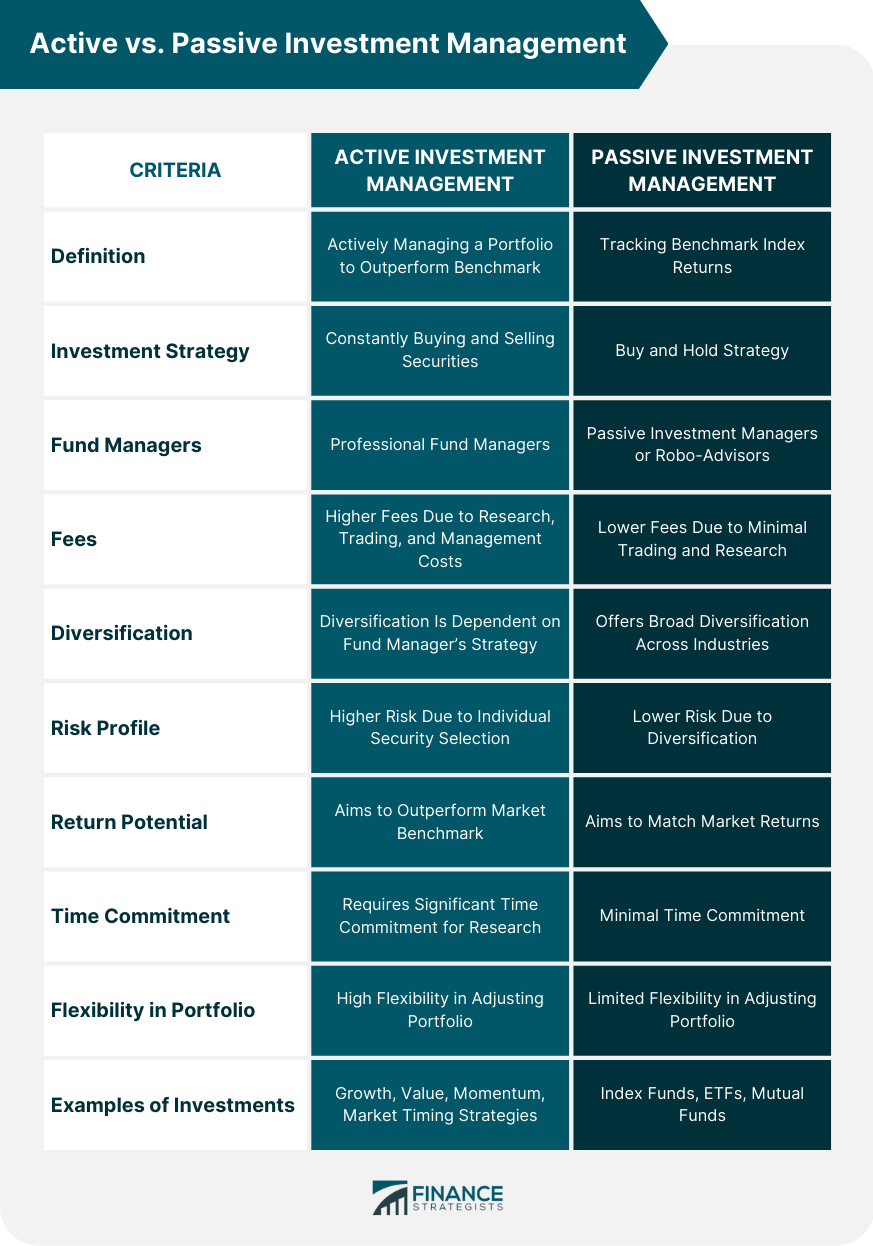
Active investment management involves actively managing a portfolio of investments with the aim of achieving higher returns than a particular benchmark, such as the S&P 500 index. The portfolio managers use their expertise and market analysis to select individual securities that they believe will outperform the market. In contrast, passive investment management aims to track a benchmark index's performance by holding a portfolio of securities that mirror the index. Passive investors do not aim to outperform the market but rather to match the market returns. Choosing between active and passive investment management is an important decision for any investor. The choice can significantly impact investment returns and fees. Understanding the difference between active and passive investment management can help you make informed investment decisions, reduce the risk of losing money, and improve your chances of achieving your investment goals. Active investment management is a strategy that involves the active selection and management of a portfolio of investments. Active managers use their knowledge and expertise to identify undervalued assets and market trends that can result in higher returns than the market benchmark. One of the significant advantages of active investment management is the potential for higher returns than the market benchmark. Active managers have the flexibility to adjust their portfolios based on market conditions and their analysis, which can result in higher returns than a passive investment strategy. Active investment management also allows investors to benefit from the expertise of professional fund managers. These managers typically have extensive knowledge and experience in the market, which can help them identify undervalued assets and avoid overvalued ones. Active investment management is associated with higher fees than passive investment management. This is because active managers spend significant amounts of time and resources on market analysis, research, and portfolio management, which can increase the costs for investors. Another disadvantage of active investment management is the risk of underperformance. Even experienced managers with excellent track records can fail to outperform the market benchmark due to unforeseen market events, volatility, or other factors. There are various active investment management strategies that investors can use, including value investing, growth investing, momentum investing, and market timing. Value investing involves identifying undervalued stocks that have a strong potential for long-term growth. Growth investing focuses on investing in stocks with high growth potential, while momentum investing seeks to identify stocks that are showing positive momentum. Market timing involves adjusting the portfolio's holdings based on market trends and forecasts. Passive investment management is a strategy that aims to track the performance of a particular benchmark index by holding a portfolio of securities that mirror the index. Passive investors do not attempt to outperform the market but rather aim to match the market returns. One of the significant advantages of passive investment management is lower fees compared to active investment management. Passive investors do not spend significant amounts of time and resources on market analysis and research, which can reduce the overall costs for investors. Passive investment management also offers diversification benefits. By investing in a broad market index, passive investors can gain exposure to a wide range of companies across different industries, which can help reduce the portfolio's overall risk. Passive investment management is associated with the risk of tracking error. The portfolio's returns may not match the benchmark index due to factors such as fund fees, taxes, and trading costs. This risk can result in underperformance compared to the market benchmark. Another disadvantage of passive investment management is the lack of flexibility. Passive investors cannot adjust the portfolio's holdings based on market conditions or their analysis, which can result in missed opportunities to generate higher returns. There are various passive investment management strategies that investors can use, including index funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and mutual funds. Index funds are mutual funds or ETFs that aim to track the performance of a particular benchmark index, such as the S&P 500. ETFs are similar to index funds but trade like stocks, providing more flexibility for investors. Active investment management is associated with higher fees than passive investment management. This is because active managers spend significant amounts of time and resources on market analysis, research, and portfolio management. Passive investment management, on the other hand, is typically associated with lower fees due to the lower costs associated with tracking a benchmark index. Active investment management has the potential to generate higher returns than passive investment management, but it also involves higher risks. Active managers can use their expertise to identify undervalued assets and market trends that can result in higher returns than the market benchmark. Passive investment management, on the other hand, aims to match the market returns, which may not result in the highest possible returns. Active investment management is associated with higher risk than passive investment management. Active managers take a more hands-on approach to managing portfolios, which can result in higher volatility and greater exposure to market risk. Passive investment management, on the other hand, offers diversification benefits and a lower risk profile. Active investment management requires significant time and effort on the part of the portfolio managers. Managers need to conduct detailed market analysis, research, and portfolio management to identify undervalued assets and market trends that can result in higher returns than the market benchmark. Passive investment management, on the other hand, requires less time and effort as the portfolio is designed to track the performance of a benchmark index. Choosing between active and passive investment management depends on individual investor goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Active investment management can generate higher returns, but it also involves higher fees and risks. Passive investment management is a low-cost, low-risk approach that aims to match market returns. It is essential to understand the difference between the two approaches to make informed investment decisions that align with your investment goals. Active and passive investment management are two popular investment strategies that differ in various ways. Active investment management involves actively managing a portfolio of investments to achieve higher returns than the market benchmark, while passive investment management aims to match the market returns by tracking a benchmark index. Understanding the difference between the two approaches can help investors make informed investment decisions that align with their goals. Ultimately, the choice between active and passive investment management depends on individual goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.Overview of Active vs. Passive Investment Management
Active Investment Management
Definition of Active Investment Management
They typically conduct detailed market analysis and research to identify individual securities that they believe will outperform the market.Advantages of Active Investment Management
Disadvantages of Active Investment Management
This risk can result in significant losses for investors.Examples of Active Investment Management Strategies
Passive Investment Management
Definition of Passive Investment Management
Advantages of Passive Investment Management
Disadvantages of Passive Investment Management
Examples of Passive Investment Management Strategies
Comparison Between Active and Passive Investment Management
Comparison of Fees
Comparison of Returns
Comparison of Risk
Comparison of Time and Effort
How to Choose Between Active vs. Passive Investment Management
Conclusion
Active vs Passive Investment Management FAQs
Active Investment Management involves actively managing a portfolio of investments to generate higher returns than a market index.
Passive Investment Management involves investing in a portfolio of assets that track a market index, such as the S&P 500, with a goal of matching the index's returns.
It depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Active management can generate higher returns, but it also involves higher fees and risks. Passive management is a low-cost, low-risk approach that aims to match market returns.
The main advantage of Active Investment Management is the potential for higher returns than market benchmarks, as skilled managers can identify undervalued assets and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
The main advantages of Passive Investment Management are low costs, low turnover, and diversification. Passive investments can provide broad exposure to a market with minimal fees, making them a popular choice for long-term investors.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















