with high employee turnover, such as lost productivity and the need for additional training. Additionally, HRP can help organizations identify opportunities for streamlining their workforce and eliminating redundancies, leading to further cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Effective HRP can contribute to reduced employee turnover by ensuring that the organization has the right people in the right roles and that employees are provided with the necessary support and development opportunities to succeed in their positions. By fostering a positive work environment and promoting employee engagement, HRP can help to improve job satisfaction and employee retention, ultimately reducing the costs associated with high turnover rates. HRP enables organizations to be more flexible and adaptable in the face of changing market conditions, technological advancements, and other external factors. Through effective workforce planning, companies can quickly adjust their human resource strategies to respond to emerging trends and capitalize on new opportunities. This increased agility is essential for maintaining a competitive advantage and ensuring long-term success in today's rapidly evolving business environment. HRP plays a crucial role in risk management by helping organizations identify and address potential workforce-related risks, such as skill gaps, labor shortages, or an aging workforce. By proactively addressing these risks through targeted HRP strategies, companies can mitigate potential negative impacts and ensure the continued success of their operations. Uncertainty is a significant challenge in HRP, as organizations must make predictions about future workforce needs based on a variety of factors, such as economic trends, technological advancements, and competitive pressures. These factors are often unpredictable and subject to change, making it difficult for companies to accurately forecast their human resource requirements. To address this challenge, organizations can leverage scenario planning techniques and continually update their HRP strategies as new information becomes available. Employees may be reluctant to embrace new organizational structures, job roles, or training programs, which can impede the organization's ability to achieve its workforce planning goals. To overcome this challenge, organizations should involve employees in the HRP process, clearly communicate the reasons for change, and provide adequate support and resources to help staff adapt to new roles and responsibilities. The lack of resources, including time, funding, and personnel, can pose a significant challenge to implementing effective HRP strategies. Organizations may struggle to allocate the necessary resources for workforce planning initiatives, particularly in times of financial constraints or competing priorities. To address this challenge, organizations should prioritize HRP as a critical component of their overall business strategy and invest in the necessary resources to ensure its successful execution. Inaccurate forecasting can undermine the effectiveness of HRP efforts by leading to imprecise estimates of future workforce needs. This can result in talent shortages or surpluses, which can negatively impact organizational performance and employee satisfaction. To improve the accuracy of their forecasting efforts, organizations can leverage a variety of forecasting techniques, such as trend analysis, regression analysis, or expert judgment, and continually update their projections based on the latest available data. Inadequate data analysis can hinder the effectiveness of HRP efforts by preventing organizations from identifying and addressing critical workforce gaps and opportunities. This can result in suboptimal HRP strategies that fail to align the workforce with the organization's strategic objectives. To overcome this challenge, organizations should invest in robust data collection and analysis tools, as well as develop the necessary skills and expertise within their HR teams to effectively analyze and interpret workforce data. Gaining the commitment and support of senior leaders is essential for the successful implementation of HRP initiatives, as it helps to ensure that workforce planning is prioritized and integrated into the organization's overall business strategy. By working together, HR professionals and departmental leaders can share insights, resources, and expertise to develop and implement targeted HRP strategies that align the workforce with the organization's strategic objectives. Leveraging technology is a best practice in HRP, as it enables organizations to streamline and automate various aspects of the workforce planning process, such as data collection, analysis, and reporting. By utilizing advanced HR software and analytics tools, companies can gain valuable insights into their workforce and make more informed decisions regarding their HRP strategies. Regular review and update of HRP strategies are essential for ensuring their ongoing effectiveness in the face of changing business conditions and workforce dynamics. Organizations should continually monitor and evaluate their HRP efforts, making adjustments as needed based on new information, emerging trends, and shifting priorities. Finally, HRP should be fully integrated with the organization's overall business strategy. This helps to ensure that workforce planning initiatives are aligned with the company's strategic objectives and that the organization has the necessary human resources to achieve its goals. Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the systematic process of analyzing and forecasting an organization's current and future human resource needs and developing strategies to meet those needs. It plays a critical role in aligning the workforce with the organization's strategic objectives and ensuring its long-term success. The HRP process involves several key steps, including environmental scanning, forecasting, job analysis, supply analysis, demand analysis, gap analysis, and action planning. Each of these steps plays a crucial role in identifying the organization's workforce needs and developing targeted strategies to address them. To ensure the success of HRP initiatives, organizations should adhere to best practices, such as involving top management, fostering collaboration between HR and other departments, leveraging technology, regularly reviewing and updating HRP strategies, and integrating HRP with the overall business strategy. By understanding and effectively implementing the HRP process, organizations can optimize their workforce, manage risks, and ensure their long-term success in today's competitive business environment.What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
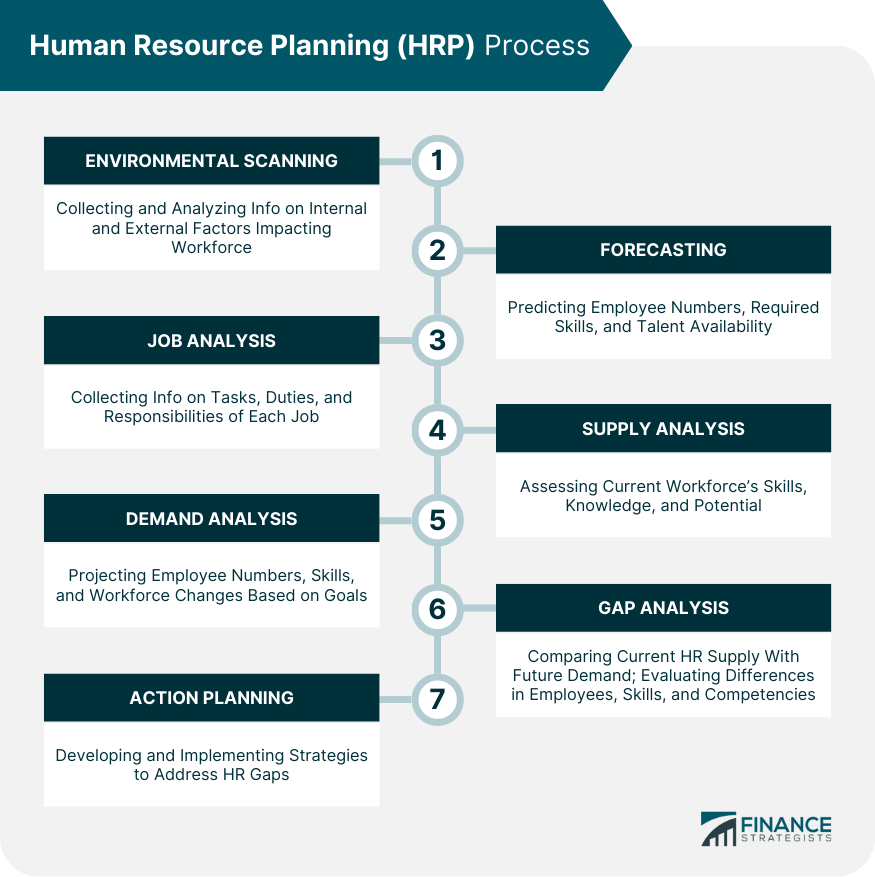
The HRP Process
Environmental Scanning
Forecasting
Job Analysis
Supply Analysis
Demand Analysis
Gap Analysis
Action Planning
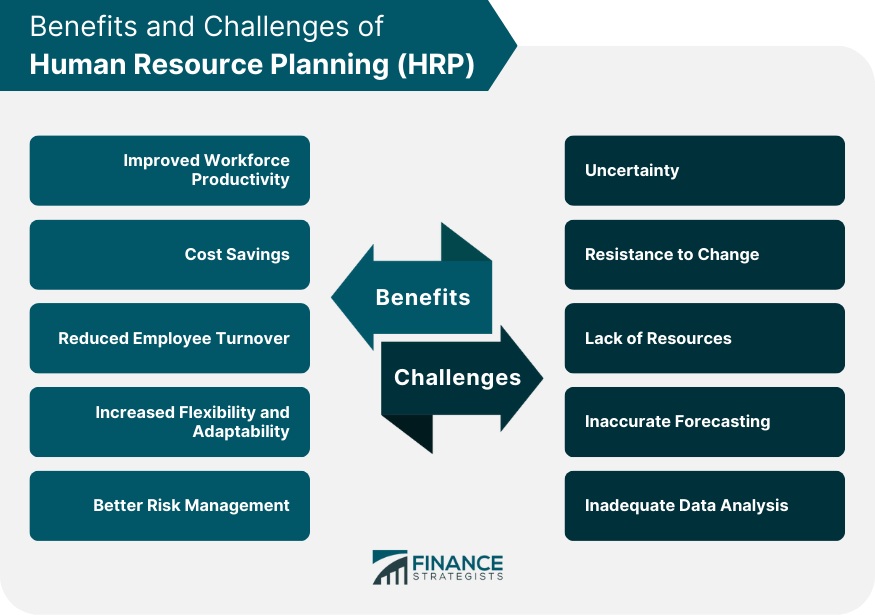
Benefits of HRP
Improved Workforce Productivity
Cost Savings
Reduced Employee Turnover
Increased Flexibility and Adaptability
Better Risk Management
Challenges of HRP
Uncertainty
Resistance to Change
Lack of Resources
Inaccurate Forecasting
Inadequate Data Analysis
Best Practices in HRP
Involvement of Top Management
Collaboration Between HR and Other Departments
Use of Technology
Regular Review and Update of HRP
Integration With Overall Business Strategy
The Bottom Line
Human Resource Planning (HRP) FAQs
Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the process of forecasting future human resource needs and developing strategies to meet them.
HRP helps businesses ensure that they have the right people with the right skills in the right positions at the right time to achieve their strategic objectives.
The HRP process typically involves environmental scanning, forecasting, job analysis, supply and demand analysis, gap analysis, and action planning.
The benefits of HRP include improved productivity, cost savings, reduced employee turnover, increased flexibility, and better risk management.
Some challenges associated with HRP include uncertainty, resistance to change, lack of resources, inaccurate forecasting, and inadequate data analysis.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











