A bond ladder is a portfolio of bonds with varying maturity dates, where the bonds are held to maturity, and their proceeds are reinvested in new bonds. This creates a "ladder" of bonds, with each rung representing a different maturity date. Bond ladders can be customized to meet an investor's specific income needs, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Bond ladders offer several advantages for investors seeking income and diversification in their fixed-income portfolios. They provide a regular income stream, reduce interest rate risk, enhance liquidity, and offer the potential for capital preservation. These benefits make bond ladders attractive for investors looking for a balanced and flexible fixed-income strategy. A bond ladder consists of several key components, including the types of bonds selected, their credit ratings, maturities, and the diversification strategies employed. The reinvestment strategy and the staggering of bond maturities are also crucial aspects of bond ladder construction. Building a bond ladder requires careful planning and execution. Investors must select the appropriate bonds, diversify their holdings, stagger maturities, and establish a reinvestment strategy. Investors can include various types of bonds in their bond ladder. These include: Government Bonds: Issued by governments, these bonds are generally considered low-risk investments. Municipal Bonds: Issued by states, cities, or other local governments, these bonds may offer tax advantages for investors. Corporate Bonds: Issued by corporations, these bonds may provide higher yields but come with higher credit risk compared to government bonds. Agency Bonds: Issued by government-sponsored entities, these bonds typically have lower credit risk than corporate bonds but higher yields than government bonds. Bond credit ratings reflect the creditworthiness of the issuer and help investors evaluate the risk associated with a particular bond. Credit rating agencies, such as Standard & Poor's, Moody's, and Fitch, assign credit ratings to bonds based on their analysis of the issuer's financial strength and ability to meet debt obligations. Investors should consider the credit rating of a bond when constructing their bond ladder, as higher-rated bonds generally carry less credit risk. Bond maturities, or the length of time until a bond's principal is repaid, play a crucial role in bond ladder construction. By selecting bonds with different maturities, investors can create a ladder that provides income at regular intervals and minimizes interest rate risk. Diversification is a key aspect of bond ladder construction, as it helps spread risk across multiple bonds and issuers. By diversifying their bond holdings, investors can reduce the impact of any single bond's poor performance on their overall portfolio. Investors can diversify their bond ladder by incorporating bonds with different credit ratings, sectors, and geographic locations. This can help spread risk and potentially improve the bond ladder's overall performance. To create a bond ladder, investors should stagger the maturities of their bonds at regular intervals, such as every one, two, or five years. This ensures that a portion of the bond ladder will mature at regular intervals, providing a consistent income stream and allowing for the reinvestment of principal into new bonds. Staggering bond maturities are essential for mitigating interest rate risk. If interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds with lower yields will decrease. However, when bonds in the ladder mature, investors can reinvest the proceeds into new bonds with higher yields, thereby reducing the impact of rising interest rates on the overall portfolio. As bonds in a ladder mature, investors should have a reinvestment strategy in place to maintain the ladder's structure and income-generating potential. This typically involves reinvesting the principal from matured bonds into new bonds with similar characteristics, such as credit rating and maturity, to maintain the bond ladder's diversification and risk profile. Investors may need to adjust their bond ladders over time to align with their changing financial goals, risk tolerance, or market conditions. This may involve extending or shortening the ladder, adding or removing bonds, or adjusting the ladder's diversification strategy. Bond ladders are just one of many fixed-income investment strategies. It is essential to compare bond ladders to other strategies to determine the best approach for an investor's specific needs and goals. Bond funds are pooled investment vehicles that invest in a diversified portfolio of bonds. Unlike bond ladders, bond funds do not have a set maturity structure and may not provide the same level of predictability in terms of income and principal repayment. However, bond funds typically offer greater diversification and professional management, which can be beneficial for investors seeking broad exposure to the bond market. Investing in individual bonds allows investors to select specific bonds based on their credit ratings, yields, and maturities. While this can provide a high level of customization, it may also require more research and ongoing management compared to bond ladders or bond funds. Additionally, investing in individual bonds may not provide the same level of diversification as other fixed-income strategies. Certificates of deposit (CDs) are fixed-income investments issued by banks and credit unions that pay a fixed interest rate over a specified term. Like bond ladders, CD ladders involve purchasing CDs with staggered maturities to create a consistent income stream and mitigate interest rate risk. However, CDs are generally considered lower-risk investments than bonds, offering FDIC or NCUA insurance up to certain limits. This may make CD ladders more suitable for conservative investors, though they may offer lower yields than bond ladders. Money market funds are mutual funds that invest in short-term, high-quality debt securities, such as Treasury bills and commercial paper. While money market funds can provide stability and liquidity, they typically offer lower yields than bond ladders. They may not be suitable for investors seeking higher income or long-term capital appreciation. Annuities are insurance products that provide a guaranteed income stream, often for life, in exchange for an upfront payment. While annuities can offer predictable income and protection against longevity risk, they may also come with higher fees, limited flexibility, and potential surrender charges if the investor needs to access their principal early. When implementing a bond ladder in an investment portfolio, investors should consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and the appropriate bond ladder structure. Before constructing a bond ladder, investors should assess their financial goals, such as income needs, investment horizon, and risk tolerance. This information can help guide the selection of bonds, maturities, and diversification strategies for the bond ladder. Based on their goals and risk tolerance, investors can determine the appropriate bond ladder structure, including the types of bonds, credit ratings, and maturities to include in the ladder. This may involve striking a balance between risk and reward, with higher-yielding bonds potentially offering more income but also carrying more credit risk. Investors should regularly monitor their bond ladder and make adjustments as needed to maintain their desired risk and return profile. This may involve reinvesting proceeds from matured bonds, adjusting the ladder's diversification strategy, or extending or shortening the ladder's maturity structure. Bond ladders can be integrated with other investment strategies to create a well-diversified and balanced portfolio. Investors can combine bond ladders with equity investments, bond funds, CDs, or other fixed-income strategies to achieve their desired risk and return profile. By incorporating multiple investment strategies, investors can manage their overall portfolio risk and potentially enhance long-term performance. Bond ladders offer several benefits for fixed-income investors, including: By staggering bond maturities, bond ladders provide a consistent and predictable income stream. This can be especially beneficial for investors seeking regular income, such as retirees. Bond ladders help reduce interest rate risk by allowing investors to reinvest maturing bonds at potentially higher yields when interest rates rise. This strategy can help protect the overall value of an investor's fixed-income portfolio. Bond ladders enhance liquidity by ensuring that a portion of the portfolio will mature at regular intervals. This allows investors to access their principal without needing to sell bonds in the open market, which can be subject to price fluctuations. By diversifying bond holdings and staggering maturities, bond ladders can help preserve capital and reduce the impact of individual bond or issuer-related risks on the overall portfolio. Bond ladders offer flexibility and customization, allowing investors to tailor their portfolios to meet specific income needs, risk tolerances, and investment horizons. While bond ladders offer several benefits, they also come with certain risks and limitations, including: Bond ladders can be exposed to credit risk if an issuer defaults on debt obligations. To manage credit risk, investors should diversify their bond holdings and consider the credit ratings of the bonds they include in their ladder. Some bonds, particularly those with lower credit ratings or smaller issuances, may be less liquid, making them difficult to buy or sell in the open market. Investors should be aware of liquidity risk when constructing their bond ladder and consider including more liquid bonds in their portfolio. Bond ladders are subject to reinvestment risk, which occurs when interest rates fall, and maturing bonds must be reinvested at lower yields. To manage reinvestment risk, investors can extend the maturities of their bonds or consider adding bonds with call protection, which limits the issuer's ability to call the bond before its maturity date. Inflation can erode the purchasing power of a bond ladder's income stream, particularly if the ladder consists primarily of long-term, fixed-rate bonds. Investors can manage inflation risk by incorporating inflation-protected securities, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), into their bond ladder. Although bond ladders can provide some diversification, they may not offer the same level of diversification as other fixed-income strategies, such as bond funds. Investors should consider their overall portfolio diversification when constructing a bond ladder and potentially incorporate other fixed-income investments to achieve their desired level of diversification. Bond ladders are a versatile and customizable fixed-income investment strategy that can provide several benefits for investors, such as a regular income stream, mitigation of interest rate risk, enhanced liquidity, and capital preservation. However, they also come with certain risks and limitations, including credit, liquidity, reinvestment, and inflation risk. When constructing a bond ladder, investors should carefully select the appropriate bonds, diversify their holdings, stagger maturities, and establish a reinvestment strategy. It is essential to compare bond ladders to other fixed-income strategies and consider integrating them with other investment approaches to create a well-balanced and diversified portfolio. By understanding the key aspects of bond ladders, their benefits and risks, and how they fit into a broader investment strategy, investors can make more informed decisions and potentially enhance their long-term financial success. Seeking the advice of a wealth management professional can provide further guidance on incorporating bond ladders and other investment strategies into a comprehensive financial plan that aligns with an investor's goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.What Are Bond Ladders?
Building a Bond Ladder
Selecting Bonds
Types of Bonds
Bond Credit Ratings
Bond Maturities
Diversification
Importance of Diversification in Bond Ladders
Diversification Strategies
Staggering Bond Maturities
Regular Intervals
Importance of Staggering Maturities
Reinvestment Strategy
Reinvesting Matured Bonds
Adjusting Bond Ladders Over Time
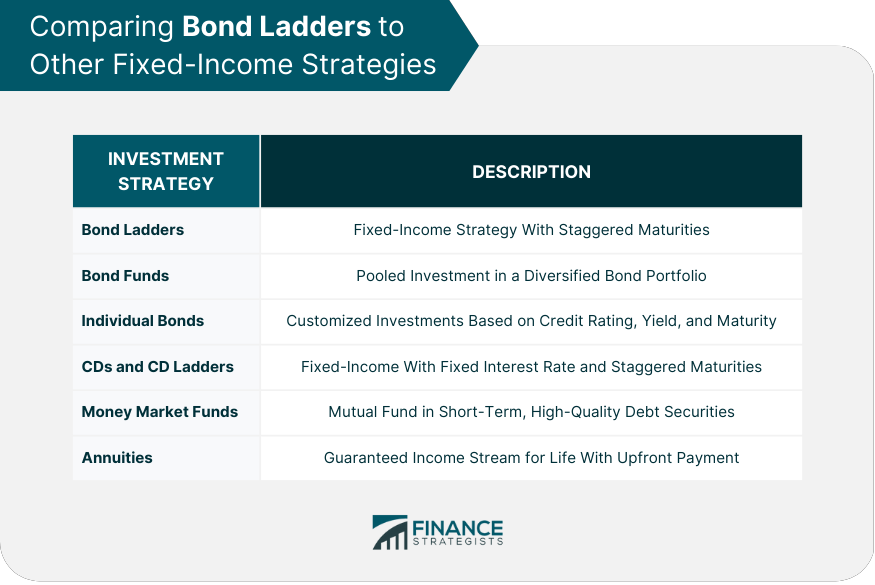
Comparing Bond Ladders to Other Fixed-Income Strategies
Bond Funds
Individual Bonds
CDs and CD Ladders
Money Market Funds
Annuities
Implementing a Bond Ladder in an Investment Portfolio
Assessing Investor Goals and Risk Tolerance
Determining the Appropriate Bond Ladder Structure
Monitoring and Adjusting the Bond Ladder Over Time
Integrating Bond Ladders With Other Investment Strategies
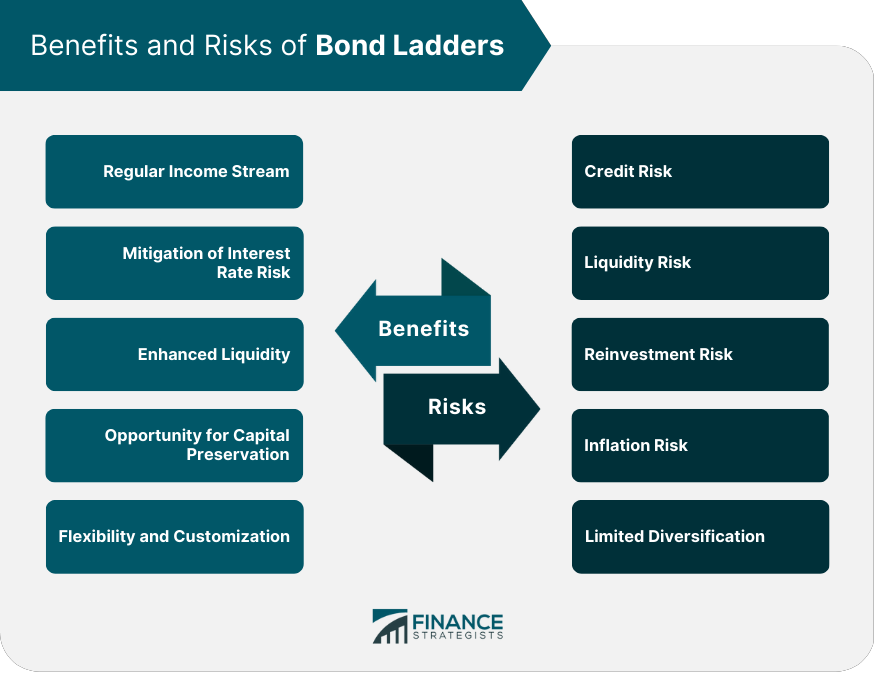
Benefits of Bond Ladders
Regular Income Stream
Mitigation of Interest Rate Risk
Enhanced Liquidity
Opportunity for Capital Preservation
Flexibility and Customization
Risks and Limitations of Bond Ladders
Credit Risk
Liquidity Risk
Reinvestment Risk
Inflation Risk
Limited Diversification
Conclusion
Bond Ladders FAQs
A bond ladder is a fixed-income investment strategy where an investor purchases a portfolio of bonds with staggered maturities to create a consistent income stream and mitigate interest rate risk.
Bond ladders can provide several benefits for investors, including a regular income stream, mitigation of interest rate risk, enhanced liquidity, and capital preservation.
Investing in bond ladders is just one of many fixed-income investment strategies. Comparing bond ladders to other strategies is essential to determine the best approach for an investor's specific needs and goals.
Bond ladders come with certain risks and limitations, including credit, liquidity, reinvestment, and inflation risk. Investors should carefully select appropriate bonds, diversify their holdings, stagger maturities, and establish a reinvestment strategy.
Yes, seeking the advice of a wealth management professional can provide further guidance on incorporating bond ladders and other investment strategies into a comprehensive financial plan that aligns with an investor's goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















