A Plan Compliance Checklist is a crucial tool used by retirement plan sponsors and administrators to ensure that their plans remain compliant with federal laws and regulations. The checklist typically includes a comprehensive list of plan compliance requirements and associated deadlines, such as required amendments, filings, and participant notices. By using a Plan Compliance Checklist, plan sponsors and administrators can identify areas of non-compliance and prioritize resources to address any issues. Retirement plan sponsors and administrators must regularly review and update their plan documents to remain compliant with federal regulations. These documents include the formal written plan, trust agreements, and any other documents that govern the operation of the plan. Plan amendments may be required due to changes in laws, regulations, or internal plan policies. When amending plan documents, it is essential to adhere to specific deadlines. Generally, plan amendments must be adopted by the end of the plan year in which they become effective. However, some amendments have specific deadlines set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or Department of Labor (DOL). It is crucial to be aware of these deadlines to avoid non-compliance. Plan sponsors and administrators must maintain records of all plan amendments, including the effective date of the amendment and any approvals or resolutions related to the amendment. This documentation is essential in the event of an audit or investigation. Retirement plans are subject to annual reporting requirements with the DOL. Most plans must file a Form 5500, Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan, to report information about the plan's financial condition, investments, and operations. This form must be filed electronically using the DOL's EFAST2 system. In addition to Form 5500, some plans may need to file other forms with the IRS, such as Form 5330, Return of Excise Taxes Related to Employee Benefit Plans, and Form 8955-SSA, Annual Registration Statement Identifying Separated Participants with Deferred Vested Benefits. Plan sponsors and administrators should be familiar with the specific filing requirements applicable to their plans. Some retirement plans may have additional filing requirements with other regulatory agencies, such as the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC) or state insurance departments. These requirements may vary depending on the type of plan and the jurisdiction in which it operates. Filing deadlines are crucial for maintaining plan compliance. Generally, Form 5500 must be filed by the last day of the seventh month following the end of the plan year. However, an extension may be requested by filing Form 5558, Application for Extension of Time to File Certain Employee Plan Returns. Other forms may have different deadlines, so it is essential to be aware of all relevant filing deadlines. Plan sponsors and administrators are required to provide participants with a Summary Plan Description that explains the plan's provisions, rights, and responsibilities. The SPD must be written in a manner that can be understood by the average participant and must be updated and distributed periodically. New participants must receive the SPD within 90 days of becoming eligible for the plan, and current participants must receive an updated SPD every five years if the plan has been amended or every ten years if no amendments have been made. When significant changes are made to a retirement plan, plan sponsors and administrators must provide participants with a Summary of Material Modifications. The SMM outlines the changes made to the plan and how they affect participants' rights and benefits. The SMM must be distributed within 210 days after the end of the plan year in which the changes were adopted. Defined benefit pension plans are required to provide participants with an annual funding notice that discloses the plan's funded status and other financial information. This notice must be provided within 120 days after the end of the plan year. Retirement plan sponsors and administrators must provide participants with fee disclosure statements that outline the plan's fees and expenses. These disclosures help participants make informed decisions about their investments and help them compare the costs of different investment options. In addition to the notices mentioned above, retirement plans may be subject to other participant notice requirements, such as automatic enrollment notices, Qualified Default Investment Alternative (QDIA) notices, and blackout period notices. Plan sponsors and administrators should familiarize themselves with all applicable notice requirements and ensure they are distributed in a timely manner. Regularly reviewing plan documents is crucial for maintaining compliance. This process ensures that plan provisions align with current laws, regulations, and internal policies. Plan sponsors and administrators should schedule regular plan document reviews and update the documents as needed to remain compliant. Administrative procedures are the operational processes used to manage the retirement plan. These procedures include plan enrollment, contributions, distributions, loans, and other plan-related activities. Ensuring that these procedures align with plan documents and applicable regulations is essential for maintaining plan compliance. Regular reviews and updates to administrative procedures can help prevent errors and non-compliance. Implementing internal controls can help prevent errors and ensure compliance with plan requirements. These controls may include separation of duties, periodic reconciliations, and monitoring of plan transactions. Plan sponsors and administrators should regularly review and improve their internal controls to enhance plan compliance. Conducting regular compliance audits is essential for identifying areas of non-compliance and prioritizing resources to address any issues. These audits can be performed internally or by hiring an external auditor. Compliance audits should evaluate plan documents, administrative procedures, and internal controls to identify potential areas of non-compliance. When non-compliance issues are identified, it is crucial to implement the required changes promptly. This may involve amending plan documents, revising administrative procedures, or improving internal controls. It is also essential to monitor progress and document any corrections made to demonstrate good faith efforts to maintain plan compliance. Continuous improvement of processes and controls can help prevent future non-compliance. Regular reviews of compliance efforts, ongoing staff training, and the implementation of best practices can reduce the risk of non-compliance and help maintain a compliant retirement plan. Proper documentation and recordkeeping are essential for demonstrating compliance efforts in the event of an audit or investigation. Plan sponsors and administrators should maintain records of plan amendments, filings, participant notices, and other compliance-related activities. It is crucial to maintain documentation of all plan amendments, filings, and participant notices. This documentation should include the effective date of amendments, any approvals or resolutions related to the amendments, copies of filed forms, and records of when and how participant notices were distributed. Maintaining this documentation can provide evidence of compliance efforts and help during audits or investigations. Federal regulations require retirement plan sponsors and administrators to retain records related to plan administration for a specific period. Generally, records must be kept for at least six years from the date the associated filing was due or filed, whichever is later. However, some records, such as those related to plan amendments and participant notices, should be retained for the life of the plan. It is crucial to establish a record retention policy that complies with applicable regulations and ensures that all necessary records are readily accessible. The Plan Compliance Checklist serves as a vital tool for retirement plan sponsors and administrators to ensure compliance with federal laws and regulations. By systematically addressing plan amendments, regulatory filings, and participant notices and reviewing plan documents, administrative procedures, and internal controls, the checklist helps identify and rectify areas of non-compliance. Furthermore, it aids in prioritizing resources, documenting compliance efforts, and implementing best practices to prevent future non-compliance. Proper documentation and recordkeeping are essential components of a successful compliance strategy, and the Plan Compliance Checklist assists in achieving these goals. By investing in compliance efforts and utilizing the checklist, plan sponsors and administrators can provide a secure and compliant retirement plan for their participants.Definition of Plan Compliance Checklist
Plan Compliance Checklist Requirements
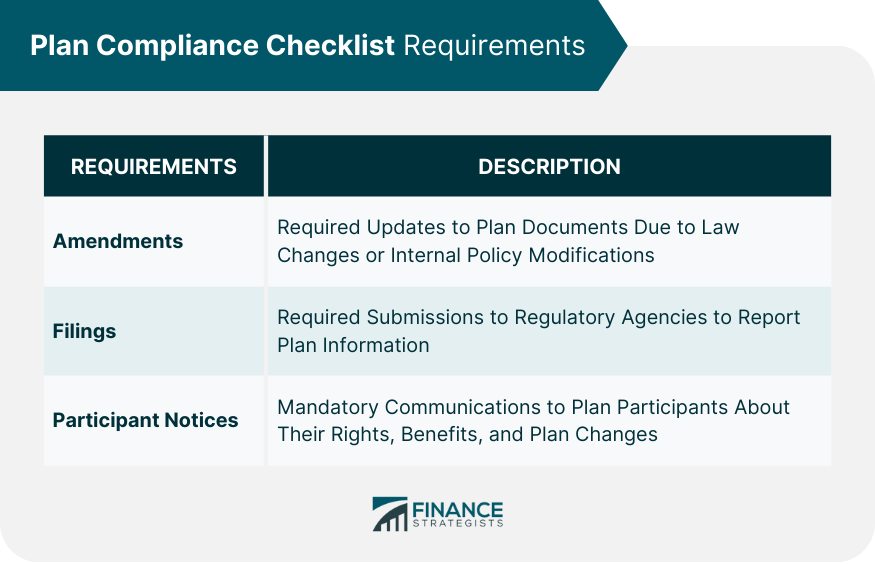

Amendments
Required Plan Document Amendments
Timelines for Implementing Amendments
Documenting the Amendment Process
Filings
Annual Filings with the Department of Labor
Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Filings
Other Required Regulatory Filings
Deadlines for Filing Submissions
Participant Notices
Summary Plan Descriptions (SPDs)
Summary of Material Modifications (SMMs)
Annual Funding Notices
Required Fee Disclosures
Other Participant Notices as Required by Law
Review of Plan Documents and Procedures for Plan Compliance Checklist
Plan Document Review
Administrative Procedures
Internal Controls
Identifying and Addressing Non-Compliance for Plan Compliance Checklist
Regular Compliance Audits
Correcting Non-Compliance
Preventing Future Non-Compliance
Documentation and Recordkeeping for Plan Compliance Checklist
Maintaining Records of Compliance Efforts
Documenting Amendments, Filings, and Participant Notices
Ensuring Proper Record Retention
Conclusion
Plan Compliance Checklist FAQs
A Plan Compliance Checklist is a tool used by retirement plan sponsors and administrators to ensure their plans remain compliant with federal laws and regulations. The checklist helps them identify areas of non-compliance, prioritize resources to address any issues, and document compliance efforts, which may be useful in the event of an audit or investigation.
A Plan Compliance Checklist provides a comprehensive list of required plan document amendments, along with their associated deadlines. By using this checklist, plan sponsors and administrators can ensure they are aware of necessary changes to plan documents and can implement amendments in a timely manner to maintain compliance.
Yes, a Plan Compliance Checklist can help plan sponsors and administrators meet participant notice requirements by outlining the various notices required by law, such as Summary Plan Descriptions, Summary of Material Modifications, and Annual Funding Notices. The checklist can serve as a reminder to distribute these notices within the required timeframes, ensuring compliance with federal regulations.
A Plan Compliance Checklist includes a review of administrative procedures and internal controls to ensure they align with regulatory requirements. By following the checklist, plan sponsors and administrators can identify potential areas of non-compliance in their procedures and controls and make necessary adjustments to maintain compliance.
A Plan Compliance Checklist encourages ongoing compliance efforts by providing a systematic approach to reviewing plan documents, administrative procedures, and internal controls. By regularly using the checklist, plan sponsors and administrators can identify and address areas of non-compliance, implement best practices, and continuously improve their processes to reduce the risk of future non-compliance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











