Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a significant aspect of modern business practices, encompassing a wide range of activities focused on creating positive social and environmental impacts. This article will explore the history, theoretical frameworks, benefits, components, and future directions of CSR, as well as the challenges and criticisms it faces. CSR refers to the voluntary efforts of businesses to contribute to sustainable development by addressing social, environmental, and economic issues. Early forms of CSR emerged in the 19th century, with philanthropic efforts by business owners to improve the lives of their employees and communities. The concept of CSR has since evolved to include a broader range of ethical, environmental, and social considerations. CSR has transformed significantly over the years, with a growing emphasis on sustainability and stakeholder engagement. In the 20th century, CSR began to focus on issues such as employee welfare, consumer rights, and environmental protection. Today, CSR encompasses a wide range of sustainable business practices, including ethical sourcing, emissions reductions, and community engagement. Several factors have contributed to the rise of CSR, including increasing public awareness of social and environmental issues, demand from consumers and investors for responsible business practices, and recognition of the potential benefits of CSR for businesses. These drivers have encouraged companies to integrate CSR into their core strategies and operations, fostering a culture of responsibility and accountability. Several theoretical frameworks have emerged to guide and explain CSR practices. These frameworks provide a foundation for understanding the motivations, goals, and potential impacts of CSR initiatives. Stakeholder theory posits that businesses have a responsibility to consider the interests of all stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, and the communities in which they operate. By addressing the needs and concerns of these diverse groups, companies can create long-term value and foster sustainable growth. The Triple Bottom Line framework emphasizes the importance of balancing economic, social, and environmental performance in business decision-making. This approach seeks to integrate financial success with social and environmental responsibility, recognizing that sustainable business practices can lead to long-term profitability and resilience. The Shared Value Concept proposes that companies can generate both economic and social value by identifying and addressing social issues that intersect with their core business strategies. This approach aims to create a positive impact on society while simultaneously driving business growth and competitive advantage. CSR offers a variety of benefits for businesses, ranging from improved reputation and financial performance to increased employee satisfaction and positive social and environmental impacts. Implementing CSR initiatives can help companies build a positive reputation and strengthen their brand image. By demonstrating a commitment to ethical, social, and environmental values, businesses can differentiate themselves in the marketplace and attract conscious consumers, investors, and employees. CSR can contribute to a company's financial success by reducing operational costs, attracting investment, and driving customer loyalty. Research has shown a positive correlation between CSR performance and financial performance, suggesting that responsible business practices can lead to long-term profitability and growth. CSR can play a significant role in attracting and retaining top talent. Companies with strong CSR programs tend to have higher levels of employee satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty, as workers feel a sense of pride and purpose in their organization's positive impact on society and the environment. Despite the growing importance of CSR, it faces several challenges and criticisms, including concerns about greenwashing, conflicts of interest, and implementation difficulties. Greenwashing refers to the practice of promoting environmentally friendly initiatives while engaging in unsustainable business practices. Critics argue that some companies use CSR as a marketing tool to improve their image without making meaningful changes to their operations. This can undermine the credibility of CSR and diminish its potential benefits. Some critics argue that the primary responsibility of businesses is to maximize shareholder value, which may conflict with broader stakeholder interests. They contend that CSR initiatives can divert resources from core business activities, potentially harming financial performance. However, proponents of CSR argue that addressing stakeholder concerns can create long-term value and enhance competitiveness. Implementing and measuring CSR can be challenging, as it often requires businesses to navigate complex ethical, environmental, and social issues. Additionally, companies may struggle to quantify the impact of their CSR initiatives, making it difficult to assess their effectiveness and compare results across organizations. CSR encompasses a wide range of ethical, environmental, and social practices aimed at promoting sustainable development and creating positive impacts on stakeholders. Ethical business practices are fundamental to CSR and include adhering to labor standards, respecting human rights, and combating corruption. By upholding these standards, businesses can foster a culture of integrity, fairness, and accountability, which ultimately contributes to their long-term success. Environmental sustainability is a critical aspect of CSR, focusing on minimizing the negative impacts of business operations on the environment. Key areas of concern include climate change mitigation, resource conservation, and waste management. By adopting sustainable practices, companies can reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to the global effort to protect our planet. Promoting social well-being is another core component of CSR, encompassing community engagement, diversity and inclusion, and philanthropy and volunteerism. By supporting social initiatives and fostering an inclusive and diverse workforce, businesses can help create a more equitable and just society, while also benefiting from the diverse perspectives and talents of their employees. As CSR has gained prominence, several reporting frameworks and standards have emerged to guide and measure corporate social responsibility efforts. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is a widely used CSR reporting framework that provides guidelines for businesses to disclose their economic, environmental, and social impacts. By adhering to GRI standards, companies can enhance the transparency and comparability of their CSR efforts, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions about their investments and purchases. The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) develops industry-specific standards for reporting material sustainability issues that affect financial performance. SASB standards help businesses identify and communicate the most relevant sustainability metrics for their industry, enabling investors to assess and compare the sustainability performance of different companies. ISO 26000 is an international standard that offers guidance on integrating social responsibility into an organization's strategy and operations. The standard covers a wide range of topics, including organizational governance, human rights, labor practices, and environmental responsibility. By following ISO 26000, companies can demonstrate their commitment to CSR and gain credibility with stakeholders. The United Nations Global Compact is a voluntary initiative that encourages businesses to adopt sustainable and socially responsible policies. Participants commit to implementing ten principles related to human rights, labor standards, environmental protection, and anti-corruption. By joining the Global Compact, companies signal their commitment to CSR and gain access to resources and networks to support their sustainability efforts. As CSR continues to evolve, new trends and opportunities are emerging for businesses to create positive change. The future of CSR lies in its integration into core business strategies and operations, rather than being treated as a separate function. This approach can help companies create synergies between their financial goals and social and environmental objectives, fostering long-term success and sustainability. Collaboration between businesses, stakeholders, and communities is essential for addressing complex social and environmental challenges. By working together, companies can pool resources, share knowledge, and drive innovation, leading to more effective and scalable CSR solutions. Advancements in technology and digital transformation have the potential to revolutionize CSR practices, making them more efficient, data-driven, and impactful. Companies can leverage technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things to monitor and manage their social and environmental performance, as well as engage with stakeholders and drive positive change. Corporate Social Responsibility is a crucial aspect of modern business that seeks to create positive social and environmental impacts while driving long-term growth and profitability. By understanding the history, theoretical frameworks, benefits, and challenges of CSR, companies can develop more effective strategies and practices that benefit both their stakeholders and the planet. As CSR continues to evolve, businesses have the opportunity to leverage collaboration, digital transformation, and innovation to make a lasting and meaningful difference in the world.What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
Theoretical Frameworks of CSR
Stakeholder Theory
Triple Bottom Line
Shared Value Concept
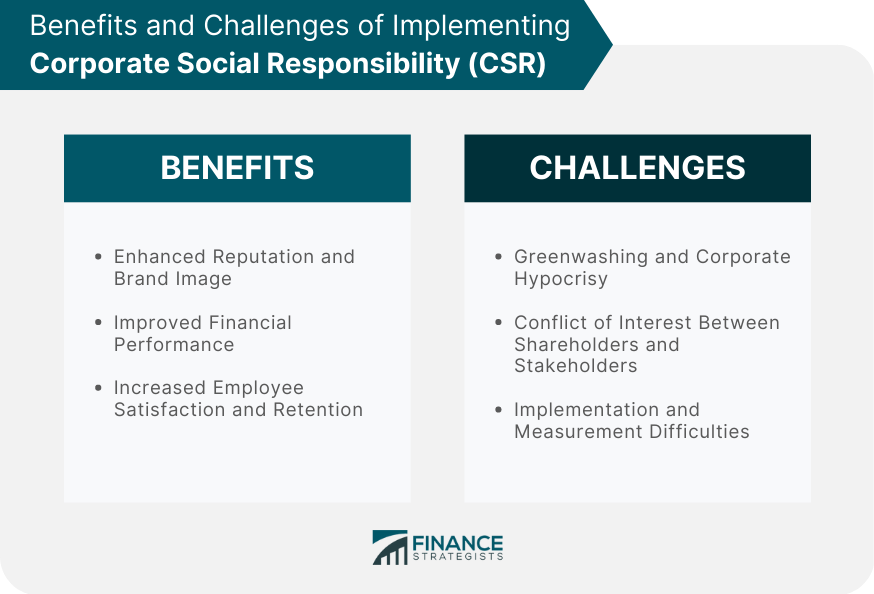
Benefits of Implementing CSR
Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image
Improved Financial Performance
Increased Employee Satisfaction and Retention
Challenges and Criticisms of CSR
Greenwashing and Corporate Hypocrisy
Conflict of Interest Between Shareholders and Stakeholders
Implementation and Measurement Difficulties
Key Components of CSR
Ethical Business Practices
Environmental Sustainability
Social Well-being
CSR Reporting and Standards
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
ISO 26000: Guidance on Social Responsibility
United Nations Global Compact
Future Directions for CSR
Integration of CSR Into Business Strategy
Greater Collaboration Among Businesses and Stakeholders
Digital Transformation and Technological Innovation in CSR
Conclusion
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) FAQs
CSR refers to a company's voluntary actions to improve society and the environment beyond legal requirements, including ethical and philanthropic initiatives.
CSR is important for businesses because it helps to build a positive reputation, attract and retain employees and customers, and improve financial performance by reducing risk and enhancing stakeholder trust.
Examples of CSR initiatives include environmental sustainability, ethical labor practices, community engagement, charitable donations, and social activism.
Companies can measure the impact of their CSR initiatives through social and environmental audits, stakeholder engagement, and impact assessments.
CSR is not mandatory for businesses, but some governments and industry bodies have introduced voluntary guidelines and reporting requirements to encourage companies to adopt CSR practices.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















