Asset class correlations refer to the degree to which the returns of different asset classes move in relation to each other. A high positive correlation indicates that two asset classes tend to move in the same direction, while a high negative correlation implies that they move in opposite directions. Understanding these correlations can help investors make informed decisions in managing their portfolios. Analyzing asset class correlations is essential for effective portfolio management. By understanding the relationships between different asset classes, investors can diversify their holdings, manage risks, and optimize investment returns. Asset class correlations are influenced by several factors, including market cycles, geopolitical events, economic indicators, monetary policies, and investor sentiment. These factors can cause correlations to change over time, necessitating regular monitoring and adjustment of investment strategies. Equities, or stocks, represent ownership in a company. They are considered one of the primary asset classes and can provide investors with capital appreciation and dividend income. Fixed income securities, such as bonds, pay periodic interest and return the principal amount at maturity. They are generally considered less risky than equities and can provide a steady income stream to investors. Cash and cash equivalents include currency, money market funds, and short-term debt instruments. They are considered the least risky asset class and provide liquidity and capital preservation. Real estate investments can involve direct ownership of property or indirect investment through real estate investment trusts (REITs). Real estate can offer diversification, income, and capital appreciation potential. Commodities include physical goods like oil, gold, and agricultural products. Investors can gain exposure to commodities through futures contracts, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or direct ownership. They can act as a hedge against inflation and provide diversification benefits. Private equity investments involve investing in privately held companies. They can offer high return potential but may also entail higher risk and illiquidity. Hedge funds are pooled investment vehicles that use various strategies to generate returns. They can provide diversification and risk management benefits but may also come with higher fees and complexity. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets that use cryptographic techniques for secure transactions. They have gained popularity in recent years and can offer diversification and capital appreciation potential, but they also come with high volatility and regulatory risks. The Pearson correlation coefficient measures the linear relationship between two variables, in this case, the returns of two asset classes. It ranges from -1 (perfect negative correlation) to 1 (perfect positive correlation), with 0 indicating no correlation. The Spearman rank correlation measures the monotonic relationship between two variables, based on their ranks rather than their actual values. It is less sensitive to outliers and can be more appropriate for non-linear relationships. A positive correlation indicates that two asset classes tend to move in the same direction. When one asset class performs well, the other is also likely to perform well. A negative correlation implies that two asset classes move in opposite directions. When one asset class performs well, the other is likely to perform poorly. No correlation means that there is no discernible relationship between the returns of two asset classes. The performance of one asset class has no bearing on the performance of the other. Different asset classes may perform differently during various market cycles. For example, equities and bonds may have low correlations during economic expansions but higher correlations during recessions. Geopolitical events, such as wars, elections, and trade disputes, can impact asset class correlations by causing shifts in investor sentiment, market dynamics, and economic conditions. Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, can influence the performance of different asset classes and, consequently, their correlations. Central banks' monetary policies, including interest rate changes and quantitative easing, can affect asset class correlations by altering market conditions and influencing investor behavior. Investor sentiment can impact asset class correlations as investors react to market events, news, and trends, causing shifts in demand for different asset classes. Historically, asset class correlations have changed over time, often due to macroeconomic factors, market cycles, and changes in investment strategies. In recent years, the correlations between some asset classes have increased due to factors such as globalization, advancements in technology, and the growing influence of passive investment strategies. Asset class correlations may continue to evolve in the future as markets respond to new developments, such as shifts in demographics, technological innovations, and changes in the global economic landscape. Understanding asset class correlations can help investors construct well-diversified portfolios by allocating assets across different asset classes with low correlations. This can help reduce portfolio volatility and improve risk-adjusted returns. By monitoring and managing asset class correlations, investors can effectively manage portfolio risk by identifying and adjusting investments with high correlations that could potentially exacerbate losses during market downturns. A comprehensive understanding of asset class correlations can inform investment decisions by highlighting opportunities for diversification, risk management, and capital appreciation. Asset class correlations can change over time, making it difficult to rely on historical correlations for future investment decisions. Investors should regularly update their analysis to account for these changes. Some asset classes may exhibit non-linear relationships, which can be challenging to capture using traditional correlation measures like the Pearson correlation coefficient. Extreme market events, such as financial crises, can lead to unexpected changes in asset class correlations, making it difficult for investors to rely solely on correlation analysis for risk management and diversification purposes. Given the dynamic nature of asset class correlations, it is essential for investors to monitor and adapt their investment strategies to changing market conditions and correlations. Understanding and managing asset class correlations play a crucial role in constructing well-diversified portfolios, managing risk, and making informed investment decisions. By staying informed and adapting to changing correlations, investors can enhance their portfolio performance and achieve their financial goals. In conclusion, asset class correlations are a critical aspect of portfolio management. By understanding the relationships between different asset classes, investors can optimize their portfolio diversification, manage risks more effectively, and make better-informed investment decisions. However, it is essential to remember that correlations can change over time due to various factors, and investors should continuously monitor and adapt their strategies to stay ahead in the ever-evolving financial landscape.What Are Asset Class Correlations?
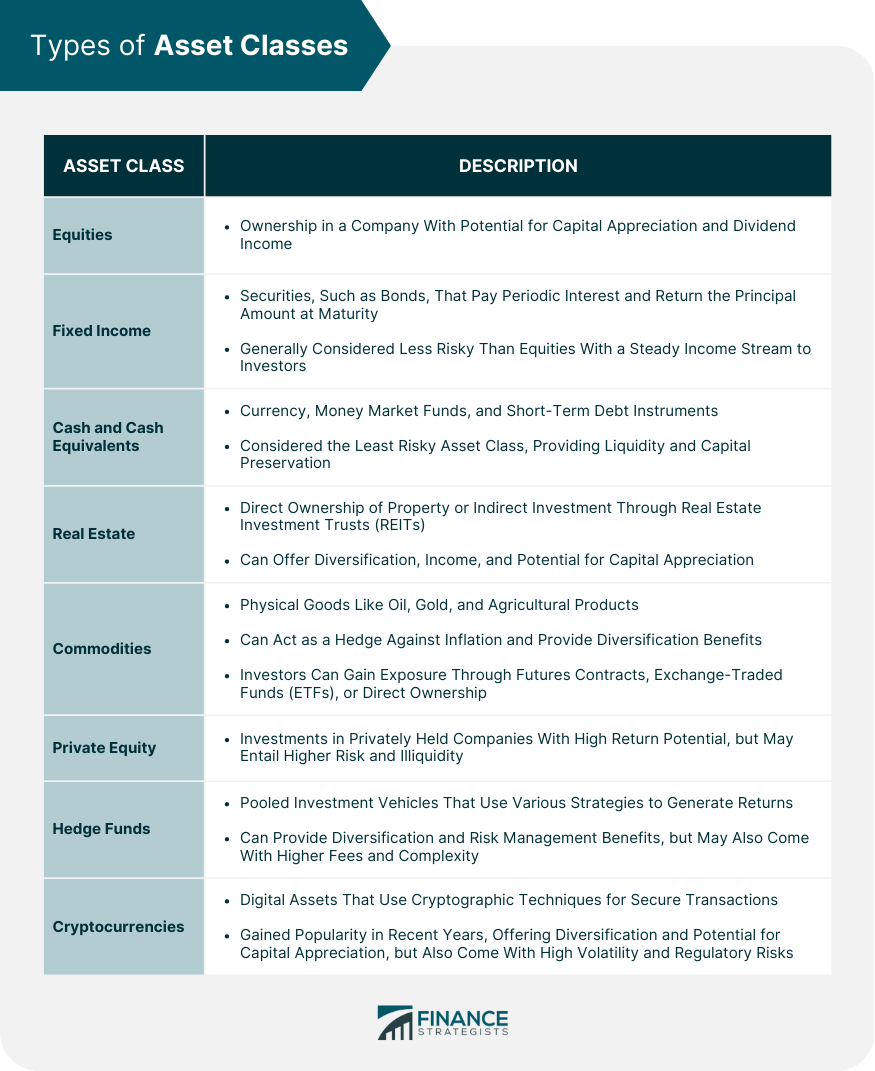
Types of Asset Classes
Traditional Asset Classes
Equities
Fixed Income
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Alternative Asset Classes
Real Estate
Commodities
Private Equity
Hedge Funds
Cryptocurrencies
Measuring Asset Class Correlations
Statistical Methods
Pearson Correlation Coefficient
Spearman Rank Correlation
Interpretation of Correlation Values
Positive Correlation
Negative Correlation
No Correlation
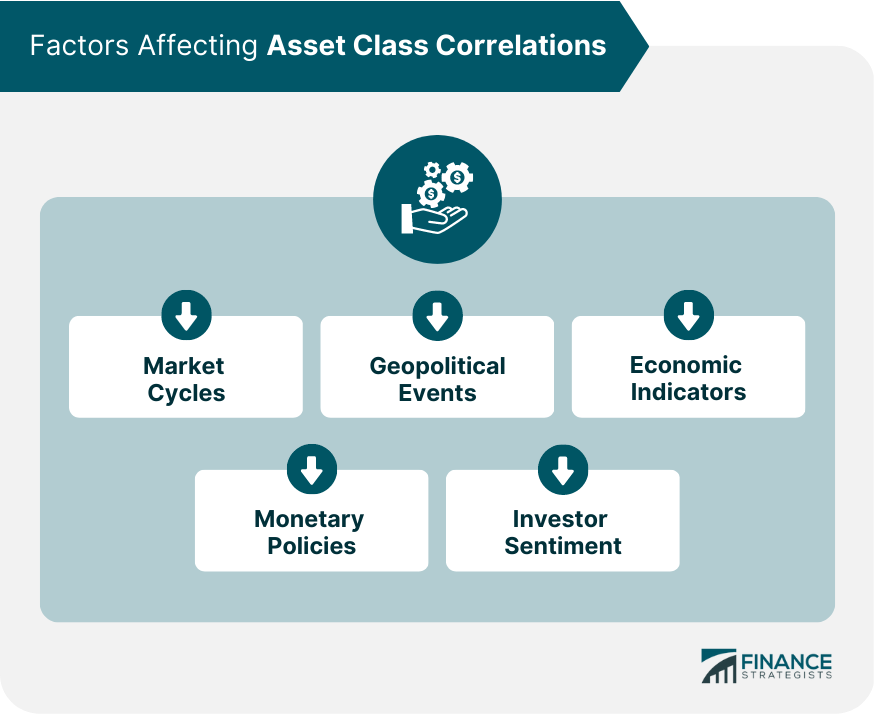
Factors Affecting Asset Class Correlations
Market Cycles
Geopolitical Events
Economic Indicators
Monetary Policies
Investor Sentiment
Asset Class Correlation Trends
Historical Perspective
Recent Trends in Correlation
Potential Future Trends
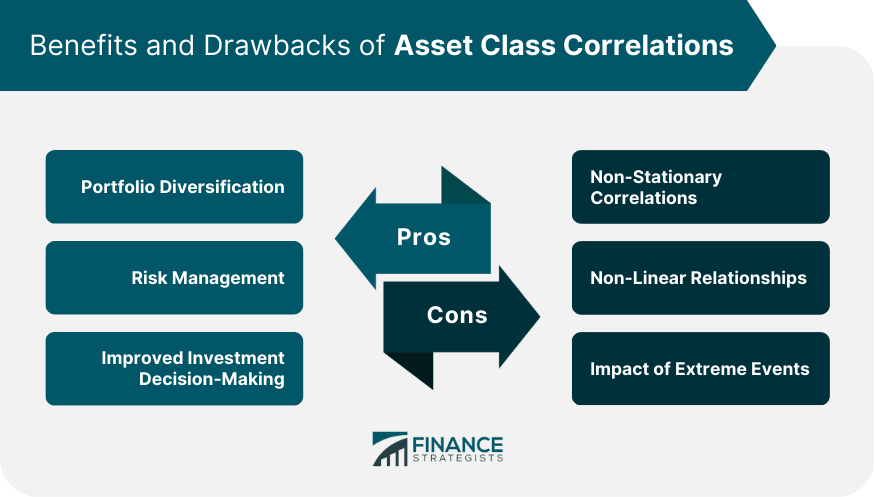
Benefits of Understanding Asset Class Correlations
Portfolio Diversification
Risk Management
Improved Investment Decision-Making
Limitations and Challenges of Asset Class Correlations
Non-Stationary Correlations
Non-Linear Relationships
Impact of Extreme Events
Conclusion
Asset Class Correlations FAQs
Asset class correlations refer to the degree of similarity or difference in the price movements of different types of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. Correlations can range from -1 (perfect negative correlation) to +1 (perfect positive correlation), with 0 indicating no correlation.
Asset class correlations are important because they can affect the risk and return of investment portfolios. If asset classes are highly correlated, a downturn in one asset class can lead to losses across the entire portfolio. Conversely, if asset classes are negatively correlated, losses in one asset class may be offset by gains in another.
Investors can use asset class correlations to diversify their portfolios by allocating their investments across different asset classes that have low or negative correlations. This can reduce the overall risk of the portfolio and potentially increase returns. For example, a portfolio that includes both stocks and bonds may be less risky than a portfolio that only includes stocks.
Asset class correlations can change over time due to various factors, such as changes in market conditions, economic events, and government policies. In general, correlations tend to be higher during times of market stress or uncertainty and lower during periods of stability.
While asset class correlations cannot be predicted with certainty, analysts and investors can use historical data and market trends to make informed assumptions about future correlations. However, it's important to note that past performance is not a guarantee of future results, and unexpected events can always disrupt correlations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















