Discretionary Investment Management is an investment strategy that involves delegating the management of an investment portfolio to a professional investment manager who has the authority to make investment decisions on behalf of the investor. This strategy is popular among high-net-worth individuals, institutions, pension funds, family offices, endowments, and other entities with investable assets. Discretionary investment management typically involves several steps. The first step in discretionary investment management is the selection and onboarding of an investment manager. Investors should research potential investment managers to ensure that they have the necessary experience and qualifications. They should also review an investment manager's track record and performance to determine whether they have a history of making successful investment decisions. Once an investor has selected an investment manager, they will typically need to complete a client agreement and provide documentation that verifies their identity and financial status. This documentation may include bank statements, tax returns, and investment account statements. The second step in discretionary investment management is the assessment of an investor's risk tolerance and goal setting. An investment manager will typically work with an investor to determine their investment objectives and risk tolerance. This information is used to construct a portfolio that is tailored to the investor's individual needs. During this step, the investment manager will typically ask the investor a series of questions to determine their risk tolerance. This may include questions about their investment goals, time horizon, and investment experience. The investment manager will then use this information to create an investment plan that is designed to achieve the investor's goals while managing their risk. The third step in discretionary investment management is portfolio construction and management. Investment managers use their expertise and experience to identify investment opportunities that align with an investor's objectives and risk tolerance. They also monitor the performance of the portfolio and make adjustments as necessary to ensure that it remains aligned with the investor's goals. During this step, the investment manager will typically create a diversified portfolio that includes a mix of different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and alternative investments. They will also use their knowledge of the market and investment opportunities to make investment decisions that are aligned with the investor's goals. The investment manager will also monitor the performance of the portfolio and make adjustments as necessary. This may include buying or selling investments or reallocating assets within the portfolio. The investment manager will typically provide the investor with regular reports that detail the performance of the portfolio. The final step in discretionary investment management is investment manager reporting and communication. Investment managers are typically required to provide investors with regular reports that detail the performance of the portfolio. They also communicate with investors regularly to ensure that they are aware of any changes to the portfolio or market conditions that may impact their investments. During this step, the investment manager will typically provide the investor with regular reports that detail the performance of the portfolio. These reports may include information about the performance of individual investments, the overall performance of the portfolio, and any fees or costs associated with investment management services. The investment manager will also communicate with the investor on a regular basis to ensure that they are aware of any changes to the portfolio or market conditions that may impact their investments. This may include providing updates on market trends or changes to investment strategies. Discretionary investment management is a popular investment strategy that allows investors to delegate the management of their portfolio to a professional investment manager. Here are the benefits of discretionary investment management: One of the primary benefits of discretionary investment management is the delegation of investment decisions to professionals. By entrusting their portfolio to an experienced investment manager, investors can free up their time and focus on other aspects of their lives. This can be particularly valuable for busy individuals who need more time or expertise to manage their own investments. Investment managers are trained to identify investment opportunities and manage risks. They have the expertise and experience needed to make informed investment decisions on behalf of their clients. This can be particularly valuable during times of market volatility or uncertainty when it can be difficult for individual investors to make investment decisions. Discretionary investment management also provides investors with access to diverse investment opportunities. Investment managers have access to a wide range of investment products and can create a diversified portfolio that is tailored to an investor's individual needs and risk tolerance. This can help to manage risk and potentially enhance returns. Finally, discretionary investment management can be a time-saving investment strategy for investors. Investment managers take care of the day-to-day management of the portfolio, including buying and selling investments, monitoring performance, and making adjustments as necessary. This can be particularly valuable for busy individuals who do not have the time or desire to manage their own investments. While discretionary investment management has many benefits, risks, and limitations are also associated with this investment strategy. By delegating their portfolio management to a professional investment manager, investors relinquish control over investment decisions. This means that they must trust their investment manager to make sound investment decisions on their behalf. Investment managers may have incentives to make certain investment decisions that are not aligned with the best interests of their clients. For example, an investment manager may be incentivized to invest in a particular stock or fund because they receive a commission or fee for doing so. It is important for investors to carefully review an investment manager's incentives and ensure that they are aligned with their own investment objectives. While investment managers are trained to identify investment opportunities and manage risks, there is always the potential for investment decisions to result in losses. Investors should carefully review an investment manager's track record and performance to determine whether they have a history of making successful investment decisions. Investment managers typically charge a fee for their services, and these fees can vary widely depending on the investment manager and the size of the portfolio. Investors should carefully review these fees and costs to ensure that they are reasonable and aligned with the expected return on investment. Choosing the right investment manager is crucial to the success of a discretionary investment management strategy. Here are the key factors to consider when choosing a discretionary investment manager: Investors should research potential investment managers to ensure that they have the necessary experience and qualifications. This may include reviewing their education, professional certifications, and investment experience. Investors should also review an investment manager's track record and performance to determine whether they have a history of making successful investment decisions. This information can typically be found in an investment manager's marketing materials or website. Investors should carefully review the fees and costs associated with investment management services. Investment managers typically charge a fee for their services, which can vary widely depending on the investment manager and the portfolio size. Investors should ensure these fees and costs are reasonable and aligned with the expected return on investment. Investors should also assess an investment manager's communication and reporting. Investment managers should be transparent and provide investors with regular reports detailing the portfolio's performance. They should also be available to communicate with investors regularly to ensure that they are aware of any changes to the portfolio or market conditions that may impact their investments. Discretionary investment management is an effective investment strategy that allows investors to delegate the management of their portfolio to a professional investment manager. It is important to be aware of the risks and limitations of discretionary investment management, including lack of control, potential conflicts of interest, uncertain investment manager performance, and associated costs and fees. To mitigate these risks and enjoy the benefits of discretionary investment management, it is crucial to carefully select an investment manager, review their track record and performance, assess their fees and costs, and evaluate their communication and reporting. With the help of a professional wealth management firm, investors can ensure that their portfolio is managed effectively and efficiently, allowing them to focus on other aspects of their lives.What Is Discretionary Investment Management?
How Discretionary Investment Management Works
Step 1: Selection and Onboarding of an Investment Manager
Step 2: Assessment of Risk Tolerance and Goal Setting
Step 3: Portfolio Construction and Management
Step 4: Investment Manager Reporting and Communication

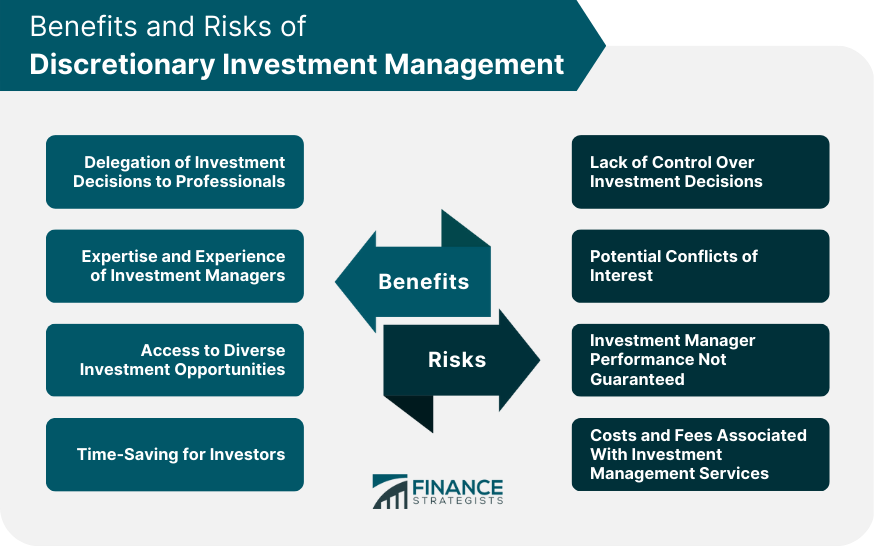
Benefits of Discretionary Investment Management
Delegation of Investment Decisions to Professionals
Expertise and Experience of Investment Managers
Access to Diverse Investment Opportunities
Time-Saving for Investors
Risks of Discretionary Investment Management
Lack of Control Over Investment Decisions
Potential Conflicts of Interest
Investment Manager Performance Not Guaranteed
Costs and Fees Associated With Investment Management Services
Choosing a Discretionary Investment Manager
Researching Potential Investment Managers
Evaluating Investment Manager Track Record and Performance
Reviewing Investment Manager Fees and Costs
Assessing Investment Manager Communication and Reporting
The Bottom Line
Discretionary Investment Management FAQs
Discretionary investment management is an investment strategy in which investors delegate the management of their portfolio to a professional investment manager.
The benefits of discretionary investment management include delegation of investment decisions to professionals, expertise and experience of investment managers, access to diverse investment opportunities, and time-saving for investors.
Risks associated with discretionary investment management include lack of control over investment decisions, potential conflicts of interest, uncertain investment manager performance, and associated costs and fees.
When selecting an investment manager for discretionary investment management, it is important to research potential investment managers, evaluate their track record and performance, review their fees and costs, and assess their communication and reporting.
The role of an investment manager in discretionary investment management is to manage an investor's portfolio, including identifying investment opportunities, constructing a diversified portfolio, monitoring performance, and making adjustments as necessary. They also provide regular reports to the investor and communicate any changes to the portfolio or market conditions that may impact their investments.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















