A Locked-In Retirement Account (LIRA) is a tax-deferred retirement savings plan designed to hold pension funds for individuals who leave their jobs or change pension plans before they reach retirement age. LIRA is specifically designed to hold locked-in pension funds, meaning the funds cannot be accessed until the account holder reaches a certain age, usually the age of retirement. The primary purpose of a LIRA is to provide a secure and tax-efficient vehicle for preserving and growing pension assets when an individual leaves their job or changes pension plans. This ensures that the funds will be available for retirement purposes, protecting the account holder's long-term financial security. LIRA also serves as a valuable tool for retirement planning, as it allows individuals to maintain control over their pension assets and invest them according to their risk tolerance and investment objectives. To be eligible to open a LIRA, an individual must meet certain criteria. Firstly, they must have accumulated locked-in pension funds, which typically occurs when they leave a job with a pension plan or change pension plans. The pension funds must be subject to provincial or federal pension legislation, which governs the rules and restrictions associated with locked-in accounts. Additionally, the individual must be a resident of Canada, and the pension plan from which the funds are transferred must allow for the transfer of locked-in funds to a LIRA. The contribution limits for a LIRA are determined by the pension legislation governing the locked-in funds. In general, LIRA contributions are limited to the total amount of locked-in pension funds that an individual has accumulated. This means that individuals cannot make additional contributions to their LIRA, as they would with a Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP). However, it is possible to transfer locked-in pension funds from multiple sources to a LIRA, subject to the rules and restrictions of the originating pension plans. A LIRA offers a range of investment options, similar to those available in an RRSP. Account holders can invest their LIRA assets in various financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). However, LIRA investments are subject to certain restrictions, as outlined by the pension legislation governing the locked-in funds. These restrictions may include limits on specific types of investments or requirements to maintain a certain level of liquidity within the account. LIRA funds are subject to strict withdrawal rules and limitations, which are designed to ensure that the funds remain available for retirement purposes. In general, LIRA assets cannot be withdrawn until the account holder reaches a specified age, usually the age of retirement. At this point, the LIRA must be converted to a Life Income Fund (LIF) or a Locked-In Retirement Income Fund (LRIF), which will provide the account holder with a regular income stream. Early withdrawals from a LIRA may be permitted under specific circumstances, such as financial hardship or shortened life expectancy, but are generally subject to strict rules and penalties. LIRA assets grow on a tax-deferred basis, meaning that investment gains are not subject to taxation until they are withdrawn from the account. When LIRA funds are eventually withdrawn, they are treated as taxable income and subject to the account holder's marginal tax rate. Additionally, LIRA accounts may be subject to various fees, such as annual administration fees or investment management fees. These fees can vary depending on the financial institution that holds the LIRA and the specific investments chosen by the account holder. A Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) is a tax-deferred retirement savings account available to Canadian residents. RRSPs allow individuals to contribute a portion of their income each year, up to a specified limit, and deduct these contributions from their taxable income. RRSP assets grow on a tax-deferred basis, and withdrawals are treated as taxable income. While LIRA and RRSP share some similarities, such as tax-deferred growth of assets, there are several key differences between these two types of accounts. The most significant difference is the locked-in nature of LIRA funds. Unlike RRSPs, which allow for withdrawals at any time (subject to taxation), LIRAs impose strict withdrawal restrictions to ensure that the funds are used for retirement purposes. Another important difference is the contribution rules. RRSPs allow for regular contributions up to an annual limit, while LIRAs do not permit additional contributions beyond the initial transfer of locked-in pension funds. The source of contributions also differs: RRSP contributions come from personal income, while LIRA contributions originate from pension plans. The locked-in nature of LIRA provides a certain advantage in terms of ensuring long-term savings for retirement. The imposed withdrawal restrictions can help individuals avoid the temptation of dipping into their retirement savings prematurely. On the other hand, the inability to make withdrawals can also be a disadvantage in case of financial hardship, as accessing LIRA funds is generally more difficult compared to RRSPs. Another advantage of LIRA is the potential for larger contribution amounts, as the transferred pension funds may exceed typical RRSP contribution limits. However, the inability to make additional contributions to a LIRA can be a drawback for those wishing to save more for retirement beyond their pension assets. LIRA serves as an essential tool in retirement planning. It allows individuals to preserve their pension assets in a tax-efficient manner, potentially grow them through investment, and ultimately convert them into a steady income stream in retirement. The fact that LIRA funds are locked-in ensures they will be used for their intended purpose, providing a level of financial security in retirement. LIRA is primarily used to hold pension assets when an individual changes jobs or leaves a pension plan. This provides continuity in retirement savings and offers the opportunity to manage pension assets more actively. Transferring pension assets to a LIRA can be a strategic move, particularly if the originating pension plan has limited investment options or if the individual wants to consolidate multiple pension assets in one place. In addition to retirement planning and pension plan transfers, LIRA can also be used for estate planning purposes. Upon the death of the account holder, LIRA assets can be transferred to a surviving spouse or common-law partner on a tax-deferred basis, or to other beneficiaries as a taxable distribution. A Locked-In Retirement Account (LIRA) is a type of retirement account designed to hold locked-in pension funds. It provides a tax-efficient vehicle for preserving and growing pension assets, ensuring they will be available for retirement purposes. LIRA is an important tool in retirement planning, particularly for those with pension assets from previous employment. LIRA offers a range of investment options, similar to an RRSP, but with certain restrictions as outlined by the governing pension legislation. It has strict withdrawal rules to ensure that the funds remain available for retirement, with taxes and potential penalties applying to early withdrawals. The importance of LIRA lies in its ability to protect and grow pension assets for individuals who have changed jobs or left a pension plan. By providing a secure and tax-efficient vehicle for managing these assets, LIRA helps ensure a more stable financial future in retirement. Additionally, LIRA's locked-in nature can serve as a safeguard against premature withdrawals, further contributing to the account holder's long-term financial security. By understanding the features and uses of LIRA, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement planning and secure their financial future.What Is a Locked-in Retirement Account (LIRA)?
Eligibility Criteria for Opening a LIRA
Contribution Limits and Rules for LIRA
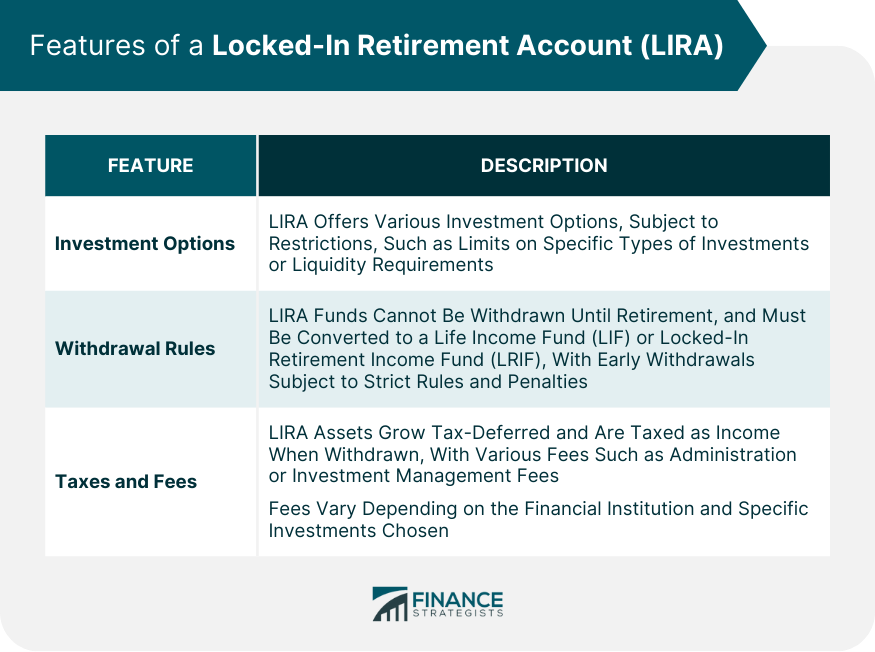
Features of a Locked-In Retirement Account (LIRA)
Investment Options and Restrictions
Withdrawal Rules and Limitations
Taxes and Fees Associated With LIRA
Differences Between LIRA and RRSP
Definition of RRSP
Key Differences Between LIRA and RRSP
Advantages and Disadvantages of LIRA Compared to RRSP
Uses of Locked-in Retirement Accounts (LIRA)
Retirement Planning
Pension Plan Transfers
Other Uses of LIRA
Final Thoughts
Locked-in Retirement Account (LIRA) FAQs
A Locked-In Retirement Account (LIRA) is a type of retirement account that holds funds that are locked-in and cannot be withdrawn until retirement.
Eligibility requirements for opening a LIRA may vary by province, but generally, it is available to individuals who have left an employer-sponsored pension plan.
The contribution limits for a LIRA are set by the government and may vary by province. Generally, they are lower than contribution limits for other types of retirement accounts.
Investment options for LIRA funds may vary by financial institution, but they generally include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other investment vehicles.
Withdrawals from a LIRA are generally not allowed before retirement. In some cases, there may be exceptions, such as financial hardship or disability, but they are limited and subject to government regulations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











