Bond yield refers to the rate of return an investor can expect to receive on their bond investment, expressed as a percentage of the bond's face value. In simple terms, it is the amount of money an investor will earn through periodic interest payments when they buy a bond. There are several types of bond yields that investors and financial analysts use to assess the potential returns and risks associated with investing in a particular bond. Nominal yield, also known as coupon yield, is the annual interest rate that a bond issuer pays to investors. It is based on the bond's face value, also known as its par value, which is the amount that the issuer will pay to investors at maturity. For example, a bond's nominal yield is 5%, and its face value is $1,000. In that case, the investor can expect to receive $50 per year in interest payments from the issuer until the bond reaches maturity. Current yield is a measure of the annual return an investor can expect to receive from a bond investment based on its current market price. It is calculated by dividing the bond's annual interest payment by its current market price. For example, if a bond has a face value of $1,000, a nominal yield of 5%, and a current market price of $900, the current yield would be calculated as follows: Yield to maturity is the total return an investor can expect to receive from a bond if they hold it until maturity. It takes into account the bond's current market price, the nominal yield, and the time remaining until maturity. Yield to maturity assumes that the investor will hold the bond until it matures and that all interest payments will be reinvested at the same rate. Yield to call is similar to yield to maturity, but it applies to callable bonds. Callable bonds are bonds that the issuer can redeem before their maturity date. Yield to call is the return an investor can expect to receive if the issuer exercises its right to call the bond at the earliest possible date. The yield curve graphically represents the correlation between bond yields and their respective maturities. It is a valuable instrument that investors and analysts utilize to measure inflation, economic growth, and interest rates in the market. Typically, the yield curve slopes upward, with long-term bonds having higher yields than short-term bonds. However, there are times when the yield curve can invert, with short-term bonds having higher yields than long-term bonds. This phenomenon is known as an inverted yield curve and can signal a potential economic recession. Several factors can affect bond yields, including credit ratings, inflation, economic growth, interest rates, and market demand and supply. Bond issuers' credit ratings can have a significant impact on bond yields. Higher credit ratings indicate that the issuer is more likely to repay its debts and, therefore, can issue bonds at lower yields. Lower credit ratings indicate a higher risk of default, which can lead to higher yields to compensate investors for the increased risk. Inflation is another critical factor that can affect bond yields. Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. Higher inflation rates can lead to higher bond yields because investors will demand higher returns to compensate for the decreased purchasing power of the interest payments they receive. On the other hand, lower inflation rates can lead to lower bond yields because investors are willing to accept lower returns due to the stability of the purchasing power of their interest payments. Economic growth can also affect bond yields. Strong economic growth can lead to higher bond yields because investors expect higher returns from companies that are growing and expanding. Conversely, weak economic growth can lead to lower bond yields because investors are more risk-averse and prefer the stability of fixed-income investments such as bonds. Interest rates are perhaps the most crucial factor affecting bond yields. When interest rates rise, bond yields tend to rise as well, and vice versa. This relationship exists because investors will demand higher yields on bonds to compensate for the opportunity cost of not investing in other, higher-yielding investments when interest rates are rising. Additionally, higher interest rates can lead to lower demand for bonds, which can drive bond prices down and yields up. Market demand and supply can also affect bond yields. When there is high demand for bonds, such as during times of economic uncertainty, bond yields tend to fall because investors are willing to accept lower returns for the safety and stability of fixed-income investments. Conversely, when there is a low demand for bonds, such as during times of economic growth, bond yields tend to rise because investors demand higher returns to invest in riskier assets. Understanding bond yields is crucial for investors, bond issuers, and central banks alike. Bond yields are essential for investors because they can help determine the potential returns and risks associated with investing in a particular bond. Investors can use bond yields to compare different investment opportunities and choose the one that offers the highest potential returns for an acceptable level of risk. Bond yields are also crucial for bond issuers because they help determine the interest rates they offer on their bonds. Higher bond yields can make it more expensive for issuers to raise capital, while lower yields can make their bonds less attractive to investors. Finally, bond yields are essential for central banks because they can provide insight into the overall health of the economy. Central banks can use bond yields to gauge market expectations for inflation, economic growth, and interest rates, which can help inform their decisions regarding monetary policy. Calculating bond yield can be complex, but there are formulas that investors and analysts can use to determine nominal yield, current yield, and yield to maturity. While bond yields are a useful tool for investors and analysts, they do have limitations that investors should be aware of. One of the main limitations of bond yields is that they make several assumptions about future interest rates, reinvestment rates, and other variables that may not be accurate. For example, yield to maturity assumes that the investor will hold the bond until maturity and reinvest all interest payments at the same rate. However, if interest rates change, the actual return an investor receives may be different from the yield to maturity calculation. Bond yields can also be affected by market volatility, which can cause bond prices to fluctuate rapidly. This volatility can make it difficult for investors to accurately predict bond yields and make informed investment decisions. Finally, bond yields are subject to interest rate risk, which is the risk that changes in interest rates will affect the value of a bond investment. When interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, which can result in capital losses for investors holding bonds. Conversely, when interest rates fall, bond prices tend to rise, which can result in capital gains for investors. Interest rate risk can make bond investments more volatile than other fixed-income investments, such as certificates of deposit or money market funds. Bond yield is a critical concept in the world of finance, as it provides investors and analysts with valuable information about the potential returns and risks associated with bond investments. Understanding the different types of bond yields, the factors that affect them, their importance for investors, bond issuers, and central banks, and how to calculate them can help investors make informed decisions about their investments. However, investors should also be aware of the limitations of bond yields, such as the assumptions made in their calculations, market volatility, and interest rate risk, to make informed investment decisions.What Is Bond Yield?
Types of Bond Yields
Nominal Yield
Current Yield

Yield to Maturity
Yield to Call
Yield Curve
Factors Affecting Bond Yields
Credit Ratings
Inflation
Economic Growth
Interest Rates
Market Demand and Supply
Importance of Bond Yields
For Investors
For Bond Issuers
For Central Banks
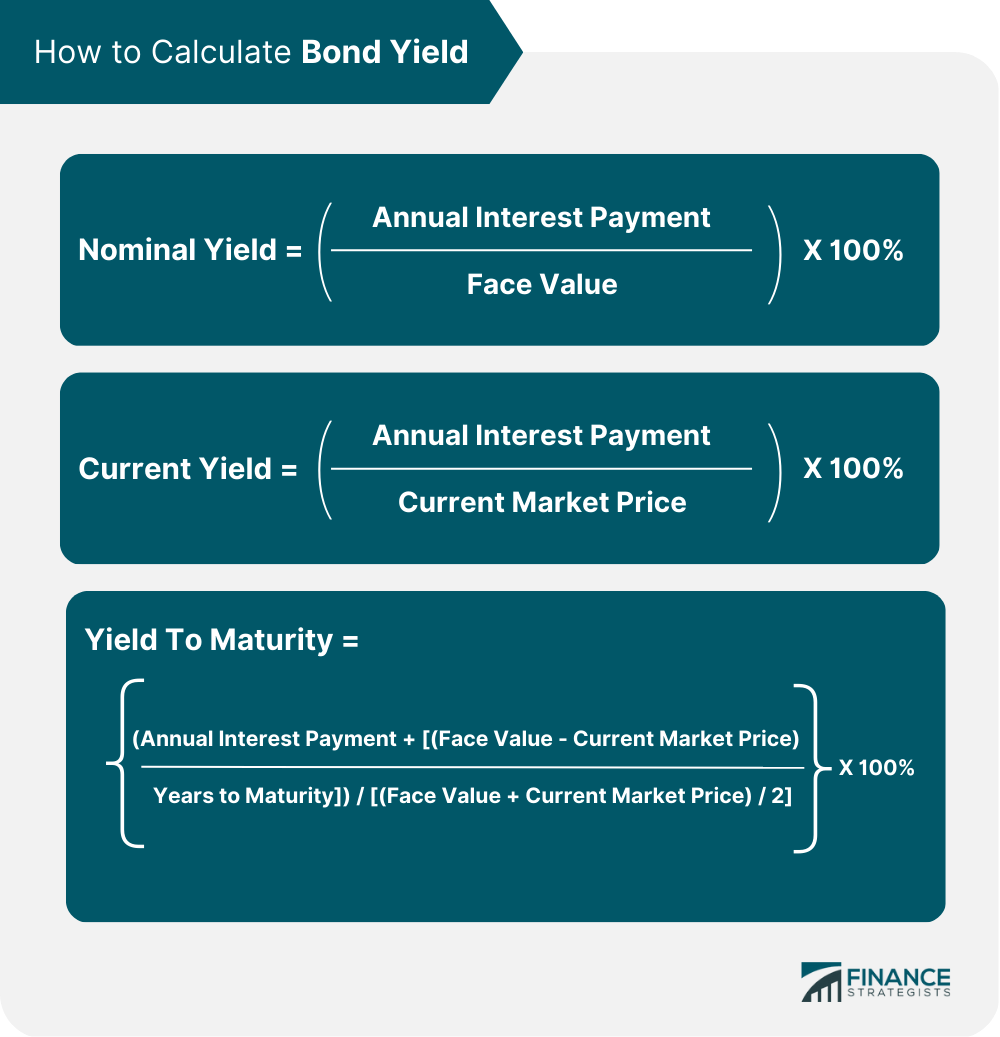
How to Calculate Bond Yield
Limitations of Bond Yields
Assumptions in Calculation
Market Volatility
Interest Rate Risk
Final Thoughts
Bond Yield FAQs
Bond yield is the rate of return an investor can expect to receive on a bond investment, expressed as a percentage of the bond's face value. It is important because it helps investors and issuers make informed decisions about investment opportunities and interest rates.
Credit ratings can have a significant impact on bond yields. Higher credit ratings indicate that the issuer is more likely to repay its debts and, therefore, can issue bonds at lower yields. Lower credit ratings indicate a higher risk of default, which can lead to higher yields to compensate investors for the increased risk.
The different types of bond yields include nominal yield, current yield, yield to maturity, yield to call, and the yield curve.
Bond yields can be calculated using formulas for nominal yield, current yield, and yield to maturity. Nominal yield is calculated by dividing the annual interest payment by the bond's face value and multiplying by 100%. The current yield is calculated by dividing the annual interest payment by the bond's current market price and multiplying by 100%. Yield to maturity is calculated by taking into account the bond's current market price, nominal yield, and time remaining until maturity.
Bond yields are subject to several limitations, including the assumptions made in their calculations, market volatility, and interest rate risk. These limitations can make it challenging for investors to accurately predict bond yields and make informed investment decisions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















