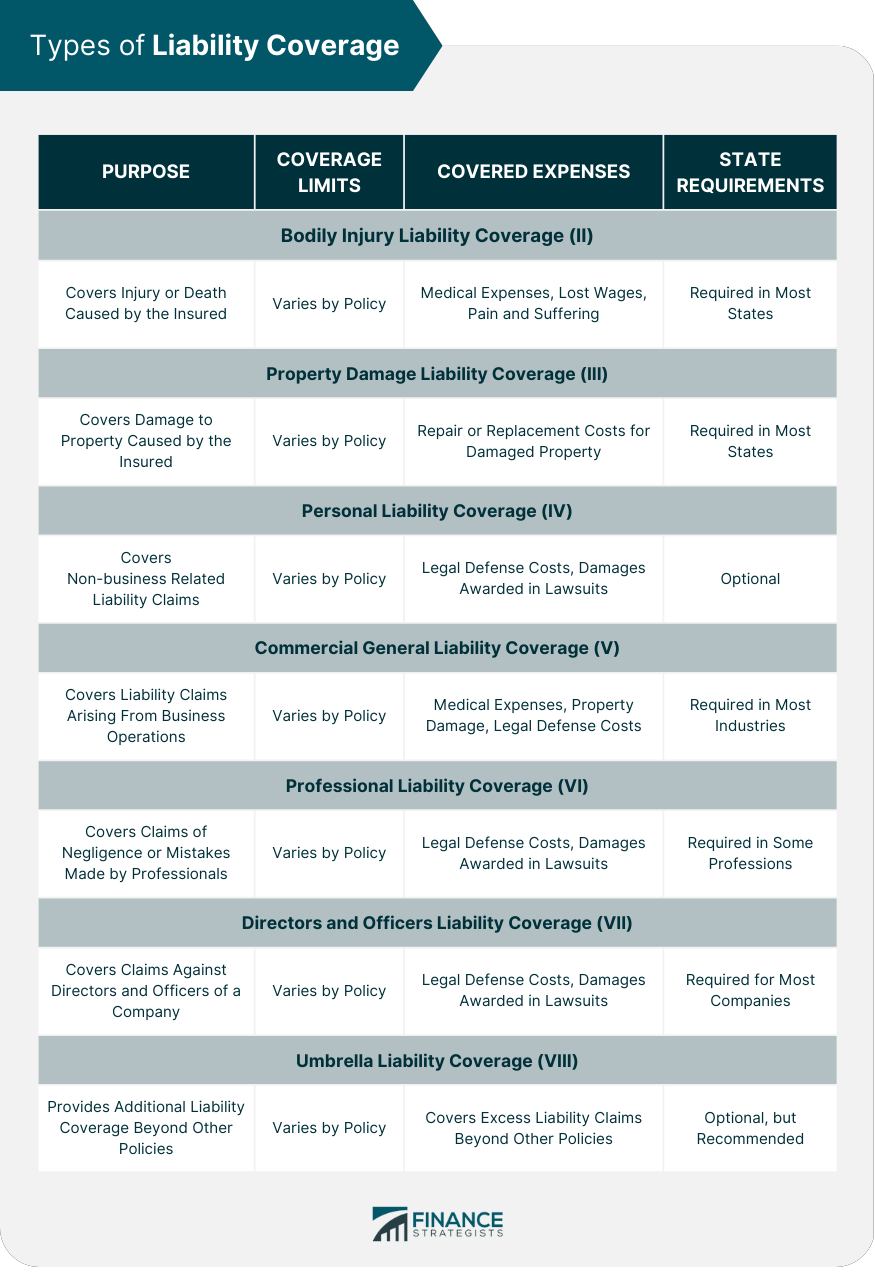
Liability coverage is a type of insurance that provides financial protection to an individual or business if they are found legally responsible for causing harm or damage to another person or their property. This coverage typically includes compensation for medical expenses, property repair or replacement, and legal fees or court costs associated with defending against a claim or lawsuit. Liability coverage is essential for managing potential risks and protecting against significant financial losses that may arise from accidents, injuries, or other incidents for which the insured party is held accountable. Bodily injury liability coverage is a mandatory insurance requirement in most states for vehicle owners. This coverage protects the policyholder if they cause an accident resulting in physical harm to another person. The insurance company will cover expenses related to the injured party's medical treatment, lost wages, and potential legal costs if the policyholder is sued. Bodily injury liability coverage is often subject to limits, which are usually expressed as a per-person and per-accident amount. For example, a policy may have a coverage limit of $50,000 per person and $100,000 per accident. This means that the maximum payout per injured person would be $50,000, and the total payout for a single accident would not exceed $100,000, regardless of the number of injured parties. Bodily injury liability coverage typically covers expenses such as: Medical bills for the injured party Rehabilitation and physical therapy costs Lost wages due to injury Pain and suffering compensation Legal fees and court costs if the policyholder is sued Each state has its own requirements for the minimum amount of bodily injury liability coverage a vehicle owner must carry. It's crucial to be aware of your state's minimums and ensure your policy meets or exceeds these requirements to avoid potential legal and financial consequences. Property damage liability coverage is another mandatory insurance requirement for vehicle owners in most states. This coverage protects the policyholder if they cause an accident that results in damage to another person's property, such as a vehicle, building, or fence. Similar to bodily injury liability coverage, property damage liability coverage also has limits. These limits indicate the maximum amount the insurer will pay to cover the cost of property damage in a single accident. For example, a policy with a $25,000 property damage limit will cover up to $25,000 in damages caused by the policyholder in an accident. Property damage liability coverage typically covers expenses such as: Repair or replacement costs for damaged vehicles Repair or replacement costs for damaged structures, such as buildings or fences Legal fees and court costs if the policyholder is sued As with bodily injury liability coverage, each state has its own minimum requirements for property damage liability coverage. It's essential to ensure your policy meets or exceeds your state's minimum requirements to remain compliant with the law. Personal liability coverage, often included in homeowners' and renters' insurance policies, provides financial protection for the policyholder if they are found responsible for causing bodily injury or property damage to others while on their property or as a result of their actions away from home. Personal liability coverage limits vary depending on the policy and the insurer. Common coverage limits range from $100,000 to $500,000, though higher limits are available for individuals with more significant assets or higher risk exposure. Personal liability coverage typically covers expenses such as: Medical bills for injured guests on the policyholder's property Repair or replacement costs for damaged property Legal fees and court costs if the policyholder is sued Compensation for pain and suffering or emotional distress experienced by the injured party Personal liability coverage is not legally required but is generally considered an essential component of homeowners' and renters' insurance policies. It provides a critical layer of financial protection against potential lawsuits and claims resulting from accidents or injuries involving the policyholder or their property. Commercial general liability (CGL) coverage is designed to protect businesses from financial losses resulting from claims of bodily injury, property damage, or personal and advertising injury caused by the business's operations, products, or services. This coverage is essential for businesses of all sizes and industries to mitigate potential legal and financial risks. CGL coverage limits vary depending on the policy and the specific needs of the business. Businesses with higher risk exposure may require higher coverage limits to ensure adequate protection. Common limits range from $1 million to $2 million per occurrence and aggregate. Commercial general liability coverage typically covers expenses such as: Medical bills for injured customers or third parties Repair or replacement costs for damaged property Legal fees and court costs if the business is sued Settlements or judgments resulting from lawsuits While CGL coverage is not legally required, it is considered essential for most businesses, regardless of their size or industry. Companies with a physical location, customer interactions, or potential exposure to third-party claims should strongly consider investing in CGL coverage. Professional liability coverage, also known as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance, provides protection for professionals who offer advice or services to clients. This coverage helps safeguard professionals against claims of negligence, errors, or omissions in the services they provide, which may result in financial losses for their clients. Professional liability coverage limits depend on the policy, the specific profession, and the professional's risk exposure. Common limits range from $1 million to $5 million per claim and aggregate. Professional liability coverage typically covers expenses such as: Legal fees and court costs if the professional is sued Settlements or judgments resulting from lawsuits Costs associated with rectifying errors or omissions made by the professional Professionals who offer advice or services to clients, such as lawyers, accountants, architects, engineers, and consultants, should strongly consider obtaining professional liability coverage to protect against potential claims and lawsuits. Directors and officers (D&O) liability coverage protects the personal assets of corporate directors and officers against claims and lawsuits related to their actions or decisions made in their official capacity. This coverage helps attract and retain qualified individuals for leadership positions by offering financial protection against potential legal risks. D&O liability coverage limits depend on the policy and the specific needs of the company. Common limits range from $1 million to $10 million per claim and aggregate. Directors and officers liability coverage typically covers expenses such as: Legal fees and court costs if the director or officer is sued Settlements or judgments resulting from lawsuits Costs associated with regulatory investigations or enforcement actions D&O liability coverage is not legally required but is strongly recommended for companies of all sizes and industries, particularly those with a corporate structure, a board of directors, or shareholders. Publicly traded companies, non-profit organizations, and private companies can all benefit from the added protection provided by D&O liability coverage. Umbrella liability coverage is an additional layer of protection that extends the limits of underlying liability policies, such as personal liability, commercial general liability, and auto liability coverage. This coverage helps ensure that individuals and businesses have adequate financial protection against large claims or lawsuits that may exceed the limits of their primary liability policies. Umbrella liability coverage limits can range from $1 million to $10 million or more, depending on the policy and the specific needs of the individual or business. These limits are in addition to the limits provided by the underlying liability policies. Umbrella liability coverage typically covers expenses such as: Legal fees and court costs if the policyholder is sued Settlements or judgments resulting from lawsuits Additional expenses not covered by primary liability policies, subject to policy terms and exclusions Individuals and businesses should consider purchasing umbrella liability coverage if they have significant assets to protect or face higher risk exposure due to their profession, location, or other factors. Umbrella coverage can offer peace of mind and financial security in the event of a substantial claim or lawsuit. When selecting liability coverage, it's essential to evaluate your risk exposure based on factors such as your profession, location, and the nature of your business or personal activities. This assessment can help determine the appropriate types and limits of coverage needed to protect against potential claims and lawsuits. It's crucial to be aware of any policy exclusions that may affect your coverage. Exclusions are specific situations or circumstances under which the insurer will not provide coverage. Understanding these exclusions can help ensure that you have adequate protection in place. When shopping for liability coverage, compare premiums and coverage limits offered by different insurers. It's essential to strike a balance between affordable premiums and sufficient coverage limits to ensure that you have adequate financial protection in place. Choose an insurer with a strong reputation and financial stability to ensure that they can pay claims when needed. Research customer reviews, financial ratings from agencies such as A.M. Best or Standard & Poor's, and consult with insurance professionals or peers for recommendations. The importance of adequate liability coverage cannot be overstated, as it offers financial protection against potential claims and lawsuits that can lead to significant financial losses. By tailoring coverage to individual or business needs and regularly reviewing and updating coverage, individuals and businesses can safeguard their assets and ensure peace of mind in the face of potential liability risks.What Is Liability Coverage?
Bodily Injury Liability Coverage
Definition and Purpose
Coverage Limits
Examples of Covered Expenses
State Requirements and Minimums
Property Damage Liability Coverage
Definition and Purpose
Coverage Limits
Examples of Covered Expenses
State Requirements and Minimums
Personal Liability Coverage
Definition and Purpose
Coverage Limits
Examples of Covered Expenses
Optional or Required Coverage
Commercial General Liability Coverage
Definition and Purpose
Coverage Limits
Examples of Covered Expenses
Industries and Businesses That Require Coverage
Professional Liability Coverage (Errors & Omissions)
Definition and Purpose
Coverage Limits
Examples of Covered Expenses
Professionals Who Require Coverage
Directors and Officers Liability Coverage
Definition and Purpose
Coverage Limits
Examples of Covered Expenses
Companies That Require Coverage
Umbrella Liability Coverage
Definition and Purpose
Coverage Limits
Examples of Covered Expenses
When to Consider Purchasing Umbrella Coverage
Factors to Consider When Choosing Liability Coverage
Assessing Risk Exposure
Understanding Policy Exclusions
Comparing Premiums and Coverage Limits
Evaluating Insurer Reputation and Financial Strength
Conclusion
Liability Coverage FAQs
Liability coverage is an insurance policy that covers you if you are found legally responsible for causing damage or injury to someone else or their property.
Liability coverage is important because it helps protect you from financial loss if you are found liable for causing damage or injury to someone else or their property. Without liability coverage, you may have to pay for the damages or injuries out of your own pocket.
Liability coverage typically covers bodily injury, property damage, and personal injury caused by you or someone else covered under your policy.
The amount of liability coverage you need depends on your individual circumstances, such as your assets and the amount of risk you face. It's recommended to have at least enough liability coverage to cover the total value of your assets.
Yes, you can purchase liability coverage as a standalone policy. However, liability coverage is often included as part of other insurance policies, such as auto insurance and homeowner's insurance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















