The Knowledge Economy stands as a transformative phase in global economics, where knowledge, rather than physical assets, emerges as the principal source of value and competitive advantage. Here, information, skills, and expertise overshadow traditional resources such as labor and raw materials. As economies continue evolving, an undeniable shift is noticeable - from factories to classrooms, from manual labor to mental prowess. This metamorphosis, though subtle, signifies an era where countries and companies no longer vie for mere physical supremacy but intellectual dominance. Knowledge becomes the new currency, driving growth, fostering innovation, and catalyzing socio-economic progress. In this modern economic landscape, intangible assets, ranging from software and patents to brands and business models, reign supreme. Their value isn't manifestly visible, nor can it be touched, but its impact is profound. Companies like Apple or Google might own fewer tangible assets compared to industrial behemoths of the past, yet their market capitalizations eclipse traditional counterparts. Data, often dubbed 'the new oil,' is a linchpin of the knowledge economy. The sheer volume of information generated daily is mind-boggling, and harnessing this data avalanche can yield transformative insights. Companies leverage this data deluge to glean customer preferences, optimize operations, or predict market trends. In essence, data becomes an instrument of precision, enabling businesses to tailor strategies with surgical accuracy. The pace at which new ideas, products, or solutions emerge is frenetic. And protecting these innovations is where intellectual property (IP) steps in. Patents, copyrights, trademarks – these aren't mere legal constructs but pivotal tools ensuring creators reap the benefits of their intellectual endeavors. Innovations, be it in computing, communications, or artificial intelligence, have dismantled barriers, democratized information access, and catalyzed knowledge dissemination. Technologies like the internet, cloud computing, and big data analytics haven't just reshaped industries but have redefined economic paradigms. The world today is an intricate web of interconnected entities. Globalization, facilitated by digital connectivity, ensures that knowledge isn't confined by geographic boundaries. An invention in Tokyo can spark a business idea in Toronto. Software coded in Silicon Valley can transform operations in Sydney. Such is the pervasive power of globalization in the knowledge economy. As manual tasks get automated and physical assets commoditized, the emphasis shifts to intellectual capabilities. Nations investing in education, skill development, and human capital not only foster innovation but also position themselves at the forefront of the knowledge-driven era. Often armed with specialized education and a plethora of skills, knowledge workers are the foot soldiers of this new economic order. Be it analysts, researchers, software developers, or consultants; they rely on their cognitive abilities to drive value. Their workspaces are bustling tech hubs, serene research labs, and vibrant startups. R&D institutions, whether academic, corporate, or governmental, incessantly churn out new ideas, solutions, and technologies. Their contributions aren't just academic; they shape industries, influence policies, and redefine societal norms. From biotechnology and information technology to financial services and creative sectors, knowledge-based industries epitomize the principles of the knowledge economy. They rely on intellectual assets, prioritize innovation, and constantly navigate the turbulence of rapidly evolving markets. Countries that have embraced the knowledge economy often experience accelerated economic growth. Knowledge-intensive sectors, be it IT or biotech, tend to have higher value additions. Moreover, as innovation becomes endemic, new industries emerge, existing ones evolve, and economic diversification ensues. The knowledge economy doesn't just boost GDPs. It elevates living standards. As countries transition, they witness improvements in healthcare, education, and infrastructure. The fusion of technology and knowledge ushers in services and solutions that enhance societal well-being. Knowledge-driven companies and economies often register higher productivity. Advanced tools, data-driven decision-making, and a relentless focus on innovation. As processes get optimized, and resources are utilized judiciously, the output per input unit surges. While the knowledge economy promises prosperity, it also risks exacerbating inequalities. Regions with robust educational infrastructures and technological ecosystems thrive while others lag. This disparity, often termed the 'knowledge divide,' poses socio-economic and political challenges. With the rise of knowledge as a primary asset, IP disputes have surged. Protecting intellectual creations in a digital, interconnected world is daunting. Piracy, patent infringements, or copyright breaches – the knowledge economy, for all its promise, is riddled with these pitfalls. The digital bedrock of the knowledge economy isn't impervious. As data becomes invaluable, it also becomes a prime target. Cyberattacks, data breaches, and privacy concerns loom large, compelling companies and countries to prioritize cybersecurity. Continuous R&D. Nations and companies need to incessantly invest in research, not as an expenditure, but as an investment. These investments lay the foundation for innovations that can redefine markets. To foster innovation, intellectual creations must be safeguarded. Strengthening IP regimes, ensuring swift legal recourse, and fostering a culture of respect for intellectual assets are pivotal. The knowledge economy necessitates a paradigm shift in education. Curriculums need to be dynamic, skills must be relevant, and learning should be lifelong. From early education to professional training, an emphasis on knowledge and skills becomes paramount. The Knowledge Economy, a paradigm shift in global economics, places knowledge at its core, driving value and competitive advantage. Information, expertise, and innovation overshadow traditional resources. This metamorphosis marks an era where intellectual dominance prevails over physical supremacy. Benefits include accelerated economic growth, elevated living standards, and increased productivity. However, challenges arise, such as the knowledge divide, intellectual property disputes, and data privacy risks. Strategies for nurturing this economy involve continuous investment in R&D, robust protection of intellectual property rights, and a focus on education and lifelong learning. As countries and companies embrace the knowledge-driven era, they pave the way for socio-economic progress and position themselves at the forefront of an interconnected, innovative future.What Is the Knowledge Economy?
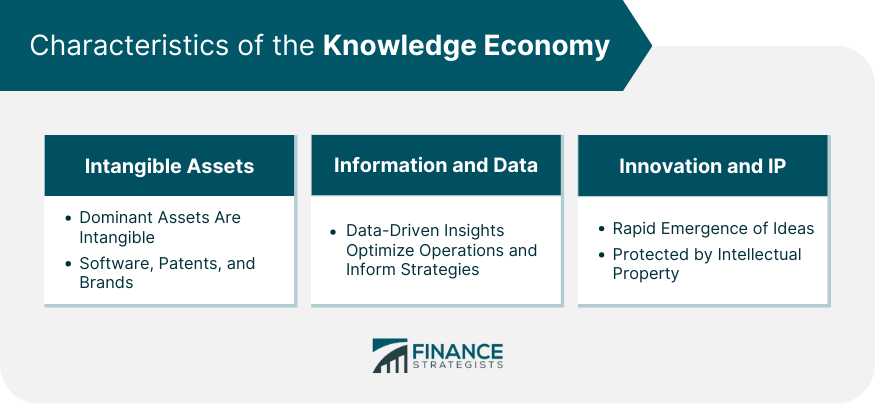
Characteristics of the Knowledge Economy
Intangible Assets
Information and Data
Innovation and Intellectual Property
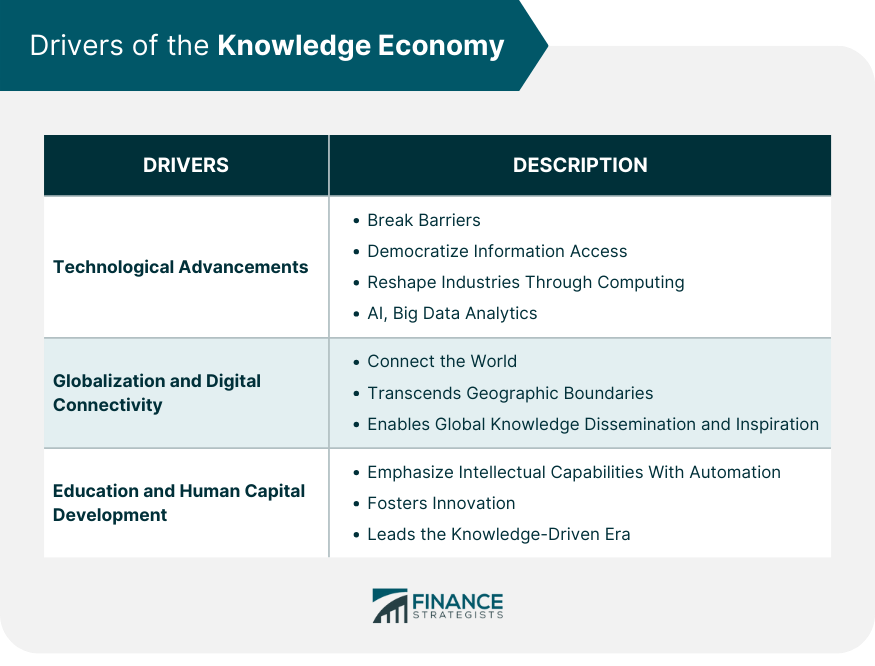
Drivers of the Knowledge Economy
Technological Advancements
Globalization and Digital Connectivity
Education and Human Capital Development
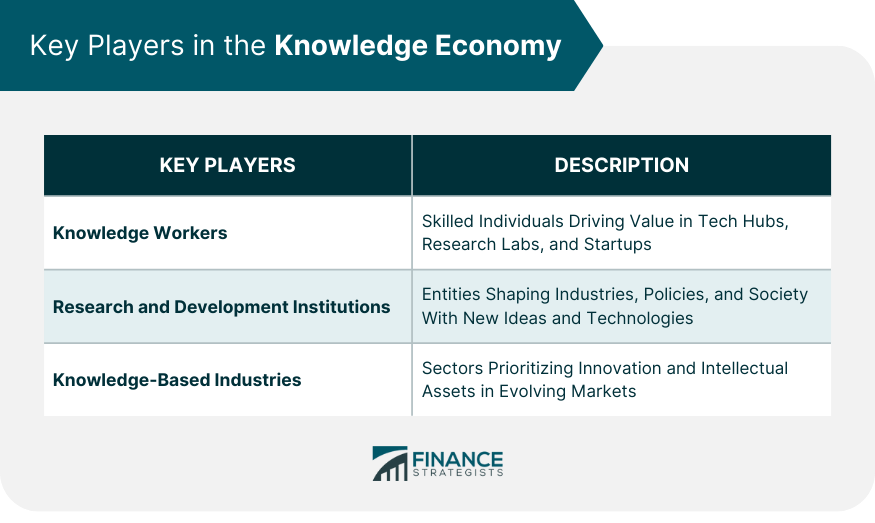
Key Players in the Knowledge Economy
Knowledge Workers
Research and Development Institutions
Knowledge-Based Industries
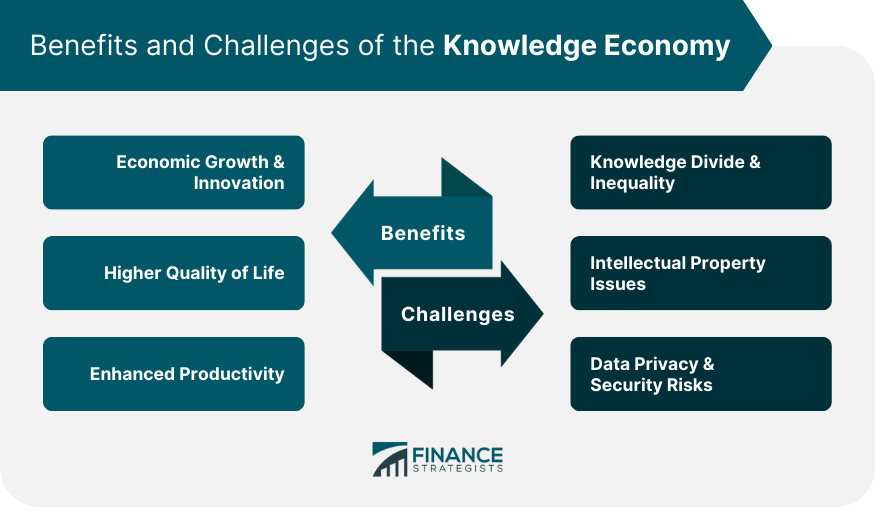
Benefits of the Knowledge Economy
Economic Growth & Innovation
Higher Quality of Life
Enhanced Productivity
Challenges of the Knowledge Economy
Knowledge Divide & Inequality
Intellectual Property Issues
Data Privacy & Security Risks
Strategies for Nurturing the Knowledge Economy
Investment in Research and Development
Intellectual Property Rights Protection
Education and Lifelong Learning Initiatives

Conclusion
Knowledge Economy FAQs
The knowledge economy primarily values intellectual capabilities and knowledge over traditional physical assets like labor and raw materials.
It leads to a surge in demand for specialized skills, often leading to the proliferation of roles like data analysts, software developers, and research scientists.
Because of its immense value in driving decisions, innovations, and strategies, much like how oil-powered industries in the past, data is termed 'the new oil' in the knowledge economy.
An example of an institution using these means of production for capital gain, is a university.
By investing in education, technological infrastructure, research & development, and creating robust intellectual property regimes, countries can transition to a knowledge economy.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















