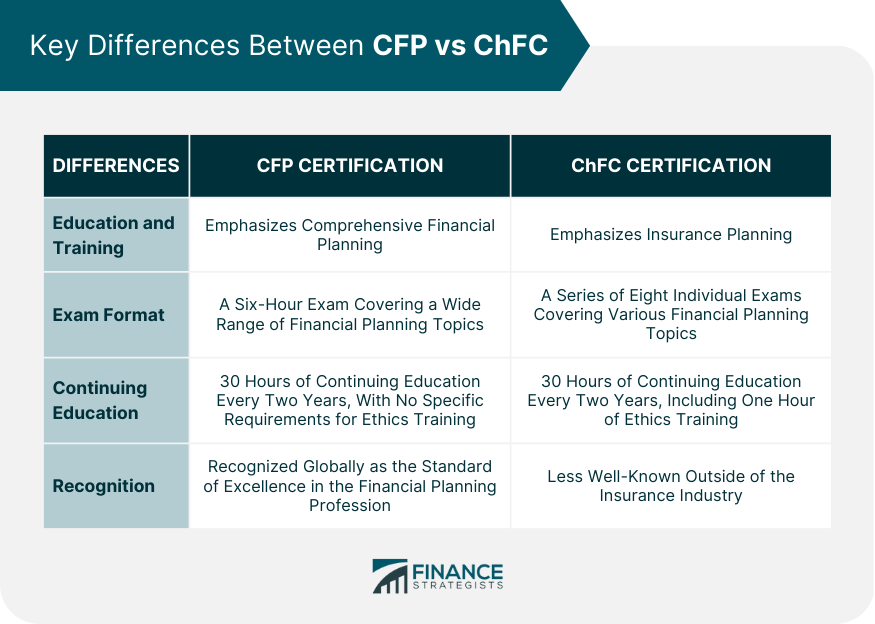
Financial planning is an important part of one's personal or professional life. It involves identifying financial goals, creating a plan to achieve them, and regularly monitoring and adjusting the plan to ensure that it remains on track. To become a qualified financial planner, one can pursue certifications such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP) and Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC). The CFP designation is recognized globally as the standard of excellence in the financial planning industry. It is issued by the Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards (CFP Board) to individuals who have demonstrated competence in financial planning through education, experience, and examination. The ChFC designation, on the other hand, is given by the American College of Financial Services to individuals who have completed a rigorous course of study in financial planning and have demonstrated their knowledge and expertise in the field. CFP professionals are qualified to provide comprehensive financial planning services to individuals and families, including retirement planning, estate planning, tax planning, investment planning, and risk management. They can also advise on employee benefits and insurance products. CFP professionals are trained to help clients set realistic financial goals, develop a plan to achieve them, and monitor progress toward those goals. CFP professionals can work in a variety of roles, including financial planners, investment advisors, and wealth managers. They can work for financial planning firms, insurance companies, banks, or be self-employed. Their primary responsibility is to provide comprehensive financial planning services to their clients. This includes analyzing their clients' financial situation, creating a customized financial plan, and regularly monitoring and adjusting the plan to ensure that it remains on track. To become a CFP professional, one must have a bachelor's degree from an approved institution and complete a CFP Board-registered program of study in financial planning. This program should cover topics such as financial planning, estate planning, tax planning, retirement planning, investment planning, and risk management. After completing the program, one must pass a comprehensive CFP exam that tests their knowledge and expertise in financial planning. In addition, CFP professionals must complete 30 hours of continuing education every two years to maintain their certification. ChFC professionals are qualified to provide comprehensive financial planning services, including retirement planning, estate planning, tax planning, investment planning, and risk management. They can also advise on employee benefits and insurance products. They are trained to help clients set realistic financial goals, develop a plan to achieve them, and monitor progress toward those goals. ChFC professionals can work in a variety of roles, including financial planners, investment advisors, and wealth managers. They can work for financial planning firms, insurance companies, banks, or be self-employed. The primary responsibility of a ChFC professional is to provide comprehensive financial planning services to their clients. This includes analyzing their clients' financial situation, creating a customized financial plan, and regularly monitoring and adjusting the plan to ensure that it remains on track. To become a ChFC professional, one must have a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution. They must complete a course of study in financial planning. This course should cover topics such as financial planning, retirement planning, estate planning, tax planning, investment planning, and risk management. After completing the course, one must pass a comprehensive ChFC exam that tests their knowledge and expertise in financial planning. In addition, ChFC professionals must complete 30 hours of continuing education every two years to maintain their certification. Despite the similarities, there are some differences: One of the key differences is the focus of their education and training. While both certifications cover a wide range of financial planning topics, the CFP certification places more emphasis on comprehensive financial planning. Whereas the ChFC certification places more emphasis on insurance planning. CFP professionals are trained to provide holistic financial planning services to their clients, including retirement planning, estate planning, investment planning, and risk management. On the other hand, ChFC professionals are trained to provide expertise in the areas of insurance planning, including life, disability, and long-term care insurance. Another difference between CFP and ChFC is the level of examination and education required. The CFP exam is widely recognized as one of the most rigorous and challenging exams in the financial industry. It consists of a six-hour exam covering a wide range of financial planning topics, including financial planning principles, tax planning, investment planning, retirement planning, and estate planning. In contrast, the ChFC exams cover various financial planning topics, including financial planning fundamentals, insurance planning, and retirement planning. The organizations that award these certifications have different requirements for continuing education. The American College of Financial Services requires 30 hours of continuing education every two years, including one hour of ethics training for ChFC holders. The CFP Board requires CFP professionals to complete 30 hours of continuing education every two years, with no specific requirements for ethics training. The CFP certification is recognized globally as the standard of excellence in the financial planning profession, while the ChFC certification is less well-known outside of the insurance industry. This difference in recognition may impact the perceived value of the certifications among clients, as those seeking financial planning services may be more likely to seek out a CFP professional due to the higher level of recognition and perceived expertise in the field. Deciding which certification is right for you depends on your career goals and aspirations. If you aspire to become a comprehensive financial planner, then the CFP certification may be the best fit for you. CFP professionals have a broad range of expertise in financial planning, making them ideal for individuals or families seeking comprehensive financial planning services. On the other hand, if you want to specialize in insurance planning, the ChFC certification may be a better fit for you. ChFC professionals are trained to provide expertise in insurance planning, making them ideal for clients who require specialized advice on life, disability, and long-term care insurance. Both the CFP and ChFC certifications are highly respected in the financial industry and are designed to provide a financial advisor with the education and training necessary to become a competent financial planner. While both certifications cover similar topics, they have different focuses and requirements. Choosing between the two certifications depends on your career goals and aspirations. If you aspire to become a comprehensive financial planner, then the CFP certification may be the best fit for you. If you want to specialize in insurance planning, then the ChFC certification may be a better fit for you. Ultimately, choosing the right certification requires careful consideration of your career goals and aspirations, as well as the education and training requirements of each certification.Overview of CFP and ChFC Designations
CFP Designation
ChFC Designation
Key Differences Between CFP and ChFC
Education and Training
Examination
Continuing Education
Recognition
Which Certification Is Right for You?
Bottom Line
CFP vs ChFC FAQs
CFP emphasizes comprehensive financial planning while ChFC emphasizes insurance planning. They have different exam formats, education and training requirements, and perceived values.
Both are qualified to provide comprehensive financial planning services, including retirement planning, estate planning, tax planning, investment planning, and risk management. ChFC professionals are specialized in insurance planning.
To become a CFP or ChFC professional, you need to have a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution, complete a program/course of study in financial planning, and pass a comprehensive exam. Both require 30 hours of continuing education every two years.
It depends on your career goals and aspirations. If you aspire to become a comprehensive financial planner, then the CFP certification may be the best fit for you. If you want to specialize in insurance planning, then the ChFC certification may be a better fit for you.
CFP is recognized globally as the standard of excellence in the financial planning profession, while ChFC is less well-known outside of the insurance industry. This may impact the perceived value of the certifications among clients seeking financial planning services.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















