The Civil Service Retirement System (CSRS) is a defined benefit plan for federal employees in the United States. Established in 1920, CSRS provides retirement, disability, and survivor benefits for eligible federal employees and their families. The primary purpose of the CSRS is to provide financial security for federal employees in retirement, ensuring a stable source of income based on years of service and salary history. The CSRS is administered by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) and is funded through employee and employer contributions, as well as investment earnings. CSRS covers most civilian federal employees who were hired before January 1, 1984. Employees hired after this date are generally covered by the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS). To be eligible for CSRS retirement benefits, employees must have at least five years of creditable civilian service. Certain categories of federal employees, such as law enforcement officers, firefighters, and air traffic controllers, have special provisions under CSRS that allow for earlier retirement and enhanced benefits. CSRS-covered employees contribute a percentage of their salary to the retirement system, typically around 7%. Federal agencies contribute a matching percentage of the employee's salary to the CSRS, ensuring the system's financial solvency. CSRS-covered employees may also make voluntary contributions to their retirement accounts, which can increase their future retirement benefits. Retirement benefits under CSRS are calculated based on the employee's highest average salary over any three consecutive years of service, known as the "high-3" average salary. The length of creditable service is another crucial factor in determining CSRS retirement benefits. CSRS benefits accrue at different rates based on years of service, with higher rates for longer tenures. CSRS provides survivor benefits for the eligible spouse or dependent children of a deceased federal employee or retiree. CSRS offers disability benefits for employees who become unable to perform their duties due to a medical condition. CSRS retirement benefits are subject to annual cost-of-living adjustments, which help protect retirees' purchasing power against inflation. Employees who meet the age and service requirements can apply for immediate retirement, with benefits beginning the day after separation from service. In certain circumstances, such as during workforce reduction initiatives, employees may be eligible for early retirement with reduced benefits. Employees who leave federal service before meeting the age and service requirements for immediate retirement may be eligible for deferred retirement benefits, which commence at a later date. CSRS retirees may be subject to the Windfall Elimination Provision, which can reduce Social Security benefits for those who also receive a government pension. The Government Pension Offset may reduce Social Security survivor benefits for spouses of CSRS retirees who also receive a government pension. Some federal employees may have both CSRS and Social Security coverage, depending on their employment history and participation in Social Security. Some CSRS employees may choose to transition to FERS to take advantage of the Thrift Savings Plan (TSP) and Social Security benefits available under FERS. Transitioning from CSRS to FERS requires employees to meet specific eligibility criteria and complete a series of administrative steps, including submitting the appropriate forms. The transition from CSRS to FERS can impact retirement benefits, as FERS benefits are calculated differently and may include Social Security and TSP benefits. CSRS Offset is a retirement system for federal employees who were rehired after a break in service and are subject to both CSRS and Social Security coverage. Employees who had a break in service of more than one year, returned to federal service after 1983, and have at least five years of creditable civilian service under CSRS are eligible for CSRS Offset. CSRS Offset retirement benefits are calculated similarly to regular CSRS benefits, but are reduced by the employee's Social Security benefits attributable to their CSRS Offset service. CSRS employees are eligible to participate in the TSP, a defined contribution plan that allows federal employees to save for retirement through pre-tax contributions and receive agency matching contributions. CSRS employees can contribute to the TSP up to the annual limit set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), with various investment options available to suit different risk tolerances and investment goals. Participation in the TSP can significantly enhance overall retirement savings for CSRS employees, providing an additional source of income during retirement. The CSRS remains an essential retirement system for many federal employees, providing financial security and stability during their retirement years. Understanding the various aspects of CSRS, including eligibility, contributions, benefits, and retirement options, is crucial for federal employees to make informed decisions about their retirement planning. Working with a financial planner or retirement specialist can help CSRS-covered employees develop a comprehensive retirement strategy that maximizes their benefits and ensures a comfortable retirement.What Is the Civil Service Retirement System (CSRS)?
Eligibility for CSRS
Types of Federal Employees Eligible for CSRS
Service Requirements for CSRS Eligibility
Special Provisions for Law Enforcement Officers, Firefighters, and Air Traffic Controllers
Contributions to CSRS
Employee Contributions
Employer Contributions
Voluntary Contributions
CSRS Benefits
Retirement Benefits Calculation
High-3 Average Salary
Years of Service
Benefit Accrual Rates
Survivor Benefits
Disability Benefits
Cost-Of-Living Adjustments (COLAs)
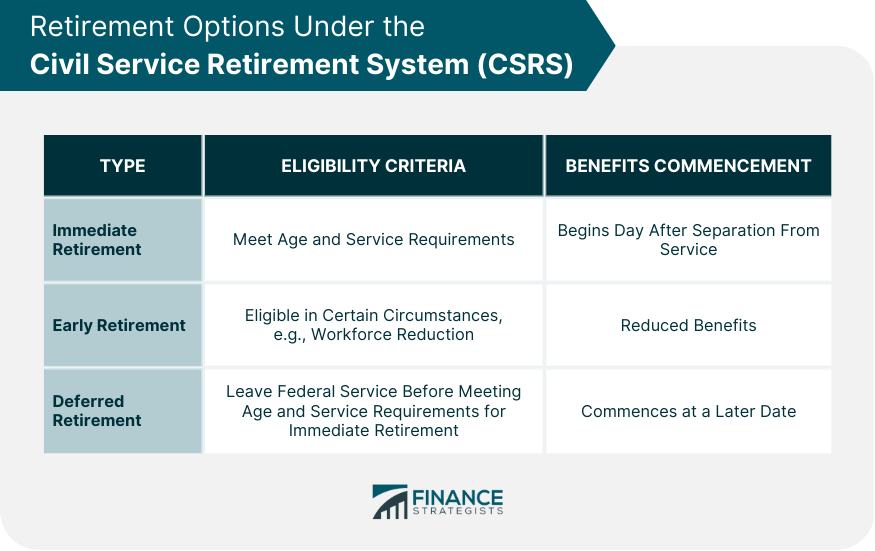
Retirement Options under CSRS
Immediate Retirement
Early Retirement
Deferred Retirement
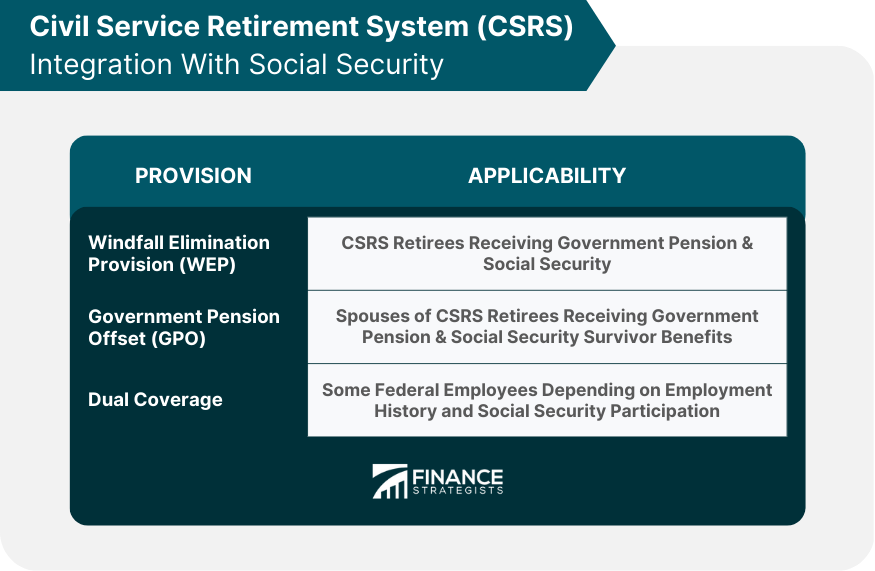
CSRS Integration With Social Security
Windfall Elimination Provision (WEP)
Government Pension Offset (GPO)
Dual CSRS and Social Security Coverage
Transition From CSRS to the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS)
Reasons for Transitioning
Requirements and Steps to Transition
Impact on Retirement Benefits
CSRS Offset
Definition and Purpose of CSRS Offset
Eligibility for CSRS Offset
Impact on Retirement Benefits
Thrift Savings Plan (TSP) and CSRS
Participation in TSP for CSRS Employees
Contribution Limits and Investment Options
Impact on Overall Retirement Savings
Conclusion
Importance of CSRS for Federal Employees
Key Considerations for Planning Retirement Under CSRS
The Role of Financial Planning in Maximizing CSRS Benefits
Civil Service Retirement System (CSRS) FAQs
The Civil Service Retirement System is a federal government retirement program for employees who were hired before January 1, 1984.
Federal employees who were hired before January 1, 1984, are generally eligible for the CSRS program.
Retirement income under the CSRS program is calculated based on the employee's length of service and average salary during the highest three consecutive years of employment.
Yes, CSRS participants are eligible to contribute to a Thrift Savings Plan to supplement their retirement income.
Yes, CSRS retirement benefits are subject to special tax rules that depend on the type of benefit received and the participant's age at retirement. For example, if the participant retires before age 62, their CSRS benefit may be subject to a reduction known as the age reduction.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















